Vuex的理解
vuex是一个状态管理模式+库。采用的是集中式存储管理状态应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
这个自管理应用包含几个部分:
状态,驱动应用的数据源;
视图,以声明方式将状态映射到视图;
操作,响应在视图上的用户输入导致的状态变化。
单向数据流的理念,如图:
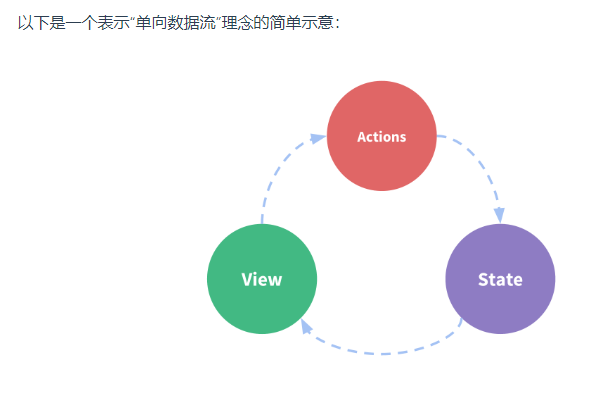
Vuex的核心概念分为五部分:
State 单一状态树,用一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。理解为状态值储存位置。
mapState辅助函数
// 在单独构建的版本中辅助函数为 Vuex.mapState
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}
Getter 作用于state列表的过滤等操作
mapGetters辅助参数:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
}
}
Mutation 同步函数,更改状态的提交。
vuex中的mutation非常类似于事件:每个mutation都有一个字符串的事件类型和一个回调函数。
store.commit('increment', {
amount: 10
})
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.amount
}
}
Action类似于mutation不同在于:
action提交的是mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
action可以包含任意异步操作。
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
可以将异步改为同步:
actions: {
async actionA ({ commit }) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
await dispatch('actionA') // 等待 actionA 完成
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData())
}
}
Module 如果使用单一状态树,所有的应用集中到一个比较大的对象。这样会使其臃肿。
所以Module的作用是使其分割。
然后每个模块都拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = createStore({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号