Triton Docs | Triton 入门(一)
Triton 入门
参考 Triton 官方教程。
算子编写 - Vector Add
triton.jit
用于使用 Triton 编译器对函数进行 JIT 编译,该函数将被编译为 Triton Kernel 并可在 GPU 上并行运行,使用 jit 装饰器的函数只能访问 Python 基础数据类型、Triton 包内的内置函数、该函数的参数以及其他 JIT 函数。
Codes
@triton.jit
def add_kernel(x_ptr, # *Pointer* to first input vector.
y_ptr, # *Pointer* to second input vector.
output_ptr, # *Pointer* to output vector.
n_elements, # Size of the vector.
BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr, # Number of elements each program should process.
# NOTE: `constexpr` so it can be used as a shape value.
):
# There are multiple 'programs' processing different data. We identify which program
# we are here:
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0) # We use a 1D launch grid so axis is 0.
# This program will process inputs that are offset from the initial data.
# For instance, if you had a vector of length 256 and block_size of 64, the programs
# would each access the elements [0:64, 64:128, 128:192, 192:256].
# Note that offsets is a list of pointers:
block_start = pid * BLOCK_SIZE
offsets = block_start + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)
# Create a mask to guard memory operations against out-of-bounds accesses.
mask = offsets < n_elements
# Load x and y from DRAM, masking out any extra elements in case the input is not a
# multiple of the block size.
x = tl.load(x_ptr + offsets, mask=mask)
y = tl.load(y_ptr + offsets, mask=mask)
output = x + y
# Write x + y back to DRAM.
tl.store(output_ptr + offsets, output, mask=mask)
参数列表中,使用 tl.constexpr 可以告诉编译器参数 BLOCK_SIZE 是常量,并且其值在编译时就已确定,有助于优化 Kernel 性能和生成高性能代码。
前提。在 Triton 中是以块为单位进行运算,而在 CUDA 中最小的单位是线程。因此,首行用于获取当前线程块的 ID,其中 axis=0 表示沿着第一个维度获取线程块 ID,然后乘以块大小 BLOCK_SIZE 以计算当前块在全局数组中的起始索引。
tl.program_id(axis=0)
通过辅助函数 (下方给出) 便于更好理解概念。实际上块数 (线程数) 是向量维数除以 BLOCK_SIZE,并进行上取整。这便于理解代码中多次进行的偏移量计算。pid 实际上是这些 BLOCK 的索引,第 pid 个线程,其起始位置为 pid * BLOCK_SIZE,每个线程处理一个大小为 BLOCK_SIZE 的数据块。
接下来生成偏移量列表和掩码,避免越界访问。
offsets = block_start + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)
mask = offsets < n_elements
从 DRAM 加载 \(x, y\),同样以块 (线程) 粒度进行
x = tl.load(x_ptr + offsets, mask=mask)
y = tl.load(y_ptr + offsets, mask=mask)
output = x + y
向 DRAM 保存结果,同上
tl.store(output_ptr + offsets, output, mask=mask)
辅助函数如下。
def add(x: torch.Tensor, y: torch.Tensor):
# We need to preallocate the output.
output = torch.empty_like(x)
assert x.device == DEVICE and y.device == DEVICE and output.device == DEVICE
n_elements = output.numel()
# The SPMD launch grid denotes the number of kernel instances that run in parallel.
# It is analogous to CUDA launch grids. It can be either Tuple[int], or Callable(metaparameters) -> Tuple[int].
# In this case, we use a 1D grid where the size is the number of blocks:
grid = lambda meta: (triton.cdiv(n_elements, meta['BLOCK_SIZE']), )
# NOTE:
# - Each torch.tensor object is implicitly converted into a pointer to its first element.
# - `triton.jit`'ed functions can be indexed with a launch grid to obtain a callable GPU kernel.
# - Don't forget to pass meta-parameters as keywords arguments.
add_kernel[grid](x, y, output, n_elements, BLOCK_SIZE=1024)
# We return a handle to z but, since `torch.cuda.synchronize()` hasn't been called, the kernel is still
# running asynchronously at this point.
return output
可以清晰看到 grid 的定义过程,与上文 tl.program_id(axis=0) 关联。这里使用了一个 Triton 独有的语法糖
add_kernel[grid](x, y, output, n_elements, BLOCK_SIZE=1024)
方括号索引用于指定 GPU 内核的执行配置 (launch grid),其返回一个被 triton.jit 修饰后的 Kernel 函数,即上文定义的 vector_add. CoPilot 给出的解释是为了与 CUDA 网格配置语法一致。这里不是很理解,保留疑问。
运行
需要修改一行代码
- DEVICE = triton.runtime.driver.active.get_active_torch_device()
+ DEVICE = torch.device('cuda:0')
如果不使用 Jupyter,需要添加 save_path
benchmark.run(print_data=True, show_plots=True, save_path='./results-01/')
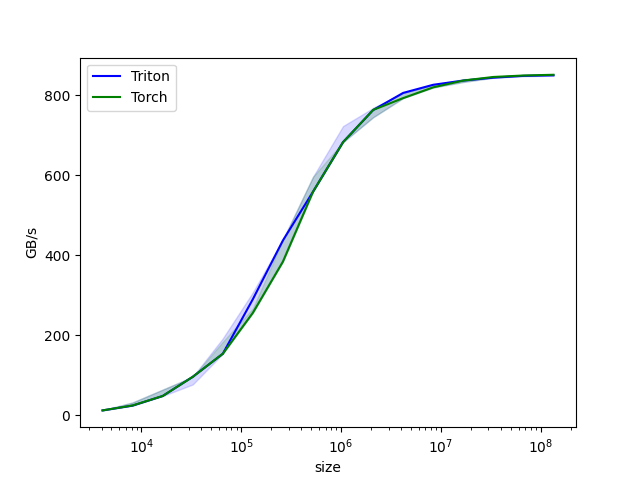
运行性能基准测试,结果如下。
(torch0) root@pve:~/share/project/triton-lang.org# python3 01-vector-add.py
tensor([1.3713, 1.3076, 0.4940, ..., 0.6724, 1.2141, 0.9733], device='cuda:0')
tensor([1.3713, 1.3076, 0.4940, ..., 0.6724, 1.2141, 0.9733], device='cuda:0')
The maximum difference between torch and triton is 0.0
vector-add-performance:
size Triton Torch
0 4096.0 12.000000 12.000000
1 8192.0 24.000000 24.000000
2 16384.0 48.000000 48.000000
3 32768.0 96.000000 96.000000
4 65536.0 153.600004 182.044451
5 131072.0 255.999991 255.999991
6 262144.0 384.000001 438.857137
7 524288.0 558.545450 558.545450
8 1048576.0 682.666643 682.666643
9 2097152.0 744.727267 744.727267
10 4194304.0 805.770507 792.774204
11 8388608.0 826.084057 819.200021
12 16777216.0 836.629789 836.629789
13 33554432.0 843.811163 845.625825
14 67108864.0 848.362445 850.010134
15 134217728.0 849.278610 851.116890
Triton 调试方法及工具
待更新


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号