[Firebase] 02 - User Management & Real-time DB
有太多东西要学,思绪不稳,干脆就跟着这哥们混就好了,完成全系列的学习。
1. Project name.
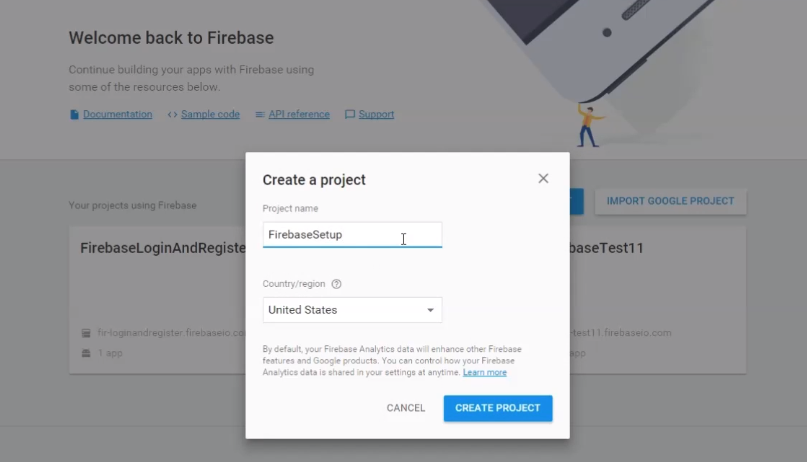
2. Package name.
Ref: Android Studio获取SHA1或MD5的方法
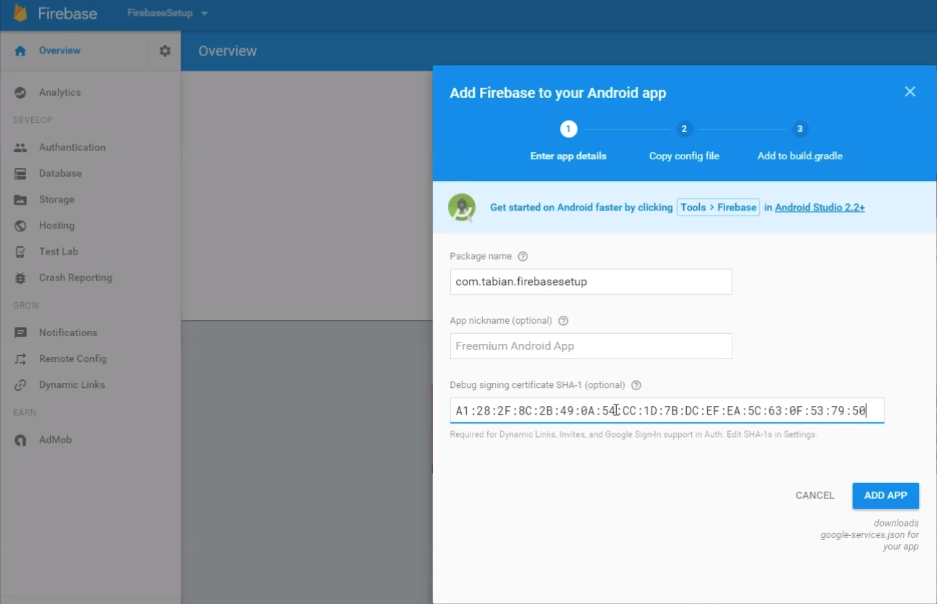
3. google-service.json in ./app
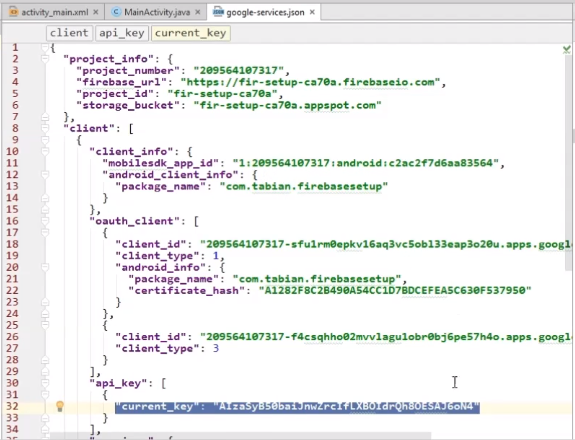
Main类:
Public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; private FirebaseAuth mAuth; private FirebaseAuth.AuthStateListener mAuthListener; // UI references. private EditText mEmail, mPassword; private Button btnSignIn,btnSignOut,btnViewDatabase; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//declare buttons and edit texts in oncreate mEmail = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.email); mPassword = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.password); btnSignIn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.email_sign_in_button); btnSignOut = (Button) findViewById(R.id.email_sign_out_button); btnViewDatabase = (Button) findViewById(R.id.view_items_screen); mAuth = FirebaseAuth.getInstance(); mAuthListener = new FirebaseAuth.AuthStateListener() { @Override public void onAuthStateChanged(@NonNull FirebaseAuth firebaseAuth) { // 指明一个参数,字段或者方法的返回值不可以为null FirebaseUser user = firebaseAuth.getCurrentUser(); if (user != null) { // User is signed in Log.d(TAG, "onAuthStateChanged:signed_in:" + user.getUid()); toastMessage("Successfully signed in with: " + user.getEmail()); } else { // User is signed out Log.d(TAG, "onAuthStateChanged:signed_out"); toastMessage("Successfully signed out."); } // ... } }; btnSignIn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { String email = mEmail.getText().toString(); String pass = mPassword.getText().toString(); if(!email.equals("") && !pass.equals("")){ mAuth.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email,pass); }else{ toastMessage("You didn't fill in all the fields."); } } }); btnSignOut.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { mAuth.signOut(); toastMessage("Signing Out..."); } }); btnViewDatabase.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, ViewDatabase.class); // ----> read info from firebase startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override public void onStart() { super.onStart(); mAuth.addAuthStateListener(mAuthListener); // 注意:触发mAuth发送mail登录信息,然后静等mAuthListener对回复结果的反应 } @Override public void onStop() { super.onStop(); if (mAuthListener != null) { mAuth.removeAuthStateListener(mAuthListener); } } /** * customizable toast * @param message */ private void toastMessage(String message){ Toast.makeText(this,message,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }
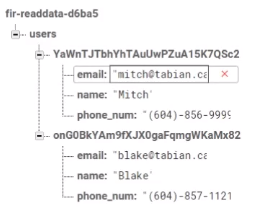
定义一个对应firebase节点的类:
public class UserInformation { private String name; private String email; private String phone_num; public UserInformation(){ } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPhone_num() { return phone_num; } public void setPhone_num(String phone_num) { this.phone_num = phone_num; } }
读firebase节点信息:
public class ViewDatabase extends AppCompatActivity { private static final String TAG = "ViewDatabase"; //add Firebase Database stuff private FirebaseDatabase mFirebaseDatabase; private FirebaseAuth mAuth; private FirebaseAuth.AuthStateListener mAuthListener; private DatabaseReference myRef; private String userID; private ListView mListView; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.view_database_layout); mListView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview); //declare the database reference object. This is what we use to access the database. //NOTE: Unless you are signed in, this will not be useable. mAuth = FirebaseAuth.getInstance(); mFirebaseDatabase = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance(); myRef = mFirebaseDatabase.getReference();
FirebaseUser user = mAuth.getCurrentUser(); userID = user.getUid(); mAuthListener = new FirebaseAuth.AuthStateListener() { @Override public void onAuthStateChanged(@NonNull FirebaseAuth firebaseAuth) { FirebaseUser user = firebaseAuth.getCurrentUser(); if (user != null) { // User is signed in Log.d(TAG, "onAuthStateChanged:signed_in:" + user.getUid()); toastMessage("Successfully signed in with: " + user.getEmail()); } else { // User is signed out Log.d(TAG, "onAuthStateChanged:signed_out"); toastMessage("Successfully signed out."); } // ... } }; myRef.addValueEventListener(new ValueEventListener() { @Override public void onDataChange(DataSnapshot dataSnapshot) { // This method is called once with the initial value and again // whenever data at this location is updated. showData(dataSnapshot); } @Override public void onCancelled(DatabaseError databaseError) { } }); } private void showData(DataSnapshot dataSnapshot) {
for(DataSnapshot ds : dataSnapshot.getChildren()){ UserInformation uInfo = new UserInformation(); uInfo.setName (ds.child(userID).getValue(UserInformation.class).getName()); //set the name uInfo.setEmail (ds.child(userID).getValue(UserInformation.class).getEmail()); //set the email uInfo.setPhone_num(ds.child(userID).getValue(UserInformation.class).getPhone_num()); //set the phone_num
技巧性比较强的:UserInformation.class
//display all the information Log.d(TAG, "showData: name: " + uInfo.getName()); Log.d(TAG, "showData: email: " + uInfo.getEmail()); Log.d(TAG, "showData: phone_num: " + uInfo.getPhone_num()); ArrayList<String> array = new ArrayList<>(); array.add(uInfo.getName()); array.add(uInfo.getEmail()); array.add(uInfo.getPhone_num()); ArrayAdapter adapter = new ArrayAdapter(this ,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, array); // <---- 套路 mListView.setAdapter(adapter); } } @Override public void onStart() { super.onStart(); mAuth.addAuthStateListener(mAuthListener); } @Override public void onStop() { super.onStop(); if (mAuthListener != null) { mAuth.removeAuthStateListener(mAuthListener); } } /** * customizable toast * @param message */ private void toastMessage(String message){ Toast.makeText(this,message,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } }
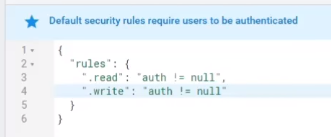
插曲:规则设置
默认规则要求进行身份验证,允许通过身份验证的应用用户具有完全读写权限。
当您希望数据对应用的所有用户开放,但不对整个世界开放时,此功能会很有用。
一、基础
Ref: 安全性与规则
| 规则类型 | |
|---|---|
| .read | 描述是否允许用户读取数据以及何时读取。 |
| .write | 描述是否允许写入数据以及何时写入。 |
| .validate | 定义值的正确格式、值是否包含子属性以及值的数据类型。 |
| .indexOn | 指定用于编制索引的子属性,以支持排序和查询。 |
- 身份验证
Firebase 身份验证支持为各种常见的身份验证方法(如 Google 和 Facebook、电子邮件地址和密码登录、匿名登录等等)使用访客身份验证。
用户身份是一个重要的安全概念。不同的用户拥有不同的数据,有时他们还拥有不同的能力权限。
例如,在聊天应用中,每条消息均与创建该消息的用户关联。用户也可以删除自己的消息,但不能删除其他用户发布的消息。
- 授权
允许任何人读取路径 /foo/,但不允许任何人对其进行写入:
{ "rules": { "foo": { ".read": true, ".write": false } } }
向已通过身份验证的用户授予对 /users/<uid>/ 的写入权限,其中 <uid> 是通过 Firebase 身份验证获取的用户 ID。
{ "rules": { "users": { "$uid": { ".write": "$uid === auth.uid" } } } }
- 数据验证
写入 /foo/ 的数据必须为少于 100 个字符的字符串:
{ "rules": { "foo": { ".validate": "newData.isString() && newData.val().length < 100" } } }
- 定义数据库索引
索引使用 .indexOn 规则进行指定。以下是索引声明的示例,将为恐龙列表的高度和长度字段编制索引:
{ "rules": { "dinosaurs": { ".indexOn": ["height", "length"] } } }
二、保障数据安全
定义数据集:
{
"messages": {
"message0": {
"content": "Hello",
"timestamp": 1405704370369
},
"message1": {
"content": "Goodbye",
"timestamp": 1405704395231
},
...
}
}
对获得的消息进行规范和限制。
{
"rules": {
"messages": {
"$message": {
// only messages from the last ten minutes can be read
".read": "data.child('timestamp').val() > (now - 600000)",
// new messages must have a string content and a number timestamp
".validate": "newData.hasChildren(['content', 'timestamp']) && newData.child('content').isString() && newData.child('timestamp').isNumber()"
}
}
}
}
- 预定义变量
在安全规则定义中可访问很多有用的预定义变量。
| 预定义变量 | |
|---|---|
| now | 当前时间,以从 Linux 计时原点开始计算的毫秒数表示。此变量非常适合验证使用 SDK 的 firebase.database.ServerValue.TIMESTAMP 创建的时间戳。 |
| root | RuleDataSnapshot,表示在尝试操作之前存在于 Firebase 数据库中的根路径。 |
| newData | RuleDataSnapshot,表示尝试操作之后应存在的数据。该数据包含写入的新数据和现有数据。 |
| data | RuleDataSnapshot,表示尝试操作之前存在的数据。 |
| $ variables | 用于表示 ID 和动态子键的通配符路径。 |
| auth | 表示通过身份验证的用户的令牌有效负载。 |
- 现有数据与新数据
{ "rules": { "foo": { // /foo is readable by the world ".read": true, // /foo is writable by the world ".write": true,
// data written to /foo must be a string less than 100 characters ".validate": "newData.isString() && newData.val().length < 100" } } }
允许我们创建新记录或删除现有记录,但不允许对现有的非 null 数据做出更改:
// we can write as long as old data or new data does not exist
// in other words, if this is a delete or a create, but not an update
".write": "!data.exists() || !newData.exists()"
- 引用其他路径的数据
".write": "root.child('allow_writes').val() === true && // /allow_writes/ 节点的值为 true
!data.parent().child('readOnly').exists() && // 父节点没有 readOnly 标志设置
newData.child('foo').exists()" // 新写入的数据中有一个名为 foo 的子节点
- 读取和写入规则级联
浅层规则将重写深层规则,例如:
只要 /foo/ 包含值为 true 的子节点 baz,此安全结构即允许读取 /bar/。
{
"rules": {
"foo": {
// allows read to /foo/*
".read": "data.child('baz').val() === true",
"bar": {
/* ignored, since read was allowed already */
".read": false // false 规则此时不起作用,因为子路径无法撤消以上的访问权限。
}
}
}
}
- 将数据编入索引
From: https://firebase.google.com/docs/database/security/indexing-data?hl=zh-cn
使用 orderByChild 编制索引
{
"lambeosaurus": {
"height" : 2.1,
"length" : 12.5,
"weight": 5000
},
"stegosaurus": {
"height" : 4,
"length" : 9,
"weight" : 2500
}
}
进一步查询优化:
{
"rules": {
"dinosaurs": {
".indexOn": ["height", "length"] // 使用 .indexOn 告诉 Firebase 也优化使用高度和长度进行的查询
}
}
}
使用 orderByValue 编制索引
{
"scores": {
"bruhathkayosaurus" : 55,
"lambeosaurus" : 21,
"linhenykus" : 80,
"pterodactyl" : 93,
"stegosaurus" : 5,
"triceratops" : 22
}
}
进一步查询优化:
{
"rules": {
"scores": {
".indexOn": ".value" // 可以通过在 /scores 节点上添加 .value 规则来优化查询
}
}
}
阅后感:
基于用户的安全机制这一部分很麻烦,这应该是数据库管理人员的事情。日后再详看,点到为止。
此链接阅读可作为学习补充。
服务器端
为了保证效率
- 多层嵌套的写法:对于效率来说是很不利。
"record" {
"record1": {
"title": "TITLE1"
"content": "..."
"writer": "S"
"reply": {
"reply1": {
"sender": "S1",
"content": "..."
}
"reply2": {
...
}
},
"record2": {
...
}
- 平展数据结构写法:说白了就是将各个属性分开成不同的树来存放,一个表拆成多个表,也就是反规范化。上面的例子就可以这样写:
"record": {
"record1": {
"title": "TITLE1"
"content": "..."
"writer": "S"
}
"record2": {
...
}
"reply": {
"record1": {
"reply1": {
"sender": "S1",
"content": "..."
}
"reply2": {
...
}
"record2": {
...
}
双向关系的解决方法
例如:对于一个用户来说可以从属于一个群组,一个群组又包含了用户。可以使用索引来解决。
存在双向关系的两个元组,将对方的元素作为”索引“来使用。这样就使得在访问这样的数据时可以保证效率,当然这里就要牺牲了一点数据冗余度了
"user": {
"u1": {
groups: {
"g1": true
...
}
}
...
}
"group": {
"g1": {
members: {
"u1": true
...
}
}
}
窗口有“数据”,“规则”,“备份”和“使用情况” 四个选项卡。
root,newData,data是RuleDataSnapshot类型。
这些都是规则所用的数据快照,因此我们可以使用相关的一些函数获得其中的信息:
| RuleDataSnapshot函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| val() | 读取明确的子节点内容,这要求需要先用child()定位到叶子节点,然后再用val()读取内容。直接对一块数据进行val()不会返回想要的“一块数据” |
| child() | 返回参数所给的相对路径,所对应的节点的快照数据 |
| parent() | 返回当前节点的父节点,所对应的快照数据。如果父节点不存在,会导致这条规则直接失败 |
| hasChild(path) | 如果这个子节点存在返回true |
| hasChildren([children]) | 如果子节点列表都存在返回true |
| exists() | 如果此数据快照中有数据则返回true |
| getPriority() | 返回此数据快照中数据的优先级 |
| isNumber() | 如果其中的数据是数字,返回true |
| isString() | 如果其中的数据是字符串,返回true |
| isBoolean() | 如果其中的数据是布尔类型,返回true |
$ 变量
获得当前节点名字的字符串。
{
"rules": {
"students": {
"$stu_id": { // <--id会有限制
"name": { // <--修改的是名字
".write": "$stu_id.contains('sysu')" // 对于修改一个学生的姓名,要求该学生的id中必须包含“sysu”
}
}
}
}
}
客户端
为了和数据库交互,需要得到数据库的一个实例,而且具体的交互对象是数据库中的某个节点,这时就需要获得这个节点的一个引用:
FirebaseDatabase database = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance(); // 数据库的实例
DatabaseReference mRef = database.getReference("students"); // 节点的引用,读写操作
write - setValue
- Boolean
- Long
- Double
- Map< String, Object > // 利用映射的特点,可以将节点路径作为键,要插入的数据作为值,就可以做到在多个位置同时进行写入
- List< Object > // 对于同时插入多个数据很有帮助
- 自定义的对象
-
- 类必须要有默认构造器
- 类必须为成员变量提供getter方法。没有getter方法的成员变量对应的键值将会被设为缺省值
write - push
在当前节点下添加一个新的子节点,该子节点的键基于时间戳,因此是唯一的。
write - updateChildren
updateChildren()方法可以修改部分数据,而不影响该节点下的其他数据,只要在参数对象中提供需要修改的数据就行了。
Firebase推荐使用平展开的数据结构,一个对象的属性可能会分散在多个JSON树中,因此对于这种数据扇出的情况,使用updateChildren(Map< String, Children >)可以很方便地一次性更新分散开来的数据,这种方式的更新具有原子性。
write - runTransaction
事务是数据库的重要课题之一。对于一篇帖子,一个用户点一次赞,数据库中对应的点赞数就要加一,这中间的过程为:客户端查找并获得该帖子的点赞数,加一,然后更新该帖子的点赞数。那么问题就来了,如果多个用户进行点赞时就需要考虑数据的同步问题 。
mRef.runTransaction(new Transaction.Handler() {
@Override
public Transaction.Result doTransaction(MutableData mutableData) {
Post post = mutableData.getValue(Post.class);
post.like = post.like + 1;
mutableData.setValue(post);
return Transaction.success(mutableData);
}
@Override
public void onComplete(DatabaseError databaseError, boolean b, DataSnapshot dataSnapshot) {
// ...
}
})
read - ValueEventListener
数据库主动告知你数据的变化,因此SDK提供的检索数据不是read形式,而是使用监听器来实时获得更新数据。
尽量监听低层节点,不要在高层节点设置监听器,以防拉取大型的数据快照 。
ValueEventListener listener = new ValueEventListener() {
@Override
public void onDataChange(DataSnapshot dataSnapshot) {
Post post = dataSnapshot.getValue(Post.class);
// ...
}
@Override
public void onCancelled(DatabaseError databaseError) {
// ...
}
};
mRef.addValueEventListener(listener);
移除 event listener:
引用调用removeEventListener(ValueEventListener)或removeEventListener(ChildEventListener),即可移除指定的监听器。
如果在同一路径设置多个监听器,则需要一个一个移除掉,因此尽量不要在addValueEventListener()和addChildEventListener()直接使用无引用的匿名内部类。
父节点移除监听器不会影响到子节点的监听器。
read - ChildEventListener
- onChildAdded():该方法会对当前的所有子节点都触发一次,并且会在未来添加子节点时触发。因此这个方法可用于遍历当前节点
- onChildChanged():每当有子节点被修改,该方法被触发
- onChildRemoved():每当有子节点被删除,该方法被触发
- onChildMoved():每当子节点的次序发生变化时(例如修改优先级),该方法被触发
排序
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| orderByChild() | 按指定子节点的值进行排序 |
| orderByKey() | 按键进行排序 |
| orderByValue() | 按值进行排序 |
| orderByPriority() | 按优先级进行排序 |
一个引用只能使用一种排序方法;引用调用了排序方法后,返回的是Query类型引用。
DatabaseReference是继承自Query类的,Query提供了各种排序和过滤的方法。
过滤
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| limitToFirst() | 从排序结果开始的最大项目数 |
| limitToLast() | 从排序结尾开始的最大项目数 |
| startAt() | 返回等于或大于指定键,值或优先级的项目 |
| endAt() | 返回小于或等于指定键,值或优先级的项目 |
| equalTo() | 返回等于指定键,值或优先级的项目 |
其中startAt(),endAt(), equal()可以指定键,值或优先级,因此有很多重载版本。
删除
数据库引用调用removeValue()方法;
通过设置值为null的方式进行删除。
离线
数据持久化
如果有数据需要写入数据库,而此时失去了网络连接,应用仍可继续运行,写操作队列会保存在缓存中,连接恢复后继续写入数据库。那如果接着用户关闭了应用呢?不用着急手动保存,开启磁盘持久化功能可以让数据保存在ROM中,即使应用重启也不会丢失。
开启磁盘持久化功能只需要一句代码:
FirebaseDatabase.getInstance().setPersistenceEnabled(true);
保持数据更新
不用添加监听器的方式来保持数据更新:【默认情况下,客户端可以在本地缓存10MB的数据】
DatabaseReference stuRef = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance().getReference("students");
stuRef.keepSynced(true);
断开连接
DatabaseReference presenceRef = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance().getReference("userLog");
presenceRef.onDisconnect().setValue("Disconnected!");
监听连接状态
客户端在数据库实例中加了一个“/.info/connected”的节点,该节点会根据连接状态而持续更新,因此可以监听这个节点的值变化,来达到监听连接状态的效果。
延迟
客户端时间和服务器时间不一定相同,两者之间存在时间偏差,因此我们在记录一些跟时间有关的数据,尽量使用ServerValue.TIMESTAMP,而不是本地时间。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号