邻接多重表
含义
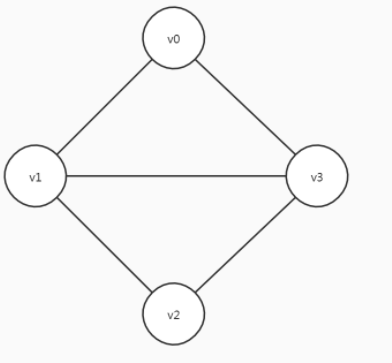
邻接多重表是无向图的一种存储方式。邻接多重表是邻接表的改进,它把边的两个顶点存放在边表结点中,所有依附于同一个顶点的边串联在同一链表中,由于每条边依附于两个顶点,则每个边表结点同时链接在两个链表中。
目的
解决邻接表存储无向图时同一条边要存储两次的问题。
代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class EdgeArc {
boolean mark;
VexNode ivex;
VexNode jvex;
EdgeArc ilink;
EdgeArc jlink;
}
class VexNode {
String name;
int data;
EdgeArc firstEdgeArc;
public VexNode(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class MultList {
int[][] graph;
List<VexNode> vexNodes;
public MultList(int[][] graph,String[] names) {
this.graph = graph;
vexNodes = buildVexNodes(graph,names);
}
public List<VexNode> buildVexNodes(int[][] graph, String[] names) {
List<VexNode> vexNodes = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][] book = new boolean[graph.length][graph.length];
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
vexNodes.add(new VexNode(names[i]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < graph[0].length; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] == 1) {
//有边,那么我们会开始构建
if (!book[i][j]) {
book[i][j] = book[j][i] = true;
EdgeArc edgeArc = new EdgeArc();
edgeArc.ivex = vexNodes.get(i);
edgeArc.jvex = vexNodes.get(j);
buildNextArc(vexNodes.get(i),edgeArc);
buildNextArc(vexNodes.get(j),edgeArc);
}
}
}
}
return vexNodes;
}
public void buildNextArc(VexNode vexNode,EdgeArc edgeArc){
if(vexNode.firstEdgeArc==null){
vexNode.firstEdgeArc = edgeArc;
return;
}
EdgeArc temp = vexNode.firstEdgeArc;
while (true){
if(temp.ivex==vexNode){
if(temp.ilink==null){
temp.ilink = edgeArc;
return;
}
temp = temp.ilink;
continue;
}
if(temp.jvex==vexNode){
if(temp.jlink==null){
temp.jlink = edgeArc;
return;
}
temp = temp.jlink;
}
}
}
public void printNodeArc(){
for(VexNode vexNode:vexNodes){
System.out.println("节点: "+vexNode.name);
EdgeArc edgeArc = vexNode.firstEdgeArc;
while (edgeArc!=null){
System.out.println(edgeArc.ivex.name+"-----"+edgeArc.jvex.name);
if(edgeArc.ivex==vexNode){
edgeArc = edgeArc.ilink;
continue;
}
if(edgeArc.jvex==vexNode){
edgeArc = edgeArc.jlink;
}
}
}
}
}
class testMultListNode{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] names = {"v1","v2","v3","v4"};
int[][] graph = {{0,1,0,1},{1,0,1,1},{0,1,0,1},{1,1,1,0}};
MultList multList = new MultList(graph,names);
multList.printNodeArc();
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号