IO流
流是一组有序的数据序列
Java由数据流处理输入/输出模式,程序从指向源的输入流中读取源中的数据,通过向输出流中写入数据把信息传递到目的地,以下图片可以说明,图片分别为输入模式、输出模式
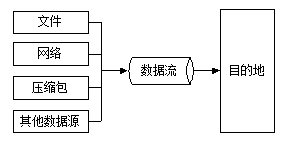
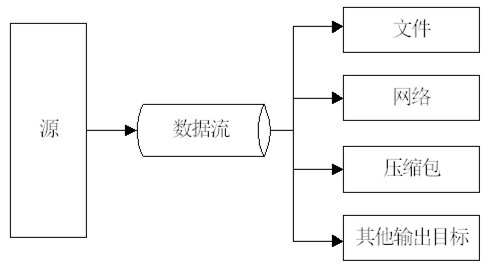
InputStream和OutputStream
InputStream类和OutputStream类都可以通过文件对象来对文件进行操作,看如下代码:
public static void readByteFromFile() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/test.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[(int) file.length()];
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
int size = is.read(bytes);
System.out.println(size+" "+new String(bytes));
is.close();
}
-
通过D盘的文件来创建一个File对象
-
创建一个字节型数组,数组长度为file.length,此时数组内的值都为默认值0
-
然后通过FileInputStream实现类将InputStream抽象类实例化,并将file加载进去
-
-
输出文件内容
-
将流关闭
接下来用OutputStream类将数据流写入目的地
public static void writeByteToFile() throws IOException {
//1.创建一个字符串
String hello = new String("Hello World!");
//2.通过getBytes方法获取字符串的字节流,返回一个byte型数组
byte[] bytes = hello.getBytes();
//3.获得一个文件对象
File file = new File("D:/test.txt");
//4.实例化OutputStream,将file对象加载进去
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
//5.调用write方法,将字节数组写入次输出流
os.write(bytes);
//6.将输出流关闭
os.close();
}
FileReader类和FileWrite类
将上面的例子修改一下
-
FileReader
public static void readByteFromFile() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/test.txt");
char[] chars = new char[(int) file.length()];
Reader reader = new FileReader(file);
int size = reader.read(chars);
System.out.println(size+" "+new String(reader));
reader.close();
}
代码顺序不变,只是将字节数组改成了字符数组,将FileOutputStream类写成了FileReader类,结果都是一样,那么两个类的不同点在哪里呢?
原来FileOutputStream这个类只提供了对字节或字节数组的读取方法,由于汉字在文件中占用两个字节,如果使用字节流,读取不好可能会出现乱码现象,采用字符流就可以避免
//System.out.println(size+" "+new String(reader));
System.out.println(size+" "+new String(chars,0,size));
可以将offset的值改变,测试一下
-
FileWrite类似
public static void writeCharToFile() throws IOException{
String hello = new String("hello world!");
File file = new File("D:/test.txt");
Writer os = new FileWriter(file);
os.write(hello);
os.close();
}
这里的write方法可以直接传入String字符串,不需要对字符串进行操作
BufferedReader类与BufferedWriter类
package com.jiang.io;
import java.io.*;
public class Student {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content[] = {"明日科技","Java部","快速入门"};
File file = new File("D:/test.txt");
try {
// FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
for (int i = 0; i < content.length; i++) {
bufw.write(content[i]);
bufw.newLine();
}
bufw.flush();
bufw.close();
bufw.close();
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
// FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String s = null;
int i = 0;
while ((s = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null)
{
i++;
System.out.println(s);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
-
这里需要注意的是BufferedWrite和BufferedReader的构造方法参数需要传入一个引用对象,使用readLine()方法不用传参,直接返回文件的一行数据
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/suifeng3051/article/details/48344587






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号