Trace 2018徐州icpc网络赛 (二分)(树状数组)
Trace
There's a beach in the first quadrant. And from time to time, there are sea waves. A wave ( xxx , yyy ) means the wave is a rectangle whose vertexes are ( 000 , 000 ), ( xxx , 000 ), ( 000 , yyy ), ( xxx , yyy ). Every time the wave will wash out the trace of former wave in its range and remain its own trace of ( xxx , 000 ) -> ( xxx , yyy ) and ( 000 , yyy ) -> ( xxx , yyy ). Now the toad on the coast wants to know the total length of trace on the coast after n waves. It's guaranteed that a wave will not cover the other completely.
Input
The first line is the number of waves n(n≤50000)n(n \le 50000)n(n≤50000).
The next nnn lines,each contains two numbers xxx yyy ,( 0<x0 < x0<x , y≤10000000y \le 10000000y≤10000000 ),the iii-th line means the iii-th second there comes a wave of ( xxx , yyy ), it's guaranteed that when 1≤i1 \le i1≤i , j≤nj \le nj≤n ,xi≤xjx_i \le x_jxi≤xj and yi≤yjy_i \le y_jyi≤yj don't set up at the same time.
Output
An Integer stands for the answer.
Hint:
As for the sample input, the answer is 3+3+1+1+1+1=103+3+1+1+1+1=103+3+1+1+1+1=10
样例输入
3 1 4 4 1 3 3
样例输出
10
题目来源
比赛的时候想的是手撸一个平衡树排序,然后二分查找这个点左右两边的点,再比较他们的边值,结果数据结构写炸了
赛后看到网上题解才想起set和list 这些stl 太弱了Orz
用set这类的话 就把一个点的边值拆成两个处理,从后往前,(后面的点总是覆盖前面),看看当今的点时候比后面的点边值高出多少
set的二分还是要%一下,毕竟没这么写过

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 typedef long long ll; 5 int n; 6 const int maxn = 5e4+5; 7 const int maxnn = 1e7+7; 8 9 vector<int>vec1,vec2; 10 ll solve(vector<int>vec) 11 { 12 ll ans = 0; 13 int sz = vec.size(); 14 set<int>st; 15 for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) 16 { 17 set<int>::iterator it = st.lower_bound(vec[i]); 18 if(it == st.begin())ans += vec[i]; 19 else 20 { 21 it--; 22 ans += vec[i] - *it; 23 } 24 st.insert(vec[i]); 25 } 26 return ans; 27 } 28 29 int main() 30 { 31 scanf("%d",&n); 32 int x,y; 33 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 34 { 35 scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); 36 vec1.push_back(x); 37 vec2.push_back(y); 38 } 39 printf("%lld\n",solve(vec1)+solve(vec2)); 40 }
除了可以二分之外 还有树状数组的写法,能树状数组肯定可以线段树。这里先补上树状数组的做法。
trex表示是一个记录相应x位置的y的值的前缀和,trey也类似
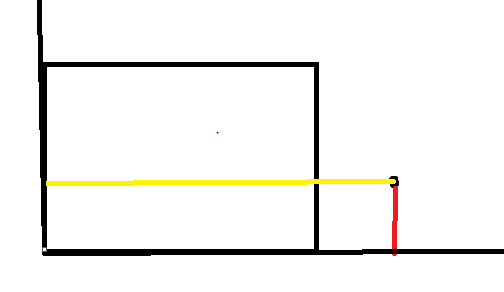
那么插入(4,1)的时候 更改trex,trey, y from 0 到 1 所遇到的横向遇到x都是3;x from 0 to 3 和 from 4 to 4 对应y值不同,这样就用到树状数组的区间更新
把query 出来的上一个位置+1的位置更新加上现在的点和之前的差值 然后在现在位置+1的位置减去 例如:trex(x在各个位置对应的y值) 3+1位置加上差值 (1-3) 4+1位置加上差值的相反数

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 const int maxn = 5e4+5; 5 const int maxx = 1e7+5; 6 int n; 7 struct Node 8 { 9 int x,y; 10 }node[maxn]; 11 int trex[maxx]; 12 int trey[maxx]; 13 14 int maxxx = 0; 15 int lowbit(int x) 16 { 17 return x &(-x); 18 } 19 void add(int x,int val,int *tre) 20 { 21 for(int i=x;i<=maxxx;i+=lowbit(i)) 22 { 23 tre[i] += val; 24 } 25 } 26 27 int query(int x,int *tre) 28 { 29 int ans = 0; 30 for(int i=x;i>0;i-=lowbit(i)) 31 { 32 ans += tre[i]; 33 } 34 return ans; 35 } 36 int main() 37 { 38 scanf("%d",&n); 39 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 40 { 41 scanf("%d%d",&node[i].x,&node[i].y); 42 maxxx = max(maxxx,max(node[i].x,node[i].y)); 43 } 44 ll ans = 0; 45 for(int i=n;i>0;i--) 46 { 47 int x = node[i].x; 48 int y = node[i].y; 49 int lenx = query(y,trey); 50 int leny = query(x,trex); 51 ans += x - lenx; 52 ans += y - leny; 53 int valy = query(x,trex); 54 int valx = query(y,trey); 55 add(valy+1,x-valx,trey); 56 add(y+1,valx-x,trey); 57 add(valx+1,y-valy,trex); 58 add(x+1,valy-y,trex); 59 //printf("%d---%d %d---%d %d----%d\n",x,y,x-valx,y-valy,valx,valy); 60 } 61 printf("%lld\n",ans); 62 }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号