结构体
1 结构体及应用
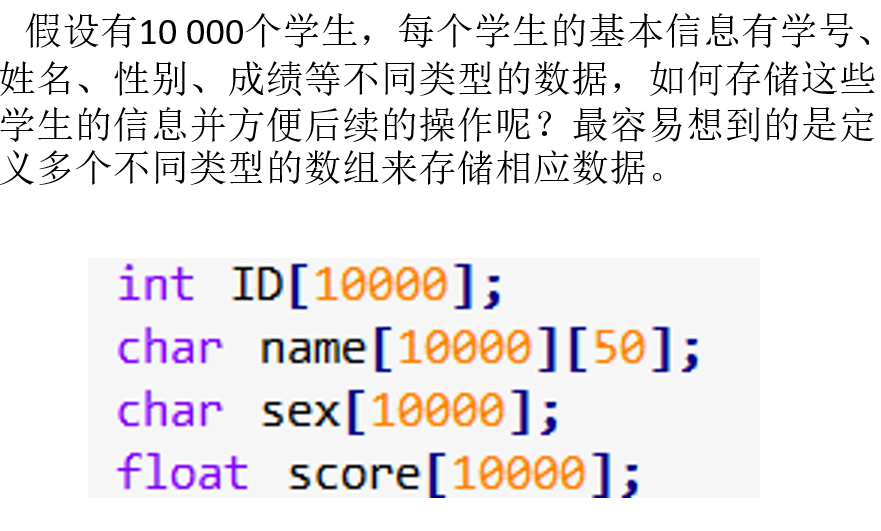


struct student { int ID; char name[20]; char sex; float score; }; struct student s[4]= {{ 10001,"张三",'M',95 }, {10002,"李四",'F',92}, {10002,"王五",'F',96} }; //定义了结构体数组stu[4]并对前两个赋值
void f1_1() { //结构体变量实例 struct student a= {1,"张三1",'M',95}; //定义变量并赋值 struct student b= {2,"李四1",'F',100}; //不能改变赋值顺序 struct student c; //结构体c未赋初值 //scanf("%d%s%c%f",&c.ID,c.name,&c.sex,&c.score);//注意c.name前无"&" cin>>c.ID>>c.name>>c.sex>>c.score; //printf("%d %s %c %f\n",a.ID,a.name,a.sex,a.score); cout<<a.ID<<" "<<a.name<<" "<<a.sex<<" "<<a.score<<" "<<endl; cout<<b.ID<<" "<<b.name<<" "<<b.sex<<" "<<b.score<<" "<<endl; cout<<c.ID<<" "<<c.name<<" "<<c.sex<<" "<<c.score<<" "<<endl; } void f1() { //结构体及其应用 //scanf("%d %s %c %f",&s[2].ID,s[2].name,&s[2].sex,&s[2].score); cin>>s[3].ID>>s[3].name>>s[3].sex>>s[3].score; for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { //printf("%d %s %c %f\n",s[i].ID,s[i].name,s[i].sex,s[i].score); cout<<s[i].ID<<s[i].name<<s[i].sex<<s[i].score<<endl; } //return 9; }
语句scanf("%d%s%c%f",&c.ID,c.name,&c.sex,&c.score)中,c.name的前面没有加取地址符“&”,因为c.name本身就是数组的首地址。
可以看出,结构体内的成员变量可以像普通变量一样进行各种操作。例如:
a.score=b.score;
sum=a.score+b.score;
a.score++;
应该逐个操作结构体内的各变量,不能将各变量作为整体一次操作完,例如输入输出写成cin>>a或者cout<<a都是错误的,应改为:
cin>>a.ID>>a.name>>a.sex>>a.score;
cout<<a.ID<<a.name<<a.sex<<a.score;
2 结构体与指针
void f2() { //结构体与指针 struct student *p; for(p=s; p<s+4; p++) //p为指向结构体的指针,自身加1即指向下一结构体元素 cout<<p->ID<<p->name<<p->sex<<p->score<<endl; } void f21() { //结构体指针变量指向结构体变量 struct student stu; //定义结构体变量stu struct student *p; //*p必须和stu一样,均为struct student类型 p=&stu; //结构体指针p指向结构体stu stu.ID=10001; strcpy(stu.name,"苏州1");//无法用"="对字符数组赋值,故用strcpy() stu.sex='M'; stu.score=100; cout<<stu.ID<<stu.name<<stu.sex<<stu.score<<endl; cout<<(*p).ID<<(*p).name<<(*p).sex<<(*p).score<<endl; }
3 选举

#include <string.h>
struct person { char name[150]; int count; } leader[200];
void f2_2() { /* 选举 */ int n,m; cin>>n; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { cin>>leader[i].name; leader[i].count=0; } cin>>m; char name[m]; for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) { cin>>name; for(int j=0; j<n; j++) if(strcmp(name,leader[j].name)==0) leader[j].count++; } for(int i=0; i<n; i++) cout<<leader[i].name<<" "<<leader[i].count<<endl; }
4 统计成绩

struct student1 { int num; char name[8]; int mark[3]; } person1[11]; #include<iomanip> void f22() { //统计成绩 freopen("score.in","r",stdin); int maxi=0; float aver,aver1,max=0,sum=0; for(int i=0; i<10; i++) { cin>>person1[i].num>>person1[i].name; cin>>person1[i].mark[0]>>person1[i].mark[1]>>person1[i].mark[2]; sum+=person1[i].mark[0]; sum+=person1[i].mark[1]; sum+=person1[i].mark[2]; aver1=(float)(person1[i].mark[0]+person1[i].mark[1]+person1[i].mark[2]); aver1=aver1/3; if(aver1>max) { max=aver1; maxi=i; } } aver=sum/30; cout<<setprecision(2)<<fixed<<aver<<endl; cout<<person1[maxi].num<<" "<<person1[maxi].name<<" "<<setprecision(2)<<fixed<<max<<endl; }
5 生日

struct Stu { string s; int y,m,d; } stu[200]; #include<algorithm> void exchange(int i,int j) { swap(stu[i].s,stu[j].s); swap(stu[i].y,stu[j].y); swap(stu[i].m,stu[j].m); swap(stu[i].d,stu[j].d); } void f23() { //生日 freopen("birthday.in","r",stdin); int n; //scanf("%d",&n); cin>>n; for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cin>>stu[i].s>>stu[i].y>>stu[i].m>>stu[i].d; for(int i=1; i<n; ++i) for(int j=i+1; j<=n; ++j) if(stu[i].y>stu[j].y) exchange(i,j); else if(stu[i].y==stu[j].y) if(stu[i].m>stu[j].m) exchange(i,j); else if(stu[i].m==stu[j].m) if(stu[i].d>=stu[j].d) exchange(i,j); for(int i=1; i<=n; ++i) cout<<stu[i].s<<endl; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号