[Airflow] 03 - Core concepts and try your first DAG
Ref: [Getting started with Airflow - 1] Installing and running Airflow using docker and docker-compose
Ref: [Getting started with Airflow - 2] Core concepts and creating your first DAG with PythonOperator
Ref: [Getting started with Airflow - 3] Understanding task retries
Ref: [Getting started with Airflow - 4] Passing metadata in between tasks with XCOM
Ref: [Getting started with Airflow - 5] Using BranchPythonOperator to branch between tasks
给客户展示,通过:https://airflow.apache.org/docs/stable/rest-api-ref.html
一、安装
-
代码
Ref: https://github.com/puckel/docker-airflow
Jeffrey: 下图第一个看上去比较复杂;第二个为简单模式。
通过如下命令安装 after changing one of the files to docker-compose.yml
$ docker-compose up
配置完毕后,通过端口映射打开airflow界面。
http://localhost:8080/admin/
-
配置解析
两个containers,一个数据库,一个则是airflow的web。
version: '3.7' services: postgres: image: postgres:9.6 environment: - POSTGRES_USER=airflow - POSTGRES_PASSWORD=airflow - POSTGRES_DB=airflow logging: options: max-size: 10m max-file: "3" webserver: image: puckel/docker-airflow:1.10.9 restart: always depends_on: - postgres environment: - LOAD_EX=n - EXECUTOR=Local logging: options: max-size: 10m max-file: "3" volumes: - ./dags:/usr/local/airflow/dags # - ./plugins:/usr/local/airflow/plugins ports: - "8080:8080" command: webserver healthcheck: test: ["CMD-SHELL", "[ -f /usr/local/airflow/airflow-webserver.pid ]"] interval: 30s timeout: 30s retries: 3
二、处理任务
最重要的就是“出错处理”。
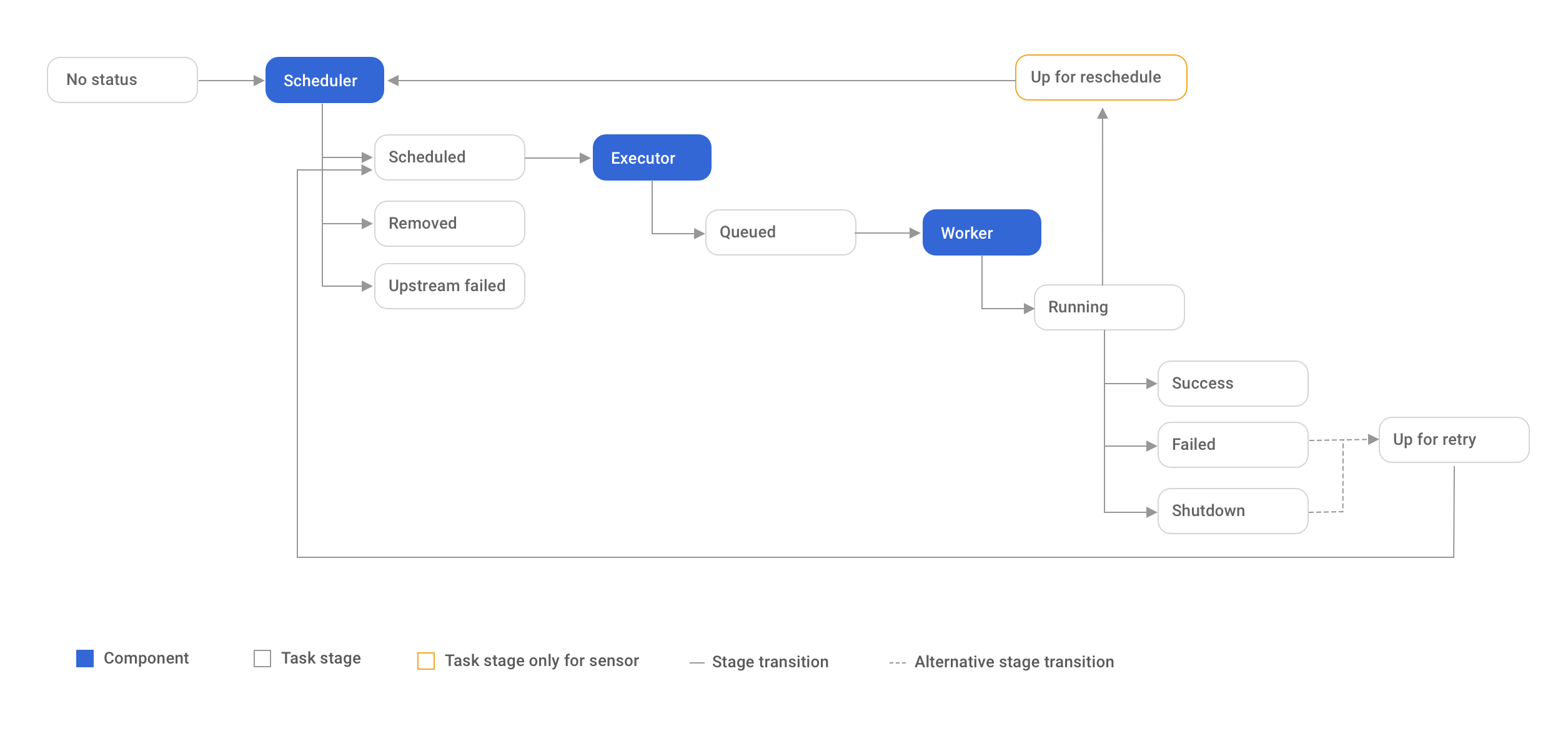
先手动clear,之后会自动再尝试运行。
如何全自动呢?
Ref: http://airflow.apache.org/docs/stable/_api/airflow/models/baseoperator/index.html
classairflow.models.baseoperator.BaseOperator(task_id, owner=conf.get('operators', 'DEFAULT_OWNER'), email=None, email_on_retry=True, email_on_failure=True, retries=conf.getint('core', 'default_task_retries', fallback=0), retry_delay=timedelta(seconds=300), retry_exponential_backoff=False, max_retry_delay=None, start_date=None, end_date=None, schedule_interval=None, depends_on_past=False, wait_for_downstream=False, dag=None, params=None, default_args=None, priority_weight=1, weight_rule=WeightRule.DOWNSTREAM, queue=conf.get('celery', 'default_queue'), pool=Pool.DEFAULT_POOL_NAME, pool_slots=1, sla=None, execution_timeout=None, on_failure_callback=None, on_success_callback=None, on_retry_callback=None, trigger_rule=TriggerRule.ALL_SUCCESS, resources=None, run_as_user=None, task_concurrency=None, executor_config=None, do_xcom_push=True, inlets=None, outlets=None, *args, **kwargs)[source]
三、传参
通过 xcom_push ,与context作为媒介,实现传递参数。
from airflow.models import DAG from airflow.utils.dates import days_ago, timedelta from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator import random args = { 'owner': 'arocketman', 'start_date': days_ago(1) } dag = DAG(dag_id='my_sample_dag_xcom', default_args=args, schedule_interval=None)
def run_this_func(**context): received_value = context['ti'].xcom_pull(key='random_value') print(f'hi, I received the following {str(received_value)}') def push_to_xcom(**context): random_value = random.random() context['ti'].xcom_push(key='random_value', value=random_value) print(f'I am okay, and i send {random_value}') with dag: run_this_task = PythonOperator( task_id='run_this', python_callable=push_to_xcom, provide_context=True, retries=10, retry_delay=timedelta(seconds=1) ) run_this_task2 = PythonOperator( task_id='run_this2', python_callable=run_this_func, provide_context=True ) run_this_task >> run_this_task2
四、工作流分支
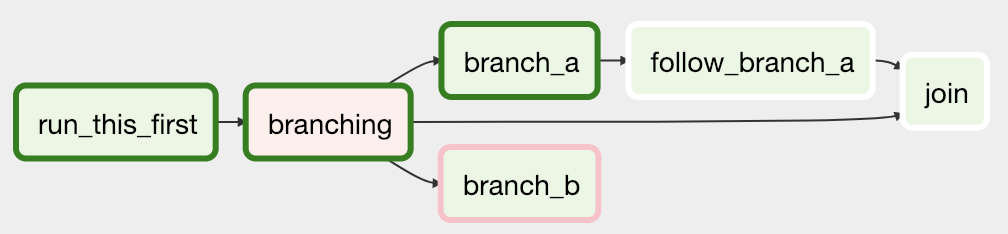
以一定的概率执行不同的分支,如下图所见。

from airflow.models import DAG from airflow.utils.dates import days_ago, timedelta from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator, BranchPythonOperator import random args = { 'owner': 'arocketman', 'start_date': days_ago(1) } dag = DAG(dag_id='my_sample_dag_branch', default_args=args, schedule_interval=None) def print_hi(**context): received_value = context['ti'].xcom_pull(key='random_value') print(f'hi, I received the following {str(received_value)}') def print_hello(**context): received_value = context['ti'].xcom_pull(key='random_value') print(f'hello, I received the following {str(received_value)}') def push_to_xcom(**context): random_value = random.random() context['ti'].xcom_push(key='random_value', value=random_value) print(f'I am okay, and i send {random_value}') def branch_func(**context): if random.random() < 0.5: return 'say_hi_task' return 'say_hello_task' with dag: run_this_task = PythonOperator( task_id='run_this', python_callable=push_to_xcom, provide_context=True, retries=10, retry_delay=timedelta(seconds=1) ) branch_op = BranchPythonOperator( task_id = 'branch_task', provide_context=True, python_callable=branch_func ) run_this_task_2 = PythonOperator( task_id='say_hi_task', python_callable=print_hi, provide_context=True ) run_this_task_3 = PythonOperator( task_id='say_hello_task', python_callable=print_hello, provide_context=True ) run_this_task >> branch_op >> [run_this_task_2, run_this_task_3]
五、操作文件
-
监听文件是否存在
每10秒,检查一次。
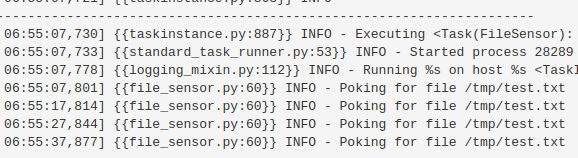
from airflow.models import DAG from airflow.utils.dates import days_ago, timedelta from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator, BranchPythonOperator import random from airflow.contrib.sensors.file_sensor import FileSensor # 有点意思 args = { 'owner': 'arocketman', 'start_date': days_ago(1) } dag = DAG(dag_id='my_sample_dag_sense', default_args=args, schedule_interval=None)
def run_this_func(**context): print('hi')
with dag: sensing_task = FileSensor( task_id = 'sensing_task', filepath = 'test.txt', fs_conn_id = 'my_file_system2', poke_interval = 10 ) run_this_task = PythonOperator( task_id = 'run_this', python_callable = run_this_func, provide_context = True ) run_this_task2 = PythonOperator( task_id = 'run_this2', python_callable = run_this_func, provide_context = True ) sensing_task >> run_this_task >> run_this_task
在 FileSensor 中需要先设置好 对应的 key值 如下: Admin --> Connections
监听是某路径下的文件。
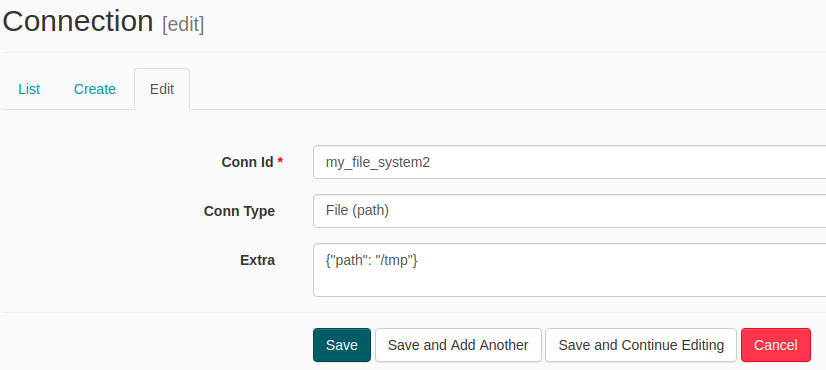
手动添加“被监听“的文件:
docker exec -it 92f42a84b32f bash
手动添加 ./tmp/test.txt 即可。
-
使用hook读取文件
如果文件存在,就开始读取,读完后顺便删除掉。
from airflow.models import DAG from airflow.utils.dates import days_ago, timedelta from airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperator, BranchPythonOperator import random import os from airflow.contrib.sensors.file_sensor import FileSensor from airflow.contrib.hooks.fs_hook import FSHook # 有点意思 args = { 'owner': 'arocketman', 'start_date': days_ago(1) } dag = DAG(dag_id='my_sample_dag_hook', default_args=args, schedule_interval=None) def print_file_content(**context):
hook = FSHook('my_file_system2') base_path = hook.get_path()
path = os.path.join(base_path, 'test.txt') # 从键值对配置中获得文件的路径 with open(path, 'r') as fp: print(fp.read()) os.remove(path) with dag: sensing_task = FileSensor( task_id = 'sensing_task', filepath = 'test.txt', fs_conn_id = 'my_file_system2', poke_interval = 10 ) read_file_content_task = PythonOperator( task_id = 'read_file_content_task_id', python_callable = print_file_content, provide_context = True, retries = 10, retry_delay = timedelta(seconds=1) ) sensing_task >> read_file_content_task
End.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号