多线程基础
多线程基础
Process and Thread
进程:
进程就是一个程序,程序就是指令与数据的有序集合,本身没有任何含义
线程:
一个进程中可以存在多个线程,但是最少有一个主线程,不然就没有存在的意义
线程的创建
Thread 继承
//extends Thead class override run method
public class threadTest01 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("study thread: " +i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//create thread start thread
new threadTest01().start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("main : " +i);
}
}
}
Runnable 实现
//implements Runnable Override run method
public class RunnableTest01 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("study thread: " +i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new RunnableTest01()).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("main : " +i);
}
}
}
Callable 实现 返回值 抛异常
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CallableTest01 implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return 10;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Future<Integer> result = service.submit(new CallableTest01());
Integer integer = result.get();
System.out.println(integer);
service.shutdownNow();
}
}
多线程并发操作一个对象
public class TestConcurrent implements Runnable{
int ticketNums = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if (ticketNums <= 0 ){
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "-->ticketNums: " + ticketNums--);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestConcurrent testConcurrent = new TestConcurrent();
new Thread(testConcurrent,"ambrose").start();
new Thread(testConcurrent,"Makael").start();
// new Thread(new TestConcurrent(),"Tom").start();
}
}
函数式接口
只有一个抽象方法的接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}
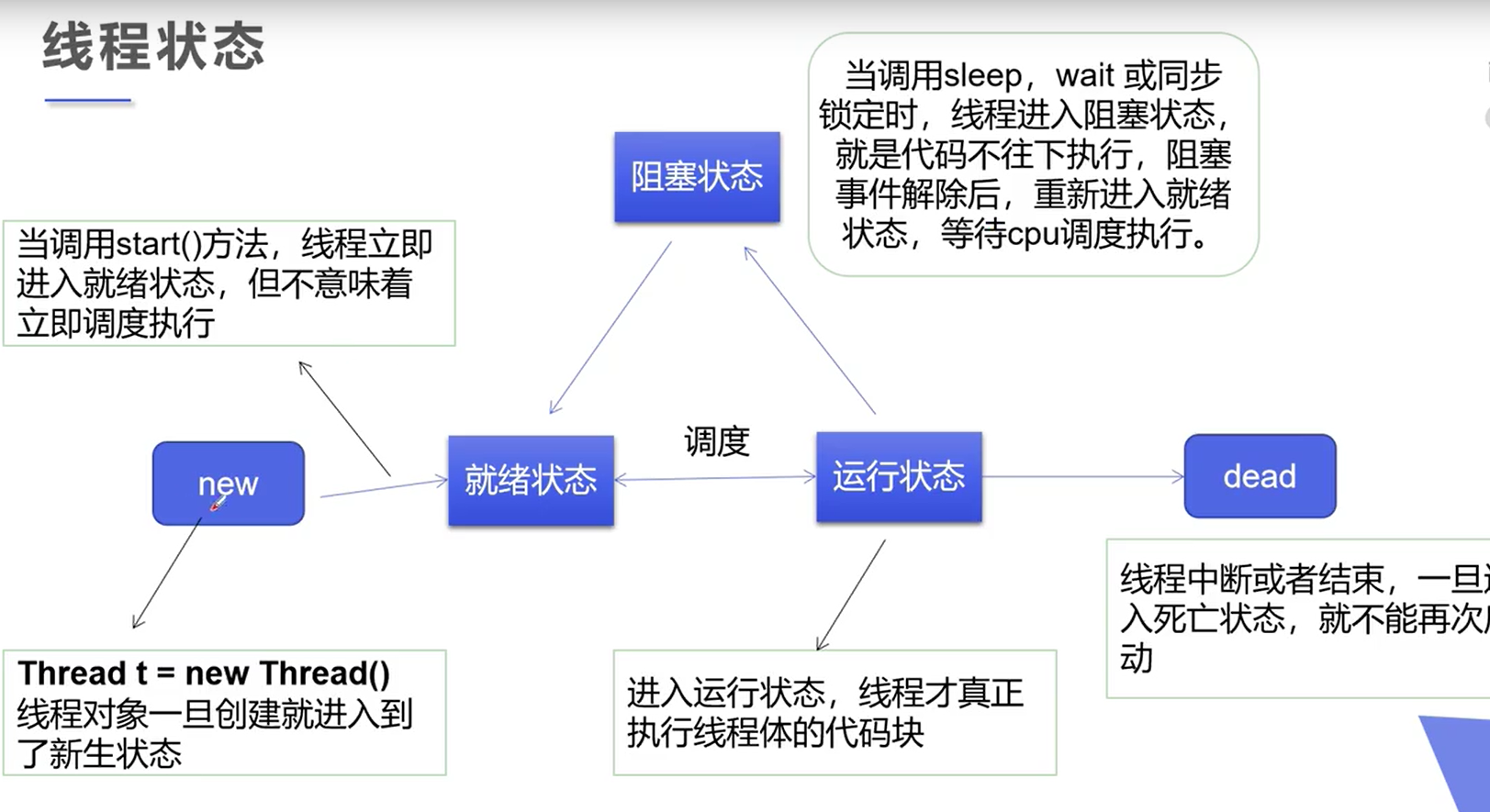
线程的状态
源码中是6种
public enum State {
NEW, //尚未启动的线程的线程状态
RUNNABLE, //可运行线程的线程状态。处于可运行状态的线程正在Java虚拟机中执行
BLOCKED, //调用wait()方法进入阻塞状态
WAITING,
TIMED_WAITING,
TERMINATED;
}
join() 插队
//test join
public class TestJoin implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("VIP: " + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();
Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
System.out.println("main: " + i);
if (i == 200){
//主线程执行到200次时,VIP线程截断执行自己
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
CopyOnWriteArrayList
集合时线程不安全的,如果需要多线程操作资源 ,可以使用juc下面的工具类
死锁
两个小孩打架互相抓着头发:
boy1: 你先放开
boy2: no 你先放
形成死锁
手持一把锁,去获取下一把
Code:
//死锁
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boy boy = new Boy();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(boy,"boy1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(boy,"boy2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class key1{
}
class key2{
}
class Boy implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("boy1")){
synchronized (key1.class){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": get key1 lock");
synchronized (key2.class){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": get key2 lock");
}
}
}
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("boy2")){
synchronized (key2.class){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": get key2 lock");
synchronized (key1.class){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": get key1 lock");
}
}
}
}
}
死锁产生的条件
- 互斥条件:一个资源只能被一个进程使用
- 一个进程因请求阻塞,对已经获得的资源保持不放
- 进程获得资源,在未使用完之前,不能强行剥夺
- 循环等待条件
显示定义同步锁
ReentrantLock 可重入锁
显示定义锁的代码块
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class ReentrantLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Object> objects = new ArrayList<>();
ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
//加锁
reentrantLock.lock();
objects.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//解锁
reentrantLock.unlock();
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(objects.size());
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号