目标检测后处理之NMS(非极大值抑制算法)
目录
一、什么是NMS
二、NMS及其优化版本
1、soft NMS
2、GIoU NMS
3、DIoU NMS
4、CIoU NMS
正文
一、什么是NMS
1、定义:
非极大值抑制算法NMS广泛应用于目标检测算法,其目的是为了消除多余的候选框,找到最佳的物体检测位置。
2、原理:
使用深度学习模型检测出的目标都有多个框,如下图,针对每一个被检测目标,为了得到效果最好的那一个,需要使用一定的过滤技术把多余的框过滤掉。NMS应运而生。
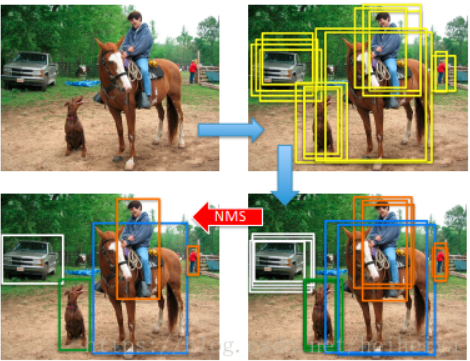
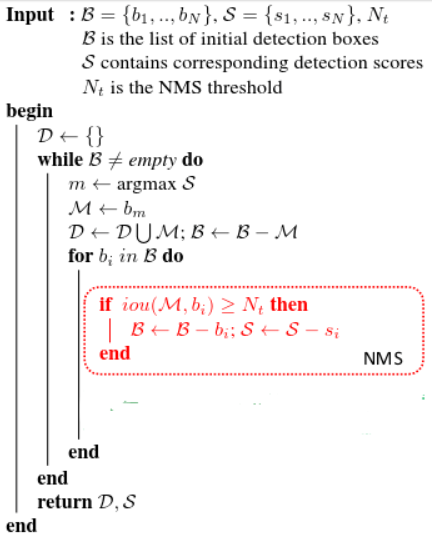
现,假设有一个候选BOXES的集合B和其对应的SCORES集合S:
1、找出分数最高的那个框M;
2、将M对应的BOX从B中删除;
3、将删除的BOX添加到集合D中;
4、从B中删除与M对应的BOX重叠区域大于阈值Nt的其他框;
5、重复上述步骤1到4。
伪代码如下:
其中Si可表述成:
![]()
源代码如下:
1、在FastRCNN中的python实现:

def nms(dets,thresh): x1 = dets[:, 0] y1 = dets[:, 1] x2 = dets[:, 2] y2 = dets[:, 3] scores = dets[:, 4] areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) order = scores.argsort()[::-1] keep = [] while order.size>0: i=order[0] keep.append(i) xx1=np.maximum(x1[i],x1[order[1:]]) yy1=np.maximum(y1[i],y1[order[1:]]) xx2=np.minimum(x2[i],x2[order[1:]]) yy2=np.minimum(y2[i],y2[order[1:]]) w=np.maximum(0.,xx2-xx1+1) h=np.maximum(0.,yy2-yy1+1) inter=w*h iou=inter/(areas[i]+areas[order[1:]]-inter) inds=np.where(iou<=thresh)[0] order=order[inds+1] return keep
2、在MaskRCNN中的python实现:

def non_max_suppression(boxes,scores,threshold): ''' 保留boxes的索引 boxes:[N,(y1,x1,y2,x2)],(y2,x2)可能会超过box的边界 scores:box分数的一数组 threshold:Float型,用于过滤IoU的阈值 ''' assert boxes.shape[0]>0 if boxes.dtpye.kind!='f': boxes=boxes.astype(np.float32) #计算box面积 y1=boxes[:,0] x1=boxes[:,1] y2=boxes[:,2] y3=boxes[:,3] area=(y2-y1)*(x2-x1) #获取根据分数排序的boxes的索引(最高的排在对前面) ixs=scores.argsort()[::-] pick=[] while len(ixs)>0: i=ixs[0] pick.append(i) iou=compute_iou(boxes[i],boxes[ixs[1:]],area[i],area[ixs[1:]]) remove_ixs=np.where(iou>threshold)[0]+1 ixs=np.delete(ixs,remove_ixs) ixs=np.delete(ixs,0) return np.array(pick,dtype=np.int32)
3、C++实现

static void sort(int n, const float* x, int* indices) { // 排序函数(降序排序),排序后进行交换的是indices中的数据 // n:排序总数// x:带排序数// indices:初始为0~n-1数目 int i, j; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (x[indices[j]] > x[indices[i]]) { //float x_tmp = x[i]; int index_tmp = indices[i]; //x[i] = x[j]; indices[i] = indices[j]; //x[j] = x_tmp; indices[j] = index_tmp; } } } int nonMaximumSuppression(int numBoxes, const CvPoint *points, const CvPoint *oppositePoints, const float *score, float overlapThreshold, int *numBoxesOut, CvPoint **pointsOut, CvPoint **oppositePointsOut, float **scoreOut) { // numBoxes:窗口数目// points:窗口左上角坐标点// oppositePoints:窗口右下角坐标点 // score:窗口得分// overlapThreshold:重叠阈值控制// numBoxesOut:输出窗口数目 // pointsOut:输出窗口左上角坐标点// oppositePoints:输出窗口右下角坐标点 // scoreOut:输出窗口得分 int i, j, index; float* box_area = (float*)malloc(numBoxes * sizeof(float)); // 定义窗口面积变量并分配空间 int* indices = (int*)malloc(numBoxes * sizeof(int)); // 定义窗口索引并分配空间 int* is_suppressed = (int*)malloc(numBoxes * sizeof(int)); // 定义是否抑制表标志并分配空间 // 初始化indices、is_supperssed、box_area信息 for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) { indices[i] = i; is_suppressed[i] = 0; box_area[i] = (float)( (oppositePoints[i].x - points[i].x + 1) * (oppositePoints[i].y - points[i].y + 1)); } // 对输入窗口按照分数比值进行排序,排序后的编号放在indices中 sort(numBoxes, score, indices); for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) // 循环所有窗口 { if (!is_suppressed[indices[i]]) // 判断窗口是否被抑制 { for (j = i + 1; j < numBoxes; j++) // 循环当前窗口之后的窗口 { if (!is_suppressed[indices[j]]) // 判断窗口是否被抑制 { int x1max = max(points[indices[i]].x, points[indices[j]].x); // 求两个窗口左上角x坐标最大值 int x2min = min(oppositePoints[indices[i]].x, oppositePoints[indices[j]].x); // 求两个窗口右下角x坐标最小值 int y1max = max(points[indices[i]].y, points[indices[j]].y); // 求两个窗口左上角y坐标最大值 int y2min = min(oppositePoints[indices[i]].y, oppositePoints[indices[j]].y); // 求两个窗口右下角y坐标最小值 int overlapWidth = x2min - x1max + 1; // 计算两矩形重叠的宽度 int overlapHeight = y2min - y1max + 1; // 计算两矩形重叠的高度 if (overlapWidth > 0 && overlapHeight > 0) { float overlapPart = (overlapWidth * overlapHeight) / box_area[indices[j]]; // 计算重叠的比率 if (overlapPart > overlapThreshold) // 判断重叠比率是否超过重叠阈值 { is_suppressed[indices[j]] = 1; // 将窗口j标记为抑制 } } } } } } *numBoxesOut = 0; // 初始化输出窗口数目0 for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) { if (!is_suppressed[i]) (*numBoxesOut)++; // 统计输出窗口数目 } *pointsOut = (CvPoint *)malloc((*numBoxesOut) * sizeof(CvPoint)); // 分配输出窗口左上角坐标空间 *oppositePointsOut = (CvPoint *)malloc((*numBoxesOut) * sizeof(CvPoint)); // 分配输出窗口右下角坐标空间 *scoreOut = (float *)malloc((*numBoxesOut) * sizeof(float)); // 分配输出窗口得分空间 index = 0; for (i = 0; i < numBoxes; i++) // 遍历所有输入窗口 { if (!is_suppressed[indices[i]]) // 将未发生抑制的窗口信息保存到输出信息中 { (*pointsOut)[index].x = points[indices[i]].x; (*pointsOut)[index].y = points[indices[i]].y; (*oppositePointsOut)[index].x = oppositePoints[indices[i]].x; (*oppositePointsOut)[index].y = oppositePoints[indices[i]].y; (*scoreOut)[index] = score[indices[i]]; index++; } } free(indices); // 释放indices空间 free(box_area); // 释放box_area空间 free(is_suppressed); // 释放is_suppressed空间 return LATENT_SVM_OK; }
二、NMS及其优化版本
1、soft NMS
NMS能解决大部分的重叠问题,但如下图的情况就无法解决,红色框和绿色框是当前的检测结果,二者的得分分别是0.95和0.80。如果按照传统的NMS进行处理,首先选中得分最高的红色框,然后绿色框就会因为与之重叠面积过大而被删掉。另一方面,NMS的阈值也不太容易确定,设小了会出现下图的情况(绿色框因为和红色框重叠面积较大而被删掉),设置过高又容易增大误检。

思路:不要简单粗暴地删除所有IOU大于阈值的框,而是降低其置信度。
伪代码如下:
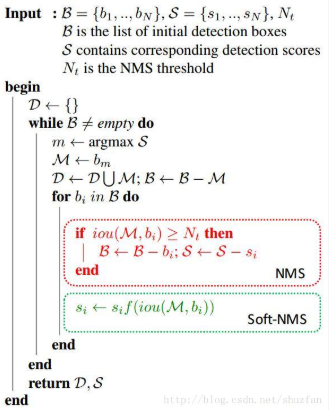
NMS可以描述如下:将IOU大于阈值的窗口的得分全部置为0。
SoftNMS改进有两种形式
一种是线性加权的:
![]()
一种是高斯加权的:
![]()
两种方法的思路都是:M为当前得分最高框,Bi是待处理框,和M的IOU越大,Bi的得分就下降的越厉害。

def cpu_soft_nms(np.ndarray[float, ndim=2] boxes, float sigma=0.5, float Nt=0.3, float threshold=0.001, unsigned int method=0): cdef unsigned int N = boxes.shape[0] cdef float iw, ih, box_area cdef float ua cdef int pos = 0 cdef float maxscore = 0 cdef int maxpos = 0 cdef float x1,x2,y1,y2,tx1,tx2,ty1,ty2,ts,area,weight,ov for i in range(N): maxscore = boxes[i, 4] maxpos = i tx1 = boxes[i,0] ty1 = boxes[i,1] tx2 = boxes[i,2] ty2 = boxes[i,3] ts = boxes[i,4] pos = i + 1 # get max box while pos < N: if maxscore < boxes[pos, 4]: maxscore = boxes[pos, 4] maxpos = pos pos = pos + 1 # add max box as a detection boxes[i,0] = boxes[maxpos,0] boxes[i,1] = boxes[maxpos,1] boxes[i,2] = boxes[maxpos,2] boxes[i,3] = boxes[maxpos,3] boxes[i,4] = boxes[maxpos,4] # swap ith box with position of max box boxes[maxpos,0] = tx1 boxes[maxpos,1] = ty1 boxes[maxpos,2] = tx2 boxes[maxpos,3] = ty2 boxes[maxpos,4] = ts tx1 = boxes[i,0] ty1 = boxes[i,1] tx2 = boxes[i,2] ty2 = boxes[i,3] ts = boxes[i,4] pos = i + 1 # NMS iterations, note that N changes if detection boxes fall below threshold while pos < N: x1 = boxes[pos, 0] y1 = boxes[pos, 1] x2 = boxes[pos, 2] y2 = boxes[pos, 3] s = boxes[pos, 4] area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1) iw = (min(tx2, x2) - max(tx1, x1) + 1) if iw > 0: ih = (min(ty2, y2) - max(ty1, y1) + 1) if ih > 0: ua = float((tx2 - tx1 + 1) * (ty2 - ty1 + 1) + area - iw * ih) ov = iw * ih / ua #iou between max box and detection box if method == 1: # linear if ov > Nt: weight = 1 - ov else: weight = 1 elif method == 2: # gaussian weight = np.exp(-(ov * ov)/sigma) else: # original NMS if ov > Nt: weight = 0 else: weight = 1 boxes[pos, 4] = weight*boxes[pos, 4] # if box score falls below threshold, discard the box by swapping with last box # update N if boxes[pos, 4] < threshold: boxes[pos,0] = boxes[N-1, 0] boxes[pos,1] = boxes[N-1, 1] boxes[pos,2] = boxes[N-1, 2] boxes[pos,3] = boxes[N-1, 3] boxes[pos,4] = boxes[N-1, 4] N = N - 1 pos = pos - 1 pos = pos + 1 keep = [i for i in range(N)] return keep
解释如下:

如上图,假如还检测出了3号框,而我们的最终目标是检测出1号和2号框,并且剔除3号框,原始的nms只会检测出一个1号框并剔除2号框和3号框,而softnms算法可以对1、2、3号检测狂进行置信度排序,可以知道这三个框的置信度从大到小的顺序依次为:1-》2-》3(由于是使用了惩罚,所有可以获得这种大小关系),如果我们再选择了合适的置信度阈值,就可以保留1号和2号,同时剔除3号,实现我们的功能。
遗留问题:
置信度的阈值设置目前还是手工设置,这依然存在很大局限性,所以还有改进的空间。
2、GIoU NMS
在IOU LOSS上增加一个惩罚项,C为包围预测框B和Bgt的最小区域大小。BBOX距离越大,惩罚项越大。
在包含的情况下,GIOU退化为IOU。
GIOU需要更多的迭代次数来收敛;
3、DIoU NMS
在YOLOV3上使用DIOU替换IOU,能提升5.9个mAp
添加一个惩罚项,用于最小化两个BBOX的中心点距离,不仅考虑了重叠区域,还考虑了中心点距离。
4、CIOU NMS(Complete IOU )
除了考虑重叠区域,中心点距离,还加入了长宽比。
Rciou=ro^2(b,bgt)/c^2+alpha*v
v=4/pi^2*(arctan(w_gt/h_gt)-arctan(w/h))^2 :用来度量长宽比的相似性
损失函数:Lciou=1-IOU+Rciou
参考链接:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号