- Idenetify the components of a Kubernetes architecture
- Identify the components of a control plane
- Identify the components of a worker plane
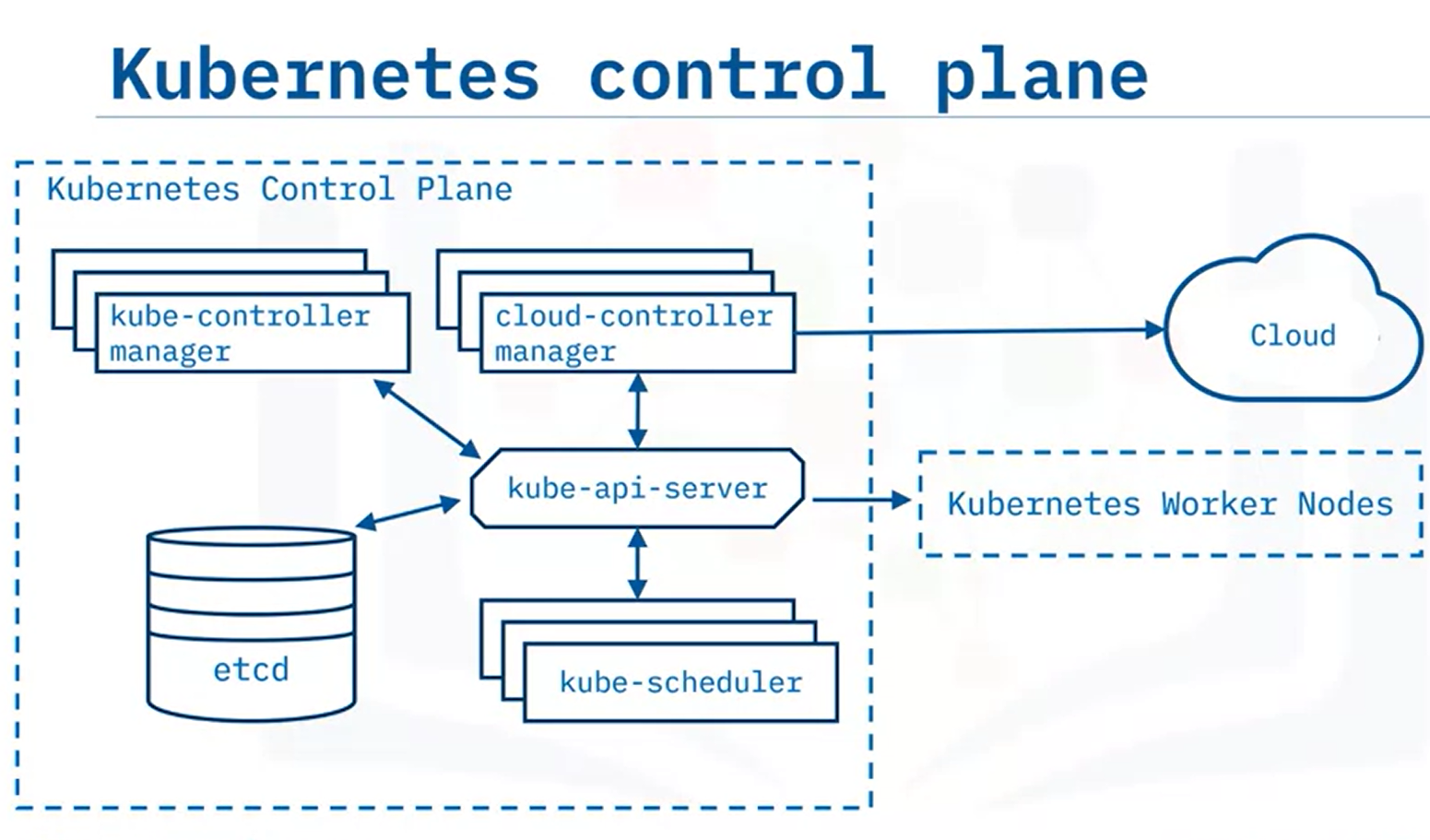
Kube-api-server:
- Exposes the kubernetes API
- Front-end for the kubernetes control plane
- All communication in the cluster utilizes this API
- Designed to scale horizontally and balance traffic between them
kube-controller-manager
- Runs controller processes that monitor cluster state
- Runs controller processes that ensure the actual state matches the desired state
cloud-controller-manager
- Runs controllers that interact with underlying cloud providers
- Links clusters into a cloud provider's API
etcd
- Highly available, distributed key-value store that contains all cluster data
- Stores deployment configuration data, the desired state, and meta can be accessed in a common location
kube-scheduler
- Assigns newly created Pods to nodes
- Selects optimal node according to Kubernetes scheduling principles, configuration options, and available resources
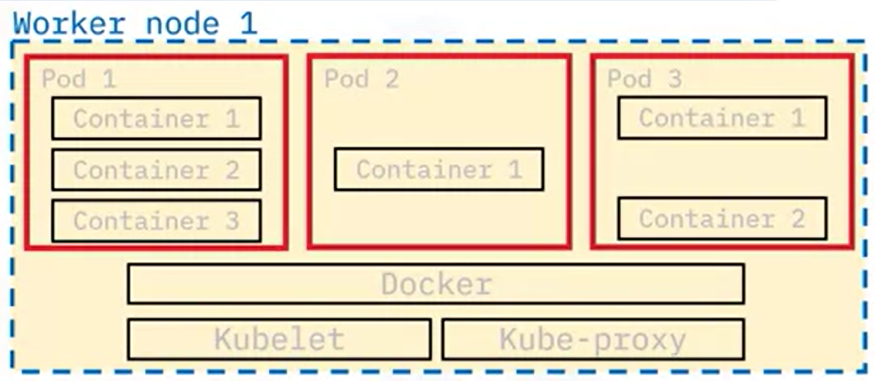
Nodes
- Are the worker machines in Kubernetes
- May be a virtual or physical machine
- Managed by the control plane
- Contain the services necessary to run applications
- Nodes include pods which are the smallest deployment entity in Kubernetes
Kubelet
- Communicates with the API server
- Ensure that Pods and their associated containers are running
- Reports to the control plane on the pods' health and status
Container runtime
- Downloads images and runs containers
- Kubernetes implements an interface so that this component is pluggable
- Docker is a well-know runtime
Kubernetes proxy
- Network proxy
- Maintains network rules that allow communication to Pods



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号