基于Java算法支持4万qps的抽奖代码实战项目案例分享
笔者16年刚入新公司不久时,曾接到一个需求要搞一个从来没搞过的抽奖项目。做摇一摇、大转盘等抽奖业务。和两个小伙伴一起,我负责服务端抽奖的所有接口,他们负责后台抽奖数据管理,一周时间搞定。当时由于刚进公司,对公司产品流量没什么经验数据,某个同事给的方案是抽奖过程查数据、存数据走Mysql数据库。刚上线时还算顺利,流量确实不是很高,但也吃紧吧。不久恰逢公司想做大力度活动,筹划了一个百万红包雨,几乎是没有开发时间的。当时产品找过来要求前端直接对接我们接口。我给的评估是流量太高,走数据库肯定撑不住的,但是大家都是新人,都不知道会有多少流量会进来,这个活动也是第一次做,时间上似乎确实是来不及了。最后强行对接了我们的抽奖接口。后果是,系统大面积瘫痪,3分钟写入几十万数据,严重线上事故。。。
事故之后,便是反思以及做系统改造,使其能够支撑现有业务。于是,我这边负责抽奖服务的改造工作。经过一系列改造和压测后,抽奖服务的性能达到了4万qps,基本满足了业务的要求。下面简单分享下我的项目改造的一些实战经验吧。
一、抽奖算法模型
以下是省略了相关业务、额外算法的单纯根据配置计算中奖概率的算法代码,方便读者理解算法
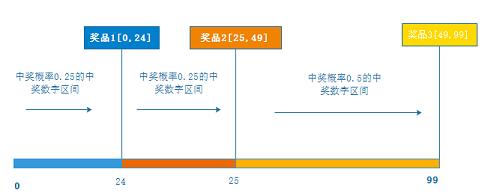
图示,阐述了算法原理,计算出抽奖活动一组数字,根据抽奖奖品的概率计算出每个奖品所在的数字区间。Random随机数落在了哪个奖品的数字区间,则用户中这个区间对应的奖品。
1)抽奖奖品对象
public class LotteryItem {
/**
* 奖品名称
*/
private String awardName;
/**
* 中奖几率
*/
private Double awardProbability;
/**
* 奖品中奖数字范围起点
*/
private Integer awardStartCode;
/**
* 奖品中奖数字范围终点
*/
private Integer awardEndCode;
/**
* 中奖数字,实际应用可不定义。
* 此处定义是为了方便读者理解
*/
private Integer awardCode;
public String getAwardName() {
return awardName;
}
public void setAwardName(String awardName) {
this.awardName = awardName;
}
public Double getAwardProbability() {
return awardProbability;
}
public void setAwardProbability(Double awardProbability) {
this.awardProbability = awardProbability;
}
public Integer getAwardStartCode() {
return awardStartCode;
}
public void setAwardStartCode(Integer awardStartCode) {
this.awardStartCode = awardStartCode;
}
public Integer getAwardEndCode() {
return awardEndCode;
}
public void setAwardEndCode(Integer awardEndCode) {
this.awardEndCode = awardEndCode;
}
public Integer getAwardCode() {
return awardCode;
}
public void setAwardCode(Integer awardCode) {
this.awardCode = awardCode;
};
}
2) 抽奖信息对象
/**
* @description: 抽奖活动中,中奖概率计算模型
* @author www.ityuan.com
* @date 2017年12月28日 上午11:48:02
*/
public class Lottery {
/**
* 中奖数字范围起点(通常0作为起点)
*/
private Integer winningStartCode;
/**
* 当前概率计算出的中奖数字范围终点
*/
private Integer winningEndCode;
/**
* 中奖的数字范围
*/
private Integer codeScope;
public Integer getWinningStartCode() {
return winningStartCode;
}
public void setWinningStartCode(Integer winningStartCode) {
this.winningStartCode = winningStartCode;
}
public Integer getWinningEndCode() {
return winningEndCode;
}
public void setWinningEndCode(Integer winningEndCode) {
this.winningEndCode = winningEndCode;
}
public Integer getCodeScope() {
return codeScope;
}
public void setCodeScope(Integer codeScope) {
this.codeScope = codeScope;
}
}
3)抽奖算法代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @description: TODO(这里用一句话描述这个类的作用)
* @author www.ityuan.com
* @date 2017年12月28日 下午9:24:40
*/
public class LotteryUtils {
private static final Random random = new Random();
private static final Integer MAXSOPE = 100000000;
public static void calAwardProbability(Lottery lottery, List<LotteryItem> lotteryItemList) {
Integer codeScope = 1;
for (LotteryItem item : lotteryItemList) {
Integer nowScope = 1;
Double awardProbability = item.getAwardProbability();
while (true) {
Double test = awardProbability * nowScope;
// 概率的精确度,调整到小数点后10位,概率太小等于不中奖,跳出
if (test < 0.0000000001) {
break;
}
if ((test >= 1L && (test - test.longValue()) < 0.0001D) || nowScope >= MAXSOPE) {
if (nowScope > codeScope) {
// 设置中奖范围
codeScope = nowScope;
}
break;
} else {
// 中奖数字范围以10倍进行增长
nowScope = nowScope * 10;
}
}
}
Integer winningStartCode = 0;
Integer winningEndCode = winningStartCode;
for (LotteryItem item : lotteryItemList) {
Integer codeNum = (int) (item.getAwardProbability() * codeScope); // 获得其四舍五入的整数值
// 无人中奖时,将中奖的起始范围设置在随机数的范围之外
if (codeNum == 0) {
item.setAwardStartCode(codeScope + 1);
item.setAwardEndCode(codeScope + 1);
} else {
item.setAwardStartCode(winningEndCode);
item.setAwardEndCode(winningEndCode + codeNum - 1);
winningEndCode = winningEndCode + codeNum;
}
}
// 设置用户的中奖随机码信息
lottery.setWinningStartCode(winningStartCode);
lottery.setWinningEndCode(winningEndCode);
lottery.setCodeScope(codeScope);
}
public static LotteryItem beginLottery(Lottery lottery, List<LotteryItem> lotteryItemList) {
// 确定活动是否有效,如果活动无效则,直接抽奖失败
Integer randomCode = random.nextInt(lottery.getCodeScope());
if (randomCode >= lottery.getWinningStartCode() && randomCode <= lottery.getWinningEndCode()) {
for (LotteryItem item : lotteryItemList) {
if (randomCode >= item.getAwardStartCode() && randomCode <= item.getAwardEndCode()) {
item.setAwardCode(randomCode);
return item;
}
}
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<LotteryItem> lotteryItemList = new ArrayList<LotteryItem>();
LotteryItem awardItem1 = new LotteryItem();
awardItem1.setAwardName("红包10元");
awardItem1.setAwardProbability(0.25D);
lotteryItemList.add(awardItem1);
LotteryItem awardItem2 = new LotteryItem();
awardItem2.setAwardName("红包20元");
awardItem2.setAwardProbability(0.25D);
lotteryItemList.add(awardItem2);
LotteryItem awardItem3 = new LotteryItem();
awardItem3.setAwardName("谢谢参与");
awardItem3.setAwardProbability(0.5D);
lotteryItemList.add(awardItem3);
Lottery lottery = new Lottery();
LotteryUtils.calAwardProbability(lottery, lotteryItemList);
System.out.println("抽奖活动中奖数字范围:["+lottery.getWinningStartCode()+","+lottery.getWinningEndCode()+")");
LotteryUtils.beginLottery(lottery, lotteryItemList);
for (LotteryItem item : lotteryItemList) {
System.out.println(item.getAwardName()+" 中奖数字范围:["+item.getAwardStartCode()+","+item.getAwardEndCode()+"]");
}
System.out.println("以下是模拟的抽奖中奖结果:");
LotteryItem award1 = LotteryUtils.beginLottery(lottery, lotteryItemList);
System.out.println("抽中的数字是:"+award1.getAwardCode()+",恭喜中奖:"+award1.getAwardName()+",数字落点["+award1.getAwardStartCode()+","+award1.getAwardEndCode()+"]");
LotteryItem award2 = LotteryUtils.beginLottery(lottery, lotteryItemList);
System.out.println("抽中的数字是:"+award2.getAwardCode()+",恭喜中奖:"+award2.getAwardName()+",数字落点["+award2.getAwardStartCode()+","+award2.getAwardEndCode()+"]");
LotteryItem award3 = LotteryUtils.beginLottery(lottery, lotteryItemList);
System.out.println("抽中的数字是:"+award3.getAwardCode()+",恭喜中奖:"+award3.getAwardName()+",数字落点["+award3.getAwardStartCode()+","+award3.getAwardEndCode()+"]");
LotteryItem award4 = LotteryUtils.beginLottery(lottery, lotteryItemList);
System.out.println("抽中的数字是:"+award4.getAwardCode()+",恭喜中奖:"+award4.getAwardName()+",数字落点["+award4.getAwardStartCode()+","+award4.getAwardEndCode()+"]");
}
}
抽奖Demo代码执行结果
抽奖活动中奖数字范围:[0,100) 红包10元 中奖数字范围:[0,24] 红包20元 中奖数字范围:[25,49] 谢谢参与 中奖数字范围:[50,99] 以下是模拟的抽奖中奖结果: 抽中的数字是:47,恭喜中奖:红包20元,数字落点[25,49] 抽中的数字是:69,恭喜中奖:谢谢参与,数字落点[50,99] 抽中的数字是:22,恭喜中奖:红包10元,数字落点[0,24] 抽中的数字是:83,恭喜中奖:谢谢参与,数字落点[50,99]
二、对核心电商系统的保护
如果因为成本控制原因,当电商系统的硬件耐压能力有限时,抽奖活动带来的瞬间高频流量可能会将防火墙击溃,从而导致整个电商或者其他正常业务受影响。这时候就需要考虑将抽奖系统与正常业务系统的环境进行隔离。例如,将抽奖系统迁移到阿里云上部署或者其他次要机房。
三、系统的过载保护
系统的过载保护目的是当流量超出预期时,自动过滤一部分流量,防止系统被拖垮。
常用的过载保护思路,大多是基于漏桶算法思想或者信号量控制。
例如:java自带的Semaphore 或者Google Guava
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(10);
if (semaphore.tryAcquire()) {// (非阻塞式)
// 获得许可证才可进行下一步操作
// semaphore.acquire();(阻塞式)
// dos somethine
// 释放许可证
semaphore.release();
}
四、前端的空包策略
在预估流量过高的情况下,可以前端采用空包的策略。即用户发起的抽奖一定概率下不调用后端接口服务,直接返回未中奖。防止过多的请求流向后端服务。
五、数据的存储策略,压测支持4万qps
如果数据查询直接走数据库,在不可预计的高频流量下,极有可能拖垮数据库,从而导致整个服务崩溃。所以,要支持高并发、高流量,需采用高效的缓存策略以及耐压的数据存储服务。
1) 本地缓存策略,抽奖的基础数据因为数据量不大,可以放入到本地缓存中。从而进行高效读取。
2) Redis缓存策略,数据查询先走本地缓存,再走Redis缓存,最后走MySql,也就是说几乎彻底隔离了抽奖过程中与数据库的直接打交道。
六、高并发下抽奖如何防止奖品因为并发超量发奖?
采用Redis的自增策略,可在高效抽奖的同时并保证类似数据库乐观锁的方式,来实现抽奖的奖品不会被超量抽中奖。实现方式如下:
参考Redis的封装:http://www.ityuan.com/coding/385.html
封装一个Redis的工具类:RedisUtils以及方法inc。RedisUtils.inc(“key”) 每执行一次,返回值自增+1。那么:
RedisUtils.inc(“Prefix”+lotteryItemId) 自增值大于奖品lotteryItem的最大可发奖品数num时,则返回谢谢参与或者未中奖即可。
七、中奖记录的保存、抽取、发奖
1) 用户中奖后,将中奖记录保存Redis中。为方便将数据取出,需要通过Redis构造一个自增主键(incKey)与抽奖活动ID构建缓存的Key。我们暂且将它命名为:lotteryAwardKey。
lotteryAwardKey = "prefix"+lotteryId+"_"+incValue。
incValue从1开始自增。nowIncValue=RedisUtils.inc(lotteryAwardKey);
2) 将中奖记录抽取并批量insert进入Mysql数据库,类似代码如下:
for (int start = awardPageNo;start < nowIncValue;start++) {
awardList.add(RedisUtils.get("prefix”+lotteryId+"_"+start));
}
(这里awardPageNo为尚未抽取数据的自增值的起点)
3)发奖操作,只需要定时器将Mysql中未发奖的中奖数据捞取,采用多线程发奖即可。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号