数据结构笔记
1. min/max heap
看到K神马的基本上就是min/max heap.
(1) Find the K closest points to the origin in a 2D plane, given an array containing N points.

1 public static List<Point> findKClosest(Point[] p, int k) { 2 3 List<Point> res = new ArrayList<Point>(); 4 Comparator<Point> comparator = new Comparator<Point>(){ 5 //@Override 6 public int compare(Point a, Point b) { 7 return (int) ( a.x*a.x + a.y*a.y- b.x*b.x -b.y*b.y); 8 } 9 }; 10 11 PriorityQueue<Point> minheap = new PriorityQueue<Point>(comparator); 12 for (Point temp : p) { 13 minheap.add(temp); 14 } 15 for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { 16 res.add(minheap.poll()); 17 } 18 19 return res; 20 }
如果只能用k个位置保留在有线队列里面的话,那么前k个可以直接加入,后面k个的话,如果比最后一个小,那么把最后1个移除,然后放入当前的点.

1 public List<Point> findKClosest(Point[] p, int k) { 2 PriorityQueue<Point> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(10, new Comparator<Point>() { 3 @Override 4 public int compare(Point a, Point b) { 5 return (b.x * b.x + b.y * b.y) - (a.x * a.x + a.y * a.y); 6 } 7 }); 8 9 for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) { 10 if (i < k) 11 pq.offer(p[i]); 12 else { 13 Point tmp = pq.peek(); 14 if ((p[i].x * p[i].x + p[i].y * p[i].y) - (tmp.x * tmp.x + tmp.y * tmp.y) < 0) { 15 pq.poll(); 16 pq.offer(p[i]); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 21 List<Point> x = new ArrayList<>(); 22 while (!pq.isEmpty()) 23 x.add(pq.poll()); 24 25 return x; 26 }
------------------------我是分割线----------------------------------------
------------------------我是分割线----------------------------------------

1 public class MinStack { 2 3 /** initialize your data structure here. */ 4 static Stack<Integer> numStack; 5 static Stack<Integer> minStack; 6 7 public MinStack() { 8 numStack = new Stack<Integer>(); 9 minStack = new Stack<Integer>(); 10 } 11 12 public void push(int x) { 13 numStack.push(x); 14 if (minStack.empty() || x <= minStack.peek()) { 15 minStack.push(x); 16 } 17 } 18 19 public void pop() { 20 if (numStack.peek().equals(minStack.peek())) { 21 //note!!! because Stack contains integer which is an object, is use == will test its pointer!!! 22 minStack.pop(); 23 numStack.pop(); 24 25 } else { 26 numStack.pop(); 27 } 28 } 29 30 public int top() { 31 return numStack.peek(); 32 } 33 34 public int getMin() { 35 return minStack.peek(); 36 } 37 }
(2) implement queue by two stack

1 class MyQueue { 2 private Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); 3 private Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>(); 4 5 // Push element x to the back of queue. 6 public void push(int x) { 7 if (!stack2.empty()){ 8 move(); 9 } 10 stack1.push(x); 11 12 } 13 private void move() { 14 if (!stack2.empty()) { 15 while (!stack2.empty()) { 16 stack1.push(stack2.pop()); 17 } 18 return; 19 } else { 20 while (!stack1.empty()) { 21 stack2.push(stack1.pop()); 22 } 23 return; 24 } 25 } 26 27 // Removes the element from in front of queue. 28 public void pop() { 29 if (!stack1.empty()) { 30 move(); 31 } 32 stack2.pop(); 33 } 34 35 // Get the front element. 36 public int peek() { 37 if (!stack1.empty()) { 38 move(); 39 } 40 return stack2.peek(); 41 } 42 43 // Return whether the queue is empty. 44 public boolean empty() { 45 if (!stack1.empty() || !stack2.empty()) { 46 return false; 47 } 48 return true; 49 } 50 }
(3)Largest rectangle in histogram
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.

Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].

The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit.
For example,
Given heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3],
return 10.
暴力方法:
for矩阵的起点
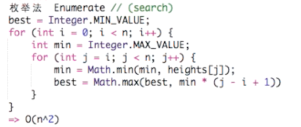
需要用到“单调栈”
这道题的核心点是:最矮的木头!
1. //for矩阵的最爱的那根木头,也就是矩阵的高度
2.记住,单调栈能够做到找到左边比一个比当前小的点,能找到右边第一个比它小的点
3. 单调栈里实际上存的是下标,在比较增序关系的时候才用值去比较

1 public class Solution { 2 public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) { 3 if (heights == null || heights.length == 0) { 4 return 0; 5 } 6 int size = heights.length; 7 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>(); 8 int max = 0; 9 for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) { 10 int current = (i == size) ? -1 : heights[i]; 11 while (!stack.isEmpty() && current < heights[stack.peek()]) { 12 int temp = stack.pop(); 13 int h = heights[temp]; 14 int wide = stack.isEmpty() ? i : i - stack.peek() - 1; 15 max = Math.max(max, h * wide); 16 } 17 stack.push(i);//千万别忘记了!debug了1年= = 18 19 } 20 return max; 21 } 22 }
------------------------我是分割线----------------------------------------


