一文入门Agent MCP
一文入门Agent MCP
作者简介
- 微信公众号:coft
- 博客园首页:https://www.cnblogs.com/informatics/
- GitHub地址:https://github.com/warm3snow
目录
背景介绍
什么是MCP?
Model Context Protocol (MCP) 是由 Anthropic 开发的一种开放标准协议,旨在解决 AI 应用程序与外部数据源和工具安全连接的问题。MCP 使大语言模型能够通过标准化的接口访问各种资源,包括数据库、文件系统、API 服务等。
产生背景
随着大语言模型(LLM)应用的快速发展,我们面临以下挑战:
- 数据孤岛问题:LLM 需要访问各种不同的数据源,但这些数据源往往相互隔离
- 安全性考虑:直接访问敏感数据可能带来安全风险
- 标准化缺失:缺乏统一的接口标准,导致集成复杂度高
- 维护困难:每个数据源都需要单独的集成方案,维护成本高
MCP 的出现正是为了解决这些痛点,提供一个:
- 标准化的协议接口
- 安全可控的访问机制
- 易于集成的开发框架
- 可扩展的架构设计
技术架构
核心组件
MCP 架构由三个核心组件构成:MCP Host、MCP Client 和 MCP Server,它们协同工作实现AI应用与外部资源的无缝集成。
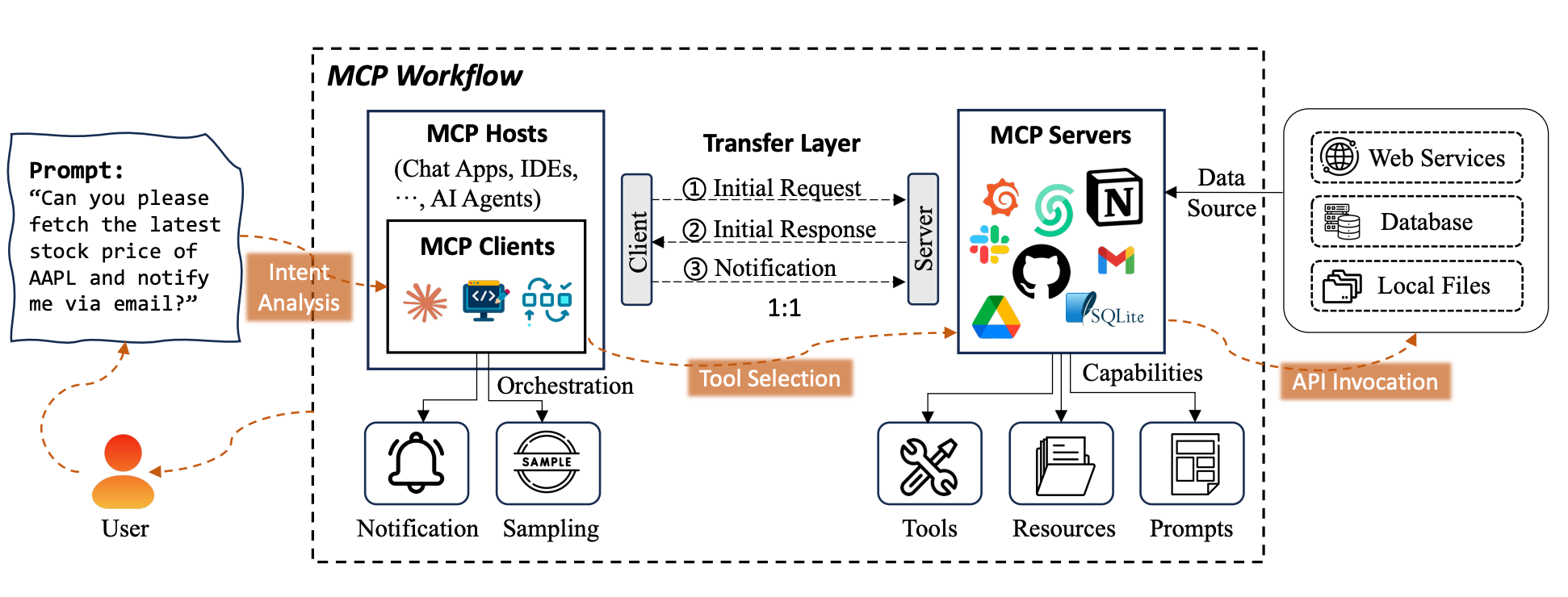
1. MCP Host(宿主环境)
- 定义:运行AI应用的执行环境,如Claude Desktop、Cursor、AI Agents等
- 职责:
- 提供LLM运行环境和用户交互界面
- 调用LLM进行意图分析和工具选择
- 管理与MCP Client的集成
2. MCP Client(客户端)
- 定义:AI应用与MCP Server之间的通信代理
- 职责:
- 建立和维护与MCP Server的连接
- 转发LLM生成的工具调用请求
- 处理响应和错误信息
3. MCP Server(服务器)
提供三大核心能力:
Tools(工具):执行外部操作
- 允许AI模型调用外部服务和API
- 支持标准化的参数传递和结果返回
- 例如:文件操作、数据查询、API调用
Resources(资源):暴露数据访问
- 通过URI模式访问结构化/非结构化数据
- 支持参数化路径和动态内容生成
- 例如:
note://{filename}、db://users/{id}
Prompts(提示):提供模板化工作流
- 预定义的任务模板和最佳实践
- 支持参数化和上下文感知
- 确保输出一致性和任务效率
通信机制
MCP基于JSON-RPC 2.0协议,支持多种传输方式:
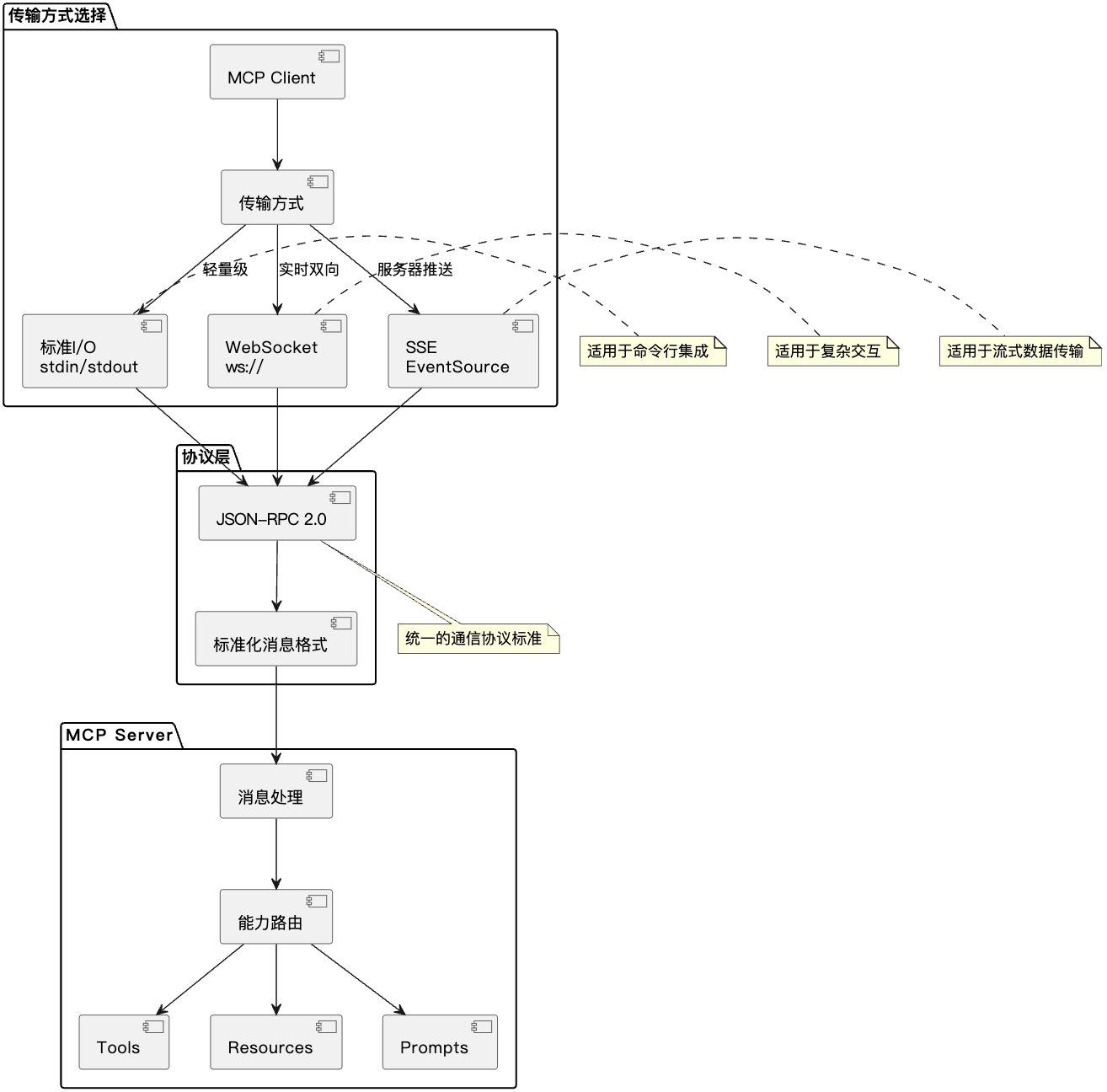
- 标准I/O:轻量级,适用于命令行集成
- WebSocket:双向实时通信,适用于复杂交互
- SSE:服务器推送,适用于流式数据传输
工作流程
以股票查询为例的完整流程:

关键步骤说明:
- 意图分析:LLM分析用户需求,识别所需的工具和服务
- 调用生成:生成标准化的MCP工具调用请求
- 协议传输:Client通过JSON-RPC 2.0协议与Server通信
- 服务执行:Server调用相应的外部API或服务
- 结果返回:格式化结果并返回给用户
MCP vs 传统方案对比
| 对比维度 | 传统函数调用 | MCP方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 集成方式 | 开发者预定义函数映射 | LLM生成标准MCP调用 |
| 开发复杂度 | 每个API单独编写代码 | 配置驱动,统一接口 |
| 维护成本 | 高(API变更需修改代码) | 低(配置文件管理) |
| 安全性 | 分散管理,易暴露密钥 | 集中管理,协议层保护 |
| 扩展性 | 难(需重新开发集成) | 易(添加配置即可) |
| 标准化 | 缺乏统一标准 | 基于JSON-RPC 2.0标准 |
MCP Server 开发指南与示例
开发环境准备
项目初始化
# 创建新项目
mkdir my-mcp-server
cd my-mcp-server
# 初始化package.json
npm init -y
# 安装依赖
npm install @modelcontextprotocol/sdk zod
# 安装开发依赖
npm install -D typescript @types/node
项目结构
my-mcp-server/
├── src/
│ └── index.ts # 主入口文件
├── package.json # 项目配置
├── tsconfig.json # TypeScript配置
└── README.md # 文档说明
配置文件
package.json:
{
"name": "my-mcp-server",
"version": "1.0.0",
"type": "module",
"main": "build/index.js",
"bin": {
"my-mcp-server": "build/index.js"
},
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc",
"start": "node build/index.js",
"dev": "tsc --watch"
},
"dependencies": {
"@modelcontextprotocol/sdk": "^0.5.0",
"zod": "^3.22.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "^20.0.0",
"typescript": "^5.0.0"
}
}
tsconfig.json:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2022",
"module": "ESNext",
"moduleResolution": "Node",
"outDir": "./build",
"rootDir": "./src",
"strict": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"skipLibCheck": true,
"forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true,
"declaration": true,
"declarationMap": true,
"sourceMap": true
},
"include": ["src/**/*"],
"exclude": ["node_modules", "build"]
}
综合示例:智能笔记管理系统
以下是一个完整的MCP Server示例,展示了Tools、Resources和Prompts的核心概念和使用方法:
#!/usr/bin/env node
// src/index.ts
import { McpServer, ResourceTemplate } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js";
import { StdioServerTransport } from "@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js";
import { z } from "zod";
import * as fs from 'fs/promises';
import * as path from 'path';
/**
* 智能笔记管理系统 MCP Server
*
* 本示例展示了MCP的三大核心能力:
* 1. Tools: 执行操作(创建、搜索、分析笔记)
* 2. Resources: 访问数据(笔记内容、元数据)
* 3. Prompts: 提供模板(笔记格式、分析模板)
*/
class NotesManager {
private notesDir: string;
constructor(notesDir: string = './notes') {
this.notesDir = notesDir;
this.ensureNotesDirectory();
}
private async ensureNotesDirectory() {
try {
await fs.access(this.notesDir);
} catch {
await fs.mkdir(this.notesDir, { recursive: true });
}
}
async createNote(title: string, content: string, tags: string[] = []): Promise<string> {
const timestamp = new Date().toISOString();
const filename = `${title.replace(/[^a-zA-Z0-9]/g, '_')}_${Date.now()}.md`;
const filepath = path.join(this.notesDir, filename);
const noteContent = `---
title: ${title}
created: ${timestamp}
tags: [${tags.join(', ')}]
---
${content}
`;
await fs.writeFile(filepath, noteContent, 'utf-8');
return filename;
}
async searchNotes(query: string): Promise<Array<{filename: string, title: string, excerpt: string}>> {
const files = await fs.readdir(this.notesDir);
const results = [];
for (const file of files) {
if (!file.endsWith('.md')) continue;
const filepath = path.join(this.notesDir, file);
const content = await fs.readFile(filepath, 'utf-8');
if (content.toLowerCase().includes(query.toLowerCase())) {
const lines = content.split('\n');
const titleLine = lines.find(line => line.startsWith('title:'));
const title = titleLine ? titleLine.replace('title:', '').trim() : file;
const excerpt = content.substring(0, 200) + '...';
results.push({ filename: file, title, excerpt });
}
}
return results;
}
async getNoteContent(filename: string): Promise<string> {
const filepath = path.join(this.notesDir, filename);
return await fs.readFile(filepath, 'utf-8');
}
async listNotes(): Promise<string[]> {
const files = await fs.readdir(this.notesDir);
return files.filter(file => file.endsWith('.md'));
}
}
// 创建MCP服务器实例
const server = new McpServer({
name: "notes-manager",
version: "1.0.0"
});
const notesManager = new NotesManager();
// ================================
// TOOLS: 执行操作的工具
// ================================
/**
* Tool 1: 创建笔记
* 功能:创建新的笔记文件,支持标题、内容和标签
*/
server.registerTool("create_note",
{
title: "Create Note",
description: "创建一个新的笔记,支持标题、内容和标签分类",
inputSchema: {
title: z.string().describe("笔记标题"),
content: z.string().describe("笔记内容(支持Markdown格式)"),
tags: z.array(z.string()).optional().describe("笔记标签,用于分类")
}
},
async ({ title, content, tags = [] }) => {
try {
const filename = await notesManager.createNote(title, content, tags);
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `✅ 笔记创建成功!\n文件名: ${filename}\n标题: ${title}\n标签: ${tags.join(', ') || '无'}`
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `❌ 创建笔记失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
}
}
);
/**
* Tool 2: 搜索笔记
* 功能:在所有笔记中搜索包含指定关键词的内容
*/
server.registerTool("search_notes",
{
title: "Search Notes",
description: "在所有笔记中搜索包含指定关键词的内容",
inputSchema: {
query: z.string().describe("搜索关键词")
}
},
async ({ query }) => {
try {
const results = await notesManager.searchNotes(query);
if (results.length === 0) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `🔍 搜索结果: 未找到包含"${query}"的笔记`
}]
};
}
const resultText = results.map((result, index) =>
`${index + 1}. **${result.title}** (${result.filename})\n ${result.excerpt}\n`
).join('\n');
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `🔍 搜索"${query}"的结果 (${results.length}个):\n\n${resultText}`
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `❌ 搜索失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
}
}
);
/**
* Tool 3: 分析笔记
* 功能:分析笔记内容,提供统计信息和摘要
*/
server.registerTool("analyze_notes",
{
title: "Analyze Notes",
description: "分析笔记集合,提供统计信息、词频分析等",
inputSchema: {}
},
async () => {
try {
const noteFiles = await notesManager.listNotes();
let totalWords = 0;
let totalChars = 0;
const tagCounts = new Map<string, number>();
for (const file of noteFiles) {
const content = await notesManager.getNoteContent(file);
const words = content.split(/\s+/).length;
const chars = content.length;
totalWords += words;
totalChars += chars;
// 提取标签
const tagMatch = content.match(/tags: \[(.*?)\]/);
if (tagMatch) {
const tags = tagMatch[1].split(',').map(tag => tag.trim()).filter(tag => tag);
tags.forEach(tag => {
tagCounts.set(tag, (tagCounts.get(tag) || 0) + 1);
});
}
}
const topTags = Array.from(tagCounts.entries())
.sort(([,a], [,b]) => b - a)
.slice(0, 5)
.map(([tag, count]) => `${tag} (${count})`)
.join(', ');
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `📊 笔记统计分析:
📝 总笔记数: ${noteFiles.length}
📄 总字数: ${totalWords.toLocaleString()}
🔤 总字符数: ${totalChars.toLocaleString()}
📖 平均每篇字数: ${noteFiles.length ? Math.round(totalWords / noteFiles.length) : 0}
🏷️ 热门标签: ${topTags || '暂无标签'}
`
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `❌ 分析失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
}
}
);
// ================================
// RESOURCES: 数据访问接口
// ================================
/**
* Resource 1: 笔记内容访问
* 功能:通过URI访问特定笔记的内容
* URI格式: note://{filename}
*/
server.registerResource(
"note-content",
new ResourceTemplate("note://{filename}", { list: undefined }),
{
title: "Note Content",
description: "访问特定笔记文件的完整内容"
},
async (uri, { filename }) => {
try {
const content = await notesManager.getNoteContent(filename);
return {
contents: [{
uri: uri.href,
text: content,
mimeType: "text/markdown"
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
contents: [{
uri: uri.href,
text: `错误: 无法读取笔记 ${filename}: ${error.message}`,
mimeType: "text/plain"
}]
};
}
}
);
/**
* Resource 2: 笔记列表
* 功能:获取所有笔记的列表信息
* URI格式: notes://list
*/
server.registerResource(
"notes-list",
new ResourceTemplate("notes://list", { list: undefined }),
{
title: "Notes List",
description: "获取所有笔记文件的列表"
},
async (uri) => {
try {
const noteFiles = await notesManager.listNotes();
const listContent = noteFiles.length > 0
? noteFiles.map((file, index) => `${index + 1}. ${file}`).join('\n')
: '暂无笔记文件';
return {
contents: [{
uri: uri.href,
text: `笔记文件列表 (${noteFiles.length}个):\n\n${listContent}`,
mimeType: "text/plain"
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
contents: [{
uri: uri.href,
text: `错误: 无法获取笔记列表: ${error.message}`,
mimeType: "text/plain"
}]
};
}
}
);
// ================================
// PROMPTS: 模板和工作流
// ================================
/**
* Prompt 1: 笔记模板
* 功能:提供标准化的笔记创建模板
*/
server.registerPrompt(
"note-template",
{
title: "Note Template",
description: "标准笔记模板,包含标题、日期、标签和内容结构"
},
async ({ title = "新笔记", topic = "通用" }) => ({
messages: [{
role: "user",
content: {
type: "text",
text: `请根据以下模板创建一篇关于"${topic}"的笔记:
标题: ${title}
日期: ${new Date().toLocaleDateString()}
主题: ${topic}
## 核心要点
- [要点1]
- [要点2]
- [要点3]
## 详细内容
[在这里写下详细内容]
## 总结
[总结要点]
## 相关链接
- [相关资源1]
- [相关资源2]
## 下一步行动
- [ ] [行动项1]
- [ ] [行动项2]
请填充上述模板,创建一篇结构化的笔记。`
}
}]
})
);
/**
* Prompt 2: 笔记分析模板
* 功能:提供笔记内容分析的标准化流程
*/
server.registerPrompt(
"note-analysis",
{
title: "Note Analysis",
description: "分析笔记内容,提取关键信息和见解"
},
async ({ noteContent = "" }) => ({
messages: [{
role: "user",
content: {
type: "text",
text: `请对以下笔记内容进行深度分析:
笔记内容:
${noteContent}
请按照以下结构进行分析:
## 1. 内容摘要
[简要概括笔记的主要内容]
## 2. 关键概念
[提取并列出关键概念和术语]
## 3. 主要观点
[总结作者的主要观点和论述]
## 4. 逻辑结构
[分析内容的逻辑结构和组织方式]
## 5. 价值评估
[评估这篇笔记的价值和重要性]
## 6. 改进建议
[提供完善和改进建议]
## 7. 相关主题
[推荐相关的研究主题或延伸阅读]
请详细分析并提供见解。`
}
}]
})
);
/**
* Prompt 3: 知识整理模板
* 功能:帮助整理和连接多个笔记的知识点
*/
server.registerPrompt(
"knowledge-synthesis",
{
title: "Knowledge Synthesis",
description: "整合多个笔记,创建知识图谱和关联分析"
},
async ({ topics = ["学习", "工作"] }) => ({
messages: [{
role: "user",
content: {
type: "text",
text: `请帮我整理和连接关于以下主题的知识:${topics.join(", ")}
请按照以下步骤进行知识整合:
## 1. 主题梳理
为每个主题创建思维导图,包括:
- 核心概念
- 子主题
- 关键要点
## 2. 知识关联
分析不同主题之间的关联性:
- 共同点
- 差异点
- 相互影响
## 3. 知识体系
构建整体知识框架:
- 层次结构
- 逻辑关系
- 重要程度
## 4. 实践应用
提供实际应用建议:
- 应用场景
- 实践方法
- 注意事项
## 5. 学习路径
规划深入学习的路径:
- 学习顺序
- 重点难点
- 学习资源
请基于我的笔记内容进行知识整合分析。`
}
}]
})
);
// ================================
// 服务器启动
// ================================
async function main() {
console.error("🚀 启动智能笔记管理 MCP Server...");
console.error("📝 支持的功能:");
console.error(" Tools: create_note, search_notes, analyze_notes");
console.error(" Resources: note://{filename}, notes://list");
console.error(" Prompts: note-template, note-analysis, knowledge-synthesis");
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
console.error("✅ MCP Server 已启动并等待连接...");
}
// 处理错误和优雅关闭
process.on('SIGINT', () => {
console.error('👋 正在关闭 MCP Server...');
process.exit(0);
});
process.on('uncaughtException', (error) => {
console.error('❌ 未捕获的异常:', error);
process.exit(1);
});
// 启动服务器
async function main() {
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
console.error("✅ 智能笔记管理 MCP Server 已启动");
}
main().catch(console.error);
配置与部署
客户端配置:
{
"mcpServers": {
"notes-manager": {
"command": "node",
"args": ["/path/to/build/index.js"]
}
}
}
构建运行:
npm run build && npm start
开发最佳实践
- 错误处理: 使用try-catch包装所有异步操作
- 参数验证: 利用Zod进行严格的输入验证
- 类型安全: 使用TypeScript确保类型正确性
- 模块化设计: 将业务逻辑封装在独立的类中
核心优势与应用
技术优势
- 标准化协议: 基于JSON-RPC 2.0,确保跨平台兼容性
- 安全可控: 协议层权限控制,隔离执行环境
- 开发友好: 丰富的TypeScript SDK支持和详细文档
应用场景
- 企业集成: 智能客服、数据分析、DevOps自动化
- 开发工具: IDE增强、代码审查、自动化测试
- 个人助手: 日程管理、文档处理、学习研究支持
总结
MCP(Model Context Protocol)通过标准化的JSON-RPC 2.0协议,为AI应用与外部系统集成提供了统一的解决方案。
核心价值:
- 标准化集成: 统一的开发接口,降低学习成本
- 组件解耦: 清晰的三层架构,支持灵活部署
- 生态协同: 工具复用和社区协作,避免重复开发
随着AI应用的广泛普及,MCP将成为连接AI与现实世界的重要桥梁,为开发者提供更高效、更安全的集成方案。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号