KMP匹配(模板)
先粘上我入门KMP时看的大佬的博客:orz orz
我觉得这篇已经讲的很详细了,希望大家能坚持看下去。
步骤
①寻找前缀后缀最长公共元素长度
对于P = p0 p1 ...pj-1 pj,寻找模式串P中长度最大且相等的前缀和后缀。如果存在p0 p1 ...pk-1 pk = pj- k pj-k+1...pj-1 pj,那么在包含pj的模式串中有最大长度为k+1的相同前缀后缀。
举个例子,如果给定的模式串为“abab”,那么它的各个子串的前缀后缀的公共元素的最大长度如下表格所示:

比如对于字符串aba来说,它有长度为1的相同前缀后缀a;而对于字符串abab来说,它有长度为2的相同前缀后缀ab(相同前缀后缀的长度为k + 1,k + 1 = 2)。
②求next数组
next 数组考虑的是除当前字符外的最长相同前缀后缀,所以通过第①步骤求得各个前缀后缀的公共元素的最大长度后,只要稍作变形即可:将第①步骤中求得的值整体右移一位,然后初值赋为-1,如下表格所示:
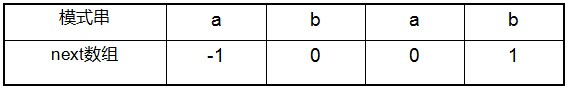
比如对于aba来说,第3个字符a之前的字符串ab中有长度为0的相同前缀后缀,所以第3个字符a对应的next值为0;而对于abab来说,第4个字符b之前的字符串aba中有长度为1的相同前缀后缀a,所以第4个字符b对应的next值为1(相同前缀后缀的长度为k,k = 1)。
③根据next数组进行匹配
匹配失配,j = next [j],模式串向右移动的位数为:j - next[j]。换言之,当模式串的后缀pj-k pj-k+1, ..., pj-1 跟文本串si-k si-k+1, ..., si-1匹配成功,但pj 跟si匹配失败时,因为next[j] = k,相当于在不包含pj的模式串中有最大长度为k 的相同前缀后缀,即p0 p1 ...pk-1 = pj-k pj-k+1...pj-1,故令j = next[j],从而让模式串右移j - next[j] 位,使得模式串的前缀p0 p1, ..., pk-1对应着文本串 si-k si-k+1, ..., si-1,而后让pk 跟si 继续匹配。如下图所示:

综上,KMP的next 数组相当于告诉我们:
当模式串中的某个字符跟文本串中的某个字符匹配失配时,模式串下一步应该跳到哪个位置。
如模式串中在j 处的字符跟文本串在i 处的字符匹配失配时,下一步用next [j] 处的字符继续跟文本串i 处的字符匹配,相当于模式串向右移动 j - next[j] 位。
下面给出模板:
next数组的求法:
1 void GetNext(char* p,int next[]) 2 { 3 int pLen = strlen(p); 4 next[0] = -1; 5 int k = -1; 6 int j = 0; 7 while (j < pLen - 1) 8 { 9 //p[k]表示前缀,p[j]表示后缀 10 if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k]) 11 { 12 ++k; 13 ++j; 14 next[j] = k; 15 } 16 else 17 { 18 k = next[k]; 19 } 20 } 21 }
求next数组的改进版:
1 //优化过后的next 数组求法 2 void GetNextval(char* p, int next[]) 3 { 4 int pLen = strlen(p); 5 next[0] = -1; 6 int k = -1; 7 int j = 0; 8 while (j < pLen - 1) 9 { 10 //p[k]表示前缀,p[j]表示后缀 11 if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k]) 12 { 13 ++j; 14 ++k; 15 //较之前next数组求法,改动在下面4行 16 if (p[j] != p[k]) 17 next[j] = k; //之前只有这一行 18 else 19 //因为不能出现p[j] = p[ next[j ]],所以当出现时需要继续递归,k = next[k] = next[next[k]] 20 next[j] = next[k]; 21 } 22 else 23 { 24 k = next[k]; 25 } 26 } 27 }
KMP算法:
1 int KmpSearch(char* s, char* p) 2 { 3 int i = 0; 4 int j = 0; 5 int sLen = strlen(s); 6 int pLen = strlen(p); 7 while (i < sLen && j < pLen) 8 { 9 //①如果j = -1,或者当前字符匹配成功(即S[i] == P[j]),都令i++,j++ 10 if (j == -1 || s[i] == p[j]) 11 { 12 i++; 13 j++; 14 } 15 else 16 { 17 //②如果j != -1,且当前字符匹配失败(即S[i] != P[j]),则令 i 不变,j = next[j] 18 //next[j]即为j所对应的next值 19 j = next[j]; 20 } 21 } 22 if (j == pLen) 23 return i - j; 24 else 25 return -1; 26 }
自己习惯用的模板(可忽略)
1 int Next[1000010]; 2 char str1[1000010]; 3 char str2[1000010]; 4 5 void getnext(char *str) 6 { 7 int len=strlen(str); 8 int j=0; 9 int k=-1; 10 Next[0]=-1; 11 while(j<len) 12 { 13 if(k==-1||str[j]==str[k]) 14 { 15 j++; 16 k++; 17 if(str[j]!=str[k]) 18 { 19 Next[j]=k; 20 } 21 else 22 Next[j]=Next[k]; 23 } 24 else 25 k=Next[k]; 26 } 27 } 28 29 int KMP(char *str1,char *str2) 30 { 31 int len1=strlen(str1); 32 int len2=strlen(str2); 33 int i=0; 34 int j=0; 35 while(i<len1&&j<len2) 36 { 37 if(j==-1||str1[i]==str2[j]) 38 { 39 i++; 40 j++; 41 } 42 else 43 { 44 j=Next[j]; 45 } 46 47 } 48 if(j==len2) 49 return i-j; 50 else 51 return -1; 52 }
觉得模板太长?看看这种方法吧:
https://www.cnblogs.com/eternhope/p/9481643.html
下面是一些入门例题:
HDU-1711 Number Sequence
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1711
Problem Description
Input
Output
Sample Input
2 13 5 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 3 2 1 2 1 2 3 1 3 13 5 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 3 2 1 2 1 2 3 2 1
Sample Output
6 -1
题意:查找子串B在字符串A中第一次出现位置
模板题,直接套板子
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <math.h> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <queue> 10 #include <set> 11 #include <map> 12 #include <math.h> 13 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 14 typedef long long LL; 15 const int mod=1e9+7; 16 const int maxn=1e6+10; 17 const int maxm=1e4+10; 18 using namespace std; 19 20 int Next[maxm]; 21 int n,m; 22 int A1[maxn]; 23 int A2[maxm]; 24 25 void Get_Next() 26 { 27 int j=1; 28 int k=0; 29 Next[1]=0; 30 while(j<m) 31 { 32 if(k==0||A2[j]==A2[k]) 33 { 34 j++; 35 k++; 36 if(A2[j]!=A2[k]) 37 Next[j]=k; 38 else 39 Next[j]=Next[k]; 40 } 41 else 42 k=Next[k]; 43 } 44 } 45 46 int KMP() 47 { 48 int i=1; 49 int j=1; 50 while(i<=n&&j<=m) 51 { 52 if(j==0||A1[i]==A2[j]) 53 { 54 i++; 55 j++; 56 } 57 else 58 j=Next[j]; 59 } 60 if(j==m+1) 61 return i-j+1; 62 else 63 return -1; 64 } 65 66 int main() 67 { 68 int T; 69 scanf("%d",&T); 70 while(T--) 71 { 72 scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); 73 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 74 { 75 scanf("%d",&A1[i]); 76 } 77 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) 78 { 79 scanf("%d",&A2[i]); 80 } 81 Get_Next(); 82 printf("%d\n",KMP()); 83 } 84 return 0; 85 }
POJ-3461 Oulipo
http://poj.org/problem?id=3461
Description
The French author Georges Perec (1936–1982) once wrote a book, La disparition, without the letter 'e'. He was a member of the Oulipo group. A quote from the book:
Tout avait Pair normal, mais tout s’affirmait faux. Tout avait Fair normal, d’abord, puis surgissait l’inhumain, l’affolant. Il aurait voulu savoir où s’articulait l’association qui l’unissait au roman : stir son tapis, assaillant à tout instant son imagination, l’intuition d’un tabou, la vision d’un mal obscur, d’un quoi vacant, d’un non-dit : la vision, l’avision d’un oubli commandant tout, où s’abolissait la raison : tout avait l’air normal mais…
Perec would probably have scored high (or rather, low) in the following contest. People are asked to write a perhaps even meaningful text on some subject with as few occurrences of a given “word” as possible. Our task is to provide the jury with a program that counts these occurrences, in order to obtain a ranking of the competitors. These competitors often write very long texts with nonsense meaning; a sequence of 500,000 consecutive 'T's is not unusual. And they never use spaces.
So we want to quickly find out how often a word, i.e., a given string, occurs in a text. More formally: given the alphabet {'A', 'B', 'C', …, 'Z'} and two finite strings over that alphabet, a word W and a text T, count the number of occurrences of W in T. All the consecutive characters of W must exactly match consecutive characters of T. Occurrences may overlap.
Input
The first line of the input file contains a single number: the number of test cases to follow. Each test case has the following format:
- One line with the word W, a string over {'A', 'B', 'C', …, 'Z'}, with 1 ≤ |W| ≤ 10,000 (here |W| denotes the length of the string W).
- One line with the text T, a string over {'A', 'B', 'C', …, 'Z'}, with |W| ≤ |T| ≤ 1,000,000.
Output
For every test case in the input file, the output should contain a single number, on a single line: the number of occurrences of the word W in the text T.
Sample Input
3 BAPC BAPC AZA AZAZAZA VERDI AVERDXIVYERDIAN
Sample Output
1 3 0
题意:查找子串A在字符串B中出现的次数
标准KMP是返回子串第一次出现的位置,这个是统计次数,稍微改一下就好了
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <vector> 6 using namespace std; 7 int Next[1000010]; 8 char str1[1000010]; 9 char str2[1000010]; 10 11 void getnext(char *str) 12 { 13 int len=strlen(str); 14 int j=0; 15 int k=-1; 16 Next[0]=-1; 17 while(j<len) 18 { 19 if(k==-1||str[j]==str[k]) 20 { 21 j++; 22 k++; 23 if(str[j]!=str[k]) 24 { 25 Next[j]=k; 26 } 27 else 28 Next[j]=Next[k]; 29 } 30 else 31 k=Next[k]; 32 } 33 } 34 35 int KMP(char *str1,char *str2) 36 { 37 int ans=0; 38 int len1=strlen(str1); 39 int len2=strlen(str2); 40 int i=0,j=0; 41 while(i<len1) 42 { 43 if(j==-1||str1[i]==str2[j]) 44 { 45 i++; 46 j++; 47 } 48 else 49 { 50 j=Next[j]; 51 } 52 if(j==len2) 53 { 54 ans++; 55 j=Next[j]; 56 // i=i-j+1; //这两行换上一行会超时 57 // j=0; 58 } 59 } 60 return ans; 61 } 62 63 int main() 64 { 65 int t; 66 scanf("%d",&t); 67 68 while(t--) 69 { 70 scanf("%s %s",str1,str2); 71 getnext(str1); 72 printf("%d\n",KMP(str2,str1)); 73 } 74 return 0; 75 }
先来个next数组模板
1 void Get_Next() 2 { 3 int j=0; 4 int k=-1; 5 Next[0]=-1; 6 while(j<m) 7 { 8 if(k==-1||str2[j]==str2[k]) 9 { 10 j++; 11 k++; 12 Next[j]=k; 13 } 14 else 15 k=Next[k]; 16 } 17 }
首先
1:i-next[i]是最小循环节的长度
2:字符串的循环条件是i%(i-next[i])==0&&next[i]!=0
3:最小循环节的循环次数是i / (i-next[i])
4:整体 在 字符串 s
L= strlen(s)
n = next[l]
L%(L-next[L])==0 有循环节
k = L - n= L - next[L] 最小循环节
1> p = L%k=L%(L-next[L]) 循环k节点若干次后剩余部分的长度
2> q = (k-p)%k =k-q q为字符串s1要想补齐成恰好整数个k所需要的最少字符数
对于1 ababa 没有循环节 next[L]=3 最小循环节L-next[L]=2 则 取余说明 还剩多少节点没有循环 如最后一个a
正对2如果最小循环节减去取余后的 则得到补齐整数时所需的字串
在KMP算法的使用中,首要任务就是获取一个字符串的next数组,所以我们得 明白next数组的含义(最好的方法是自己弄个例子,在草稿纸上模拟一下),在这里,通俗一点讲,next[k] 表示,在模式串的 k 个字符失配了,然后下一次匹配从 next[k] 开始(next[k] 中保存的是该失配字符的前一个字符在前面出现过的最近一次失配的字符后面的一个字符的位置,有点绕口,自己写个例子看看就明白了,也可以继续往下看,有介 绍,然后再自己尝试写写 )。
至于next数组为什么可以用来求重复前缀呢,而且求出来的重复前缀是最小的呢?
next数组的求法:
void getnext(int len){
int i=0,j=-1;
next[0]=-1;
while(i<len){
if(j==-1 || str[i]==str[j]){
i++;j++;
next[i]=j;
}else
j=next[j];
}
}
个人认为,next数组在求解的过程中,用到了KMP的思想,当前失配了,就回溯到上一个next,请见 j=next[j] ,先说个结论,如果到位置 i ,如果有 i%(i-next(i))==0 , 那说明字符串开始循环了,并且循环到 i-1 结束,为什么这样呢?
我们先假设到达位置 i-1 的时候,字符串循环了(到i-1完毕),那么如果到第i个字符的时候,失配了,根据next数组的求法,我们是不是得回溯?
然而回溯的话,由于字符串是循环的了(这个是假定的),next[i] 是不是指向上一个循环节的后面一个字符呢??
是的,上一个循环节的末尾是 next[i]-1 ,然后现在循环节的末尾是 i-1 ,然么循环节的长度是多少呢?
所以,我们有 (i - 1) - ( next[i] - 1 ) = i - next[i] 就是循环节的长度(假设循环成立的条件下),但是我们怎么知道这个循环到底成立吗?
现在我们已经假设了 0————i-1 循环了,那么我们就一共有i 个字符了,如果有 i % ( i - next[i] ) == 0,总的字符数刚好是循环节的倍数,那么说明这个循环是成立的。
注意还有一点,如果 next[i] == 0,即使符合上述等式,这也不是循环的,举个反例
0 1 2 3 4 5
a b c a b d
-1 0 0 0 1 2
下标为1,2,3的next值均为0,那么 i%(i-next【i】)=i%i==0,但是这个并不是循环。
解释完毕,然后再来看下,为什么求出来的循环节长度是最小的呢?
因为next数组失配的时候,总是回溯到最近的循环节,所以i-next【i】就是最小的循环节长度
为什么求出来的循环次数是最多的呢?
循环节长度是最小的了,那么循环次数肯定是最多的了。
总结一下,如果对于next数组中的 i, 符合 i % ( i - next[i] ) == 0 && next[i] != 0 , 则说明字符串循环,而且
循环节长度为: i - next[i]
循环次数为: i / ( i - next[i] )
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43768644/article/details/94644776
https://blog.csdn.net/dyx404514/article/details/41831947
https://www.cnblogs.com/vivym/p/3927955.html
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008663857
https://subetter.com/algorithm/extended-kmp-algorithm.html
扩展 KMP
问题定义:给定两个字符串 S 和 T(长度分别为 n 和 m),下标从 0 开始,定义extend[i]等于S[i]...S[n-1]与 T 的最长相同前缀的长度,求出所有的extend[i]。举个例子,看下表:
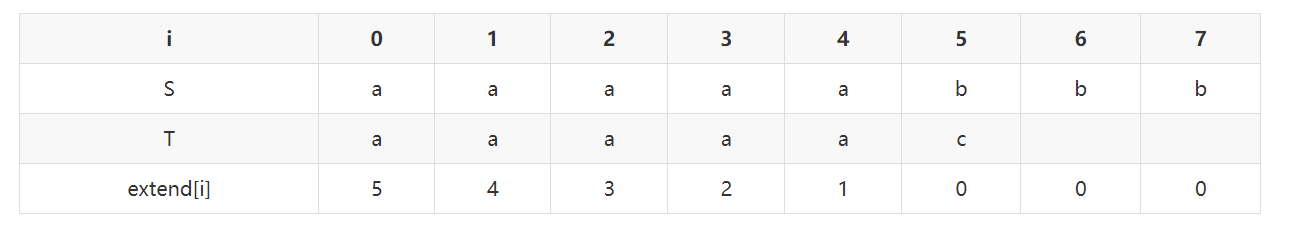
为什么说这是 KMP 算法的扩展呢?显然,如果在 S 的某个位置 i 有extend[i]等于 m,则可知在 S 中找到了匹配串 T,并且匹配的首位置是 i。而且,扩展 KMP 算法可以找到 S 中所有 T 的匹配。接下来具体介绍下这个算法。
一:算法流程
(1)
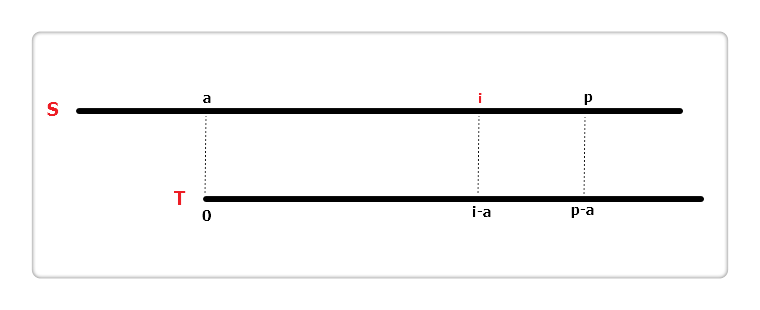
如上图,假设当前遍历到 S 串位置 i,即extend[0]...extend[i - 1]这 i 个位置的值已经计算得到。设置两个变量,a 和 p。p 代表以 a 为起始位置的字符匹配成功的最右边界,也就是 "p = 最后一个匹配成功位置 + 1"。相较于字符串 T 得出,S[a...p) 等于 T[0...p-a)。
再定义一个辅助数组int next[],其中next[i]含义为:T[i]...T[m - 1]与 T 的最长相同前缀长度,m 为串 T 的长度。举个例子:

(2)
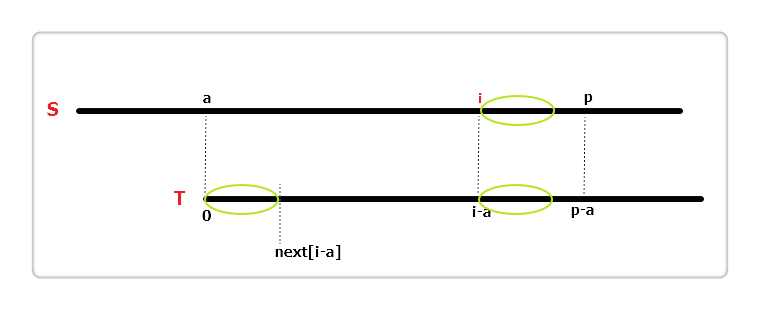
S[i]对应T[i - a],如果i + next[i - a] < p,如上图,三个椭圆长度相同,根据 next 数组的定义,此时extend[i] = next[i - a]。
(3)
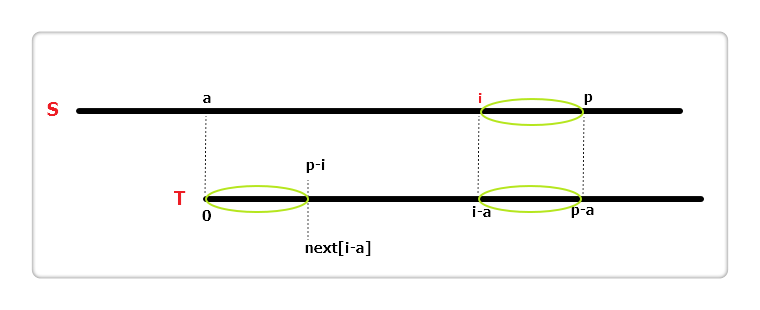
如果i + next[i - a] == p呢?如上图,三个椭圆都是完全相同的,S[p] != T[p - a]且T[p - i] != T[p - a],但S[p]有可能等于T[p - i],所以我们可以直接从S[p]与T[p - i]开始往后匹配,加快了速度。
(4)
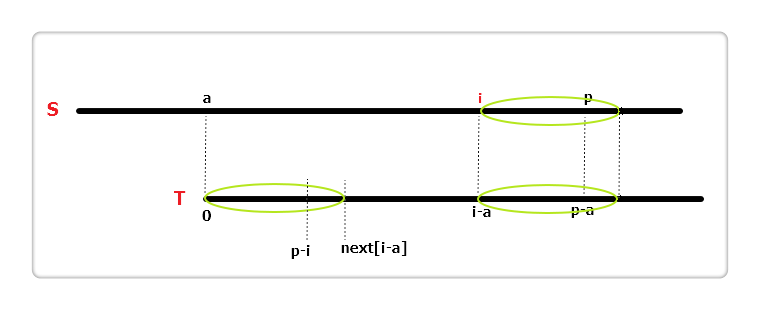
如果i + next[i - a] > p呢?那说明S[i...p)与T[i-a...p-a)相同,注意到S[p] != T[p - a]且T[p - i] == T[p - a],也就是说S[p] != T[p - i],所以就没有继续往下判断的必要了,我们可以直接将extend[i]赋值为p - i。
(5)最后,就是求解 next 数组。我们再来看下next[i]与extend[i]的定义:
- next[i]:
T[i]...T[m - 1]与 T 的最长相同前缀长度; - extend[i]:
S[i]...S[n - 1]与 T 的最长相同前缀长度。
恍然大悟,求解next[i]的过程不就是 T 自己和自己的一个匹配过程嘛,下面直接看代码。
二:代码
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 /* 求解 T 中 next[],注释参考 GetExtend() */ 7 void GetNext(string & T, int & m, int next[]) 8 { 9 int a = 0, p = 0; 10 next[0] = m; 11 12 for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) 13 { 14 if (i >= p || i + next[i - a] >= p) 15 { 16 if (i >= p) 17 p = i; 18 19 while (p < m && T[p] == T[p - i]) 20 p++; 21 22 next[i] = p - i; 23 a = i; 24 } 25 else 26 next[i] = next[i - a]; 27 } 28 } 29 30 /* 求解 extend[] */ 31 void GetExtend(string & S, int & n, string & T, int & m, int extend[], int next[]) 32 { 33 int a = 0, p = 0; 34 GetNext(T, m, next); 35 36 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 37 { 38 if (i >= p || i + next[i - a] >= p) // i >= p 的作用:举个典型例子,S 和 T 无一字符相同 39 { 40 if (i >= p) 41 p = i; 42 43 while (p < n && p - i < m && S[p] == T[p - i]) 44 p++; 45 46 extend[i] = p - i; 47 a = i; 48 } 49 else 50 extend[i] = next[i - a]; 51 } 52 } 53 54 int main() 55 { 56 int next[100]; 57 int extend[100]; 58 string S, T; 59 int n, m; 60 61 while (cin >> S >> T) 62 { 63 n = S.size(); 64 m = T.size(); 65 GetExtend(S, n, T, m, extend, next); 66 67 // 打印 next 68 cout << "next: "; 69 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) 70 cout << next[i] << " "; 71 72 // 打印 extend 73 cout << "\nextend: "; 74 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 75 cout << extend[i] << " "; 76 77 cout << endl << endl; 78 } 79 return 0; 80 }
数据测试如下:
aaaaabbb aaaaac next: 6 4 3 2 1 0 extend: 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 0 abc def next: 3 0 0 extend: 0 0 0
先溜了,以后在填坑



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号