二、栈和队列
1.栈Stack
- 线性结构
- 栈对应的操作 是数组的子集
- 只能从一端存取元素
- 这一端称为栈顶

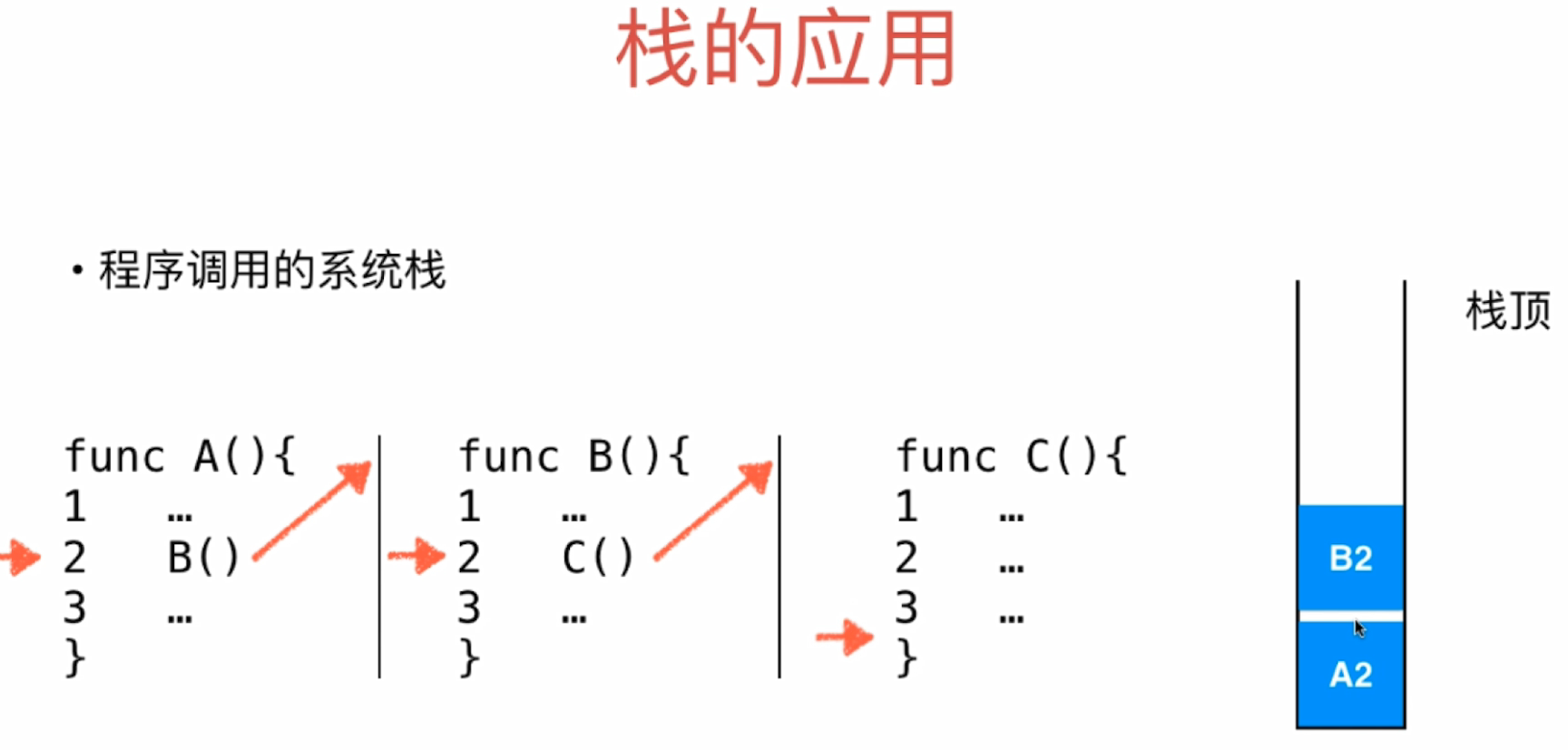
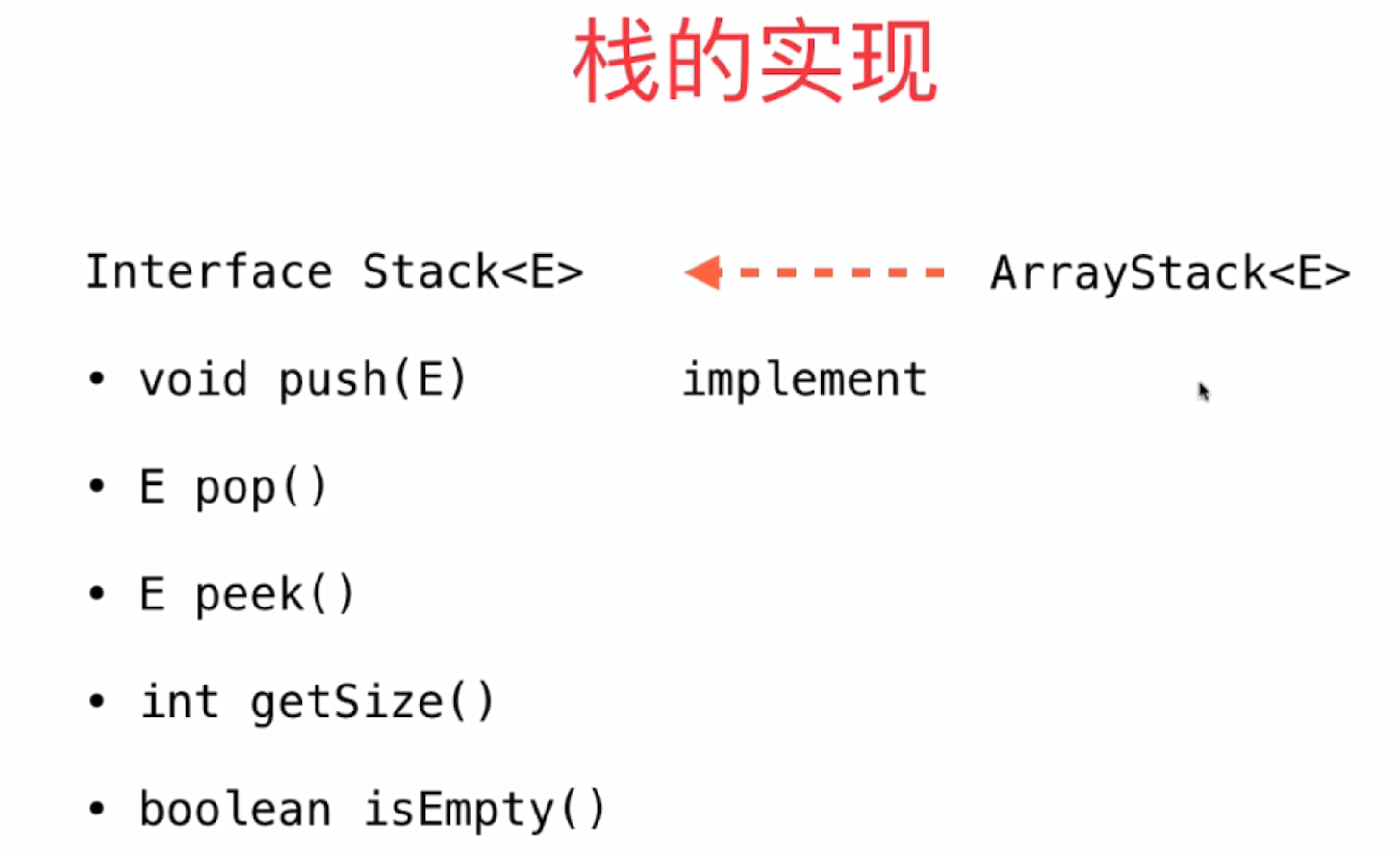
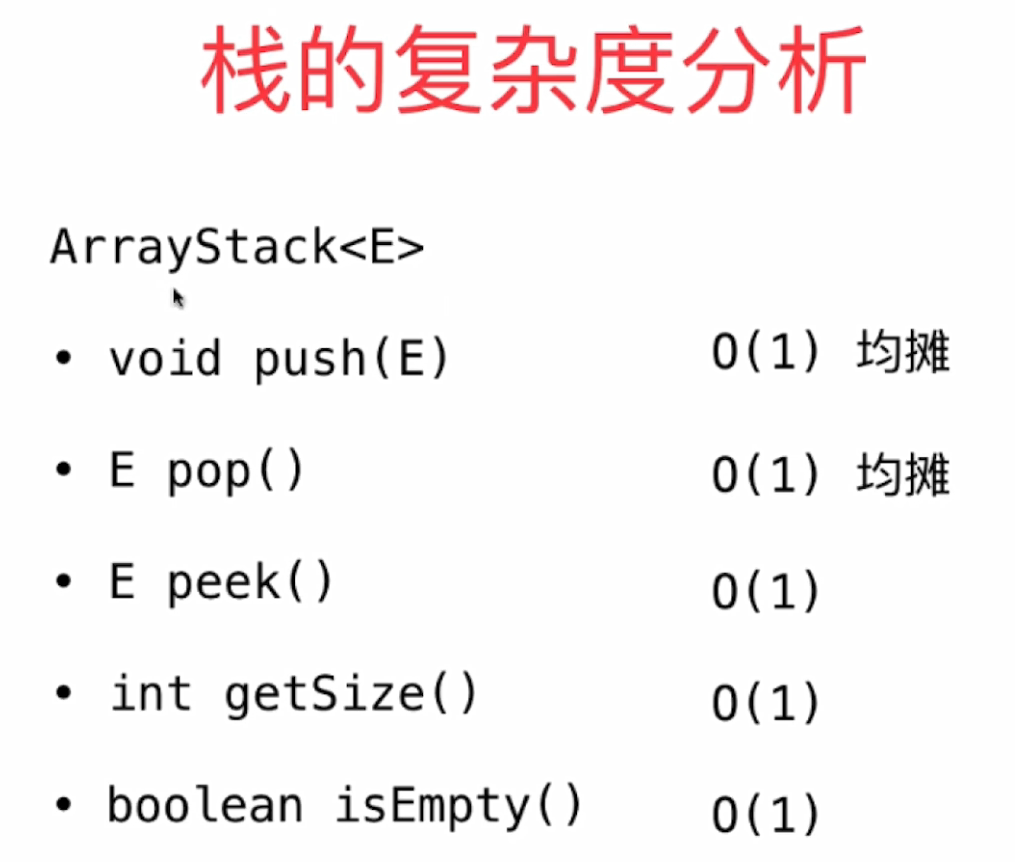
构建代码
package dataStructure.stack;
// 栈接口
public interface Stack<E> {
void push(E e);
E pop();
E peek();
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
}
package dataStructure.stack;
// 栈接口实现类
import dataStructure.arrays.Array;
public class ArrayStack<E> implements Stack<E> {
Array<E> array;
public ArrayStack(int capacity){
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public ArrayStack(){
array = new Array<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return array.getSize();
}
public int getCapacity(){
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return array.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public E peek(){
return array.getLast();
}
@Override
public void push(E e){
array.addLast(e);
}
@Override
public E pop(){
return array.removeLast();
}
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("stack: ");
res.append("[");
for(int i=0;i<array.getSize();i++){
res.append(array.get(i));
if(i != array.getSize() - 1){
res.append(",");
}
}
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
}
栈应用:有效括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
注意空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
示例 1:
输入: "()"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: "()[]{}"
输出: true
示例 3:
输入: "(]"
输出: false
示例 4:
输入: "([)]"
输出: false
示例 5:
输入: "{[]}"
输出: true
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s){
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i<s.length(); i++){
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if(ch == '(' || ch == '[' || ch == '{'){
stack.push(ch);
}else{
if(stack.isEmpty()){
return false;
}
char topChar = stack.pop();
if(ch == ')' && topChar != '('){ return false;
}
if(ch == ']' && topChar != '['){ return false;
}
if(ch == '}' && topChar != '{'){ return false;
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
2.队列Queue
- 线性结构
- 队列的操作是数组的子集
- 只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,从另一端(队首)取出元素


代码实现
package dataStructure.queue;
public interface Queue<E> {
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
void enqueue(E e);
E dequeue();
E getFront();
}
package dataStructure.queue;
import dataStructure.arrays.Array;
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
Array<E> array;
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public ArrayQueue() {
array = new Array<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return array.getSize();
}
public int getCapacity() {
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return array.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) {
array.addLast(e);
}
@Override
public E dequeue() {
return array.removeFirst();
}
@Override
public E getFront() {
return array.getFirst();
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: ");
res.append("front [");
for (int i = 0; i < array.getSize(); i++) {
res.append(array.get(i));
if (i != array.getSize() - 1) {
res.append(",");
}
}
res.append("] tail");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) {
queue.enqueue(i);
if (i % 3 == 0) {
queue.dequeue();
}
System.out.println(queue.toString());
}
}
}

3.循环队列

实现代码
package dataStructure.loopqueue;
import dataStructure.queue.Queue;
import java.util.Objects;
public class LoopQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private E[] data;
private int front;
private int tail;
private int size;
public LoopQueue(int capacity) {
this.data = (E[]) new Object[capacity + 1];
this.front = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
public LoopQueue() {
this(10);
}
public int getCapacity() {
return this.data.length - 1;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.front == this.tail;
}
/**
* 循环队列入队
*
* @param e 传入入队元素
*/
@Override
public void enqueue(E e) {
if ((this.tail + 1) % this.data.length == this.front) {
this.reSize(this.getCapacity() * 2);
}
this.data[this.tail] = e;
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % this.data.length;
this.size++;
}
/**
* 循环队列出队
*
* @return 返回出队元素
*/
@Override
public E dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("空");
}
E ret = this.data[this.front];
this.data[this.front] = null;
this.front = (this.front + 1) % this.data.length;
this.size--;
if (this.size == this.getCapacity() / 4 && this.getCapacity() / 2 != 0) {
this.reSize(this.getCapacity() / 2);
}
return ret;
}
@Override
public E getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("空");
}
return this.data[this.front];
}
/**
* 队列容量增大缩小
*
* @param newCapacity
*/
private void reSize(int newCapacity) {
E[] newData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
newData[i] = data[(i + front) % this.data.length];
}
this.data = newData;
this.front = 0;
this.tail = this.size;
}
/**
* @return 以固定格式返回队列容量,有效元素个数,元素值
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Queue size=%d,capacity=%d\n", this.size, this.getCapacity()));
res.append("front [");
for (int i = this.front; i != this.tail; i = (i + 1) % this.data.length) {
res.append(this.data[i]);
if ((i + 1) % this.data.length != this.tail) {
res.append(", ");
}
}
res.append("] tail");
return res.toString();
}
}
测试代码
package dataStructure.loopqueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LoopQueue<Integer> loopqueue = new LoopQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
loopqueue.enqueue(i);
if(i % 3 == 0){
loopqueue.dequeue();
}
System.out.println(loopqueue.toString());
}
}
}
打印结果
Queue size=0,capacity=10
front [] tail
Queue size=1,capacity=10
front [1] tail
Queue size=2,capacity=10
front [1, 2] tail
Queue size=2,capacity=5
front [2, 3] tail
Queue size=3,capacity=5
front [2, 3, 4] tail
Queue size=4,capacity=5
front [2, 3, 4, 5] tail
Queue size=4,capacity=5
front [3, 4, 5, 6] tail
Queue size=5,capacity=5
front [3, 4, 5, 6, 7] tail
Queue size=6,capacity=10
front [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] tail
Queue size=6,capacity=10
front [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] tail
测试循环队列入队出队用时
package dataStructure.loopqueue;
import dataStructure.queue.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q, int opCount) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < opCount; i++) {
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
for (int j = 0; j < opCount; j++) {
q.dequeue();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime-startTime)/1E9;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000;
LoopQueue<Integer> lq = new LoopQueue<>();
double t2 = testQueue(lq,opCount);
System.out.println(t2);
}
}






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号