
- Define Kubernetes
- Also know as K8S, is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- An open source containerization orchestration paltform.
- Easoly portable across clouds and on-premises
- Includes a growing ecosystem of projects, products and partners
- Facilitates declarative management.
- Explain what Kubernetes is not
- Is not a traditional, all-inclusive paltform as a services
- Is not rigid or opinionated but a flexible model that supports a diverse variety of workloads and containerized applications.
- Does not provide integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines to deploy source code or build applications
- Does not prescribe logging, monitoring, or alerting solutions.
- Does not provide build-in middleware, databases, or other services
- Relate Kubernetes concepts
- Pods and Workloads: Pods are the smallest deployable compute object in Kubernetes and the higher-level abstractions to run workoads.
- Services: A service exposes application running on a set of Pods.
- Storage: Kubernetes supports both persistent and temporary Pods
- Confiuration: Resources that Kubernetes provides for configuring Pods.
- Security: Security for cloud-native workload enforces security for Pod and API access.
- Policies: Create policies for groups of resources help ensure that Pods match to the Nodes so that the Kubelet can find then and run the Pod
- Schedule, Eviction: Runs and proactively terminates one or more Pods on resource-starved Nodes
- Preemption: Terminates lower priority Pods so that higher priority Pods can run on Nodes
- Administration: Management details necessary to administer a Kubenetes cluster
- Describe Kubernetes capabilities
- Autmated rollouts and rollbacks
- Progrssively rolls out changes to application or configuration
- Monitors application health and ensures instances are running
- Rolls back changes
- Storage orchestration
- Automatically mounts your chosen storage system whether from local storage, network storage, or public cloud
- Horizontal scaling
- Scales load automatically based on metrics or via commands
- Automated bin packing
- Increaes resource utilization and cost savings using a mix of critcal and best-effort workloads
- Performs container auto-placement based on resource requirements and conditions without sacrificing high availiblity(HA)
- Secret and configuration management
- Stores and manages sesitive inforation (credentials, keys or tokens) securely
- Depolys and updates secrets and configuration without rebuilding images
- IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack
- Assings both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses to Pods and Services
- Batch execution
- Manages batch and continuous integration workloads, and replaces failed containers, if configured
- Self-healing
- Restarts, replaces, reschedules, and kills failing or unresponsive containers.
- Exposes containers to clients only if healthy and running
- Service discovery and load balancing
- Discovers Pods using their own IP addresses or a single DNS name
- Load-balances traffic acrossPods for better performance and high availabilty
- Designed for extensibility
- Easily extensible by adding or providing addtional features to your Kubernetes cluster without any source code modifications
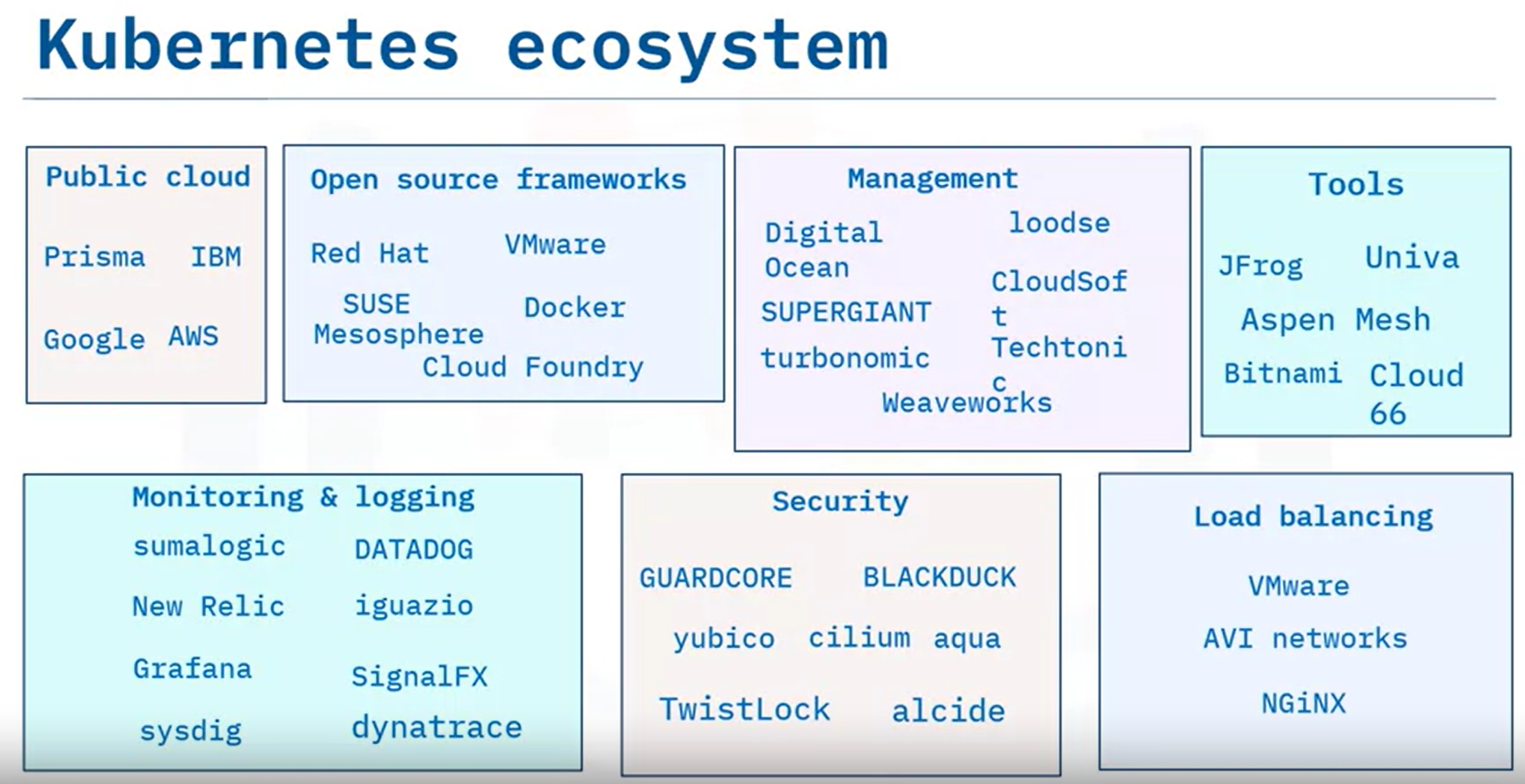
- Describe the Kubernetes ecosystem
- COntains services, support and tools that are widely available
- Provides additonal Kubernetes services
- Buidling container images
- Storing images in a container registry
- Application logging and monitoring
- Continuous improvement and continuous delivery CI/CD
-
![]()





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号