[WIP]红黑树 - libcxx 源码
通过阅读libcxx源码,学习stl实现方式,以及高级cpp技巧. 这是第一篇
红黑树背景知识
下面先回顾二叉搜索树(BST)和 AVL 树的特点,再把红黑树放到同一个框架里对比,帮助你在脑海中建立联系。
1. 二叉搜索树(BST)
- 定义:每个节点的左子树所有键 < 节点键 < 右子树所有键。
- 优点:实现简单,插入/查找/删除平均 O(log n)。
- 缺点:不做任何平衡维护,最坏会退化成链表,操作退化到 O(n)。
2. AVL 树
-
是什么:对 BST 加入“严格高度平衡”机制的自平衡树。
-
平衡条件:每个节点的两棵子树高度之差 ≤ 1。
-
实现手段:插入或删除后,如果某个节点失衡(|左高–右高|>1),就做一次或两次旋转(LL、RR、LR、RL)。
-
复杂度:
- 查找:O(log n),树高 ≈1.44 log₂n。
- 插入/删除:O(log n),但可能在多层节点上触发旋转和高度更新。
-
特点:
- 查找最优(高度最小化)。
- 旋转次数较多,插入/删除开销相对红黑树更高。
3. 红黑树
-
是什么:另一种自平衡 BST,通过“节点染色 + 旋转”来弱化 AVL 的严格平衡。
-
平衡条件:
- 每个节点红或黑;
- 根为黑;
- 叶子(null)视为黑;
- 红节点不能有红孩子;
- 任一路径黑节点数相同。
-
实现手段:插入/删除后,只需少量染色和 1–2 次旋转,就能恢复平衡。
-
复杂度:
- 查找:O(log n),树高 ≤ 2 log₂(n+1)。
- 插入/删除:O(log n),平均旋转次数低于 AVL。
-
特点:
- 相比 AVL 树稍“松”一点的平衡,允许更高一些的树高,但插入/删除更轻量。
- 工程应用中(如 C++
std::map/set、JavaTreeMap)极为常见。
4. 三者对比小结
| 特性 | BST | AVL 树 | 红黑树 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 平衡保证 | 无 | 严格平衡(子树高度差≤1) | 弱平衡(黑高一致 + 红节点限制) |
| 最坏树高 | n | ≈1.44 log₂n | ≤2 log₂(n+1) |
| 查找 | 平均 O(log n) 最坏 O(n) |
O(log n) | O(log n) |
| 插入/删除旋转次数 | 0–n(退化) | 1–2 次/节点高度更新 | ≤2 次/少量染色 |
| 插入/删除开销 | 平均 O(log n) 最坏 O(n) |
较高(多次旋转 + 维护高度) | 较低(少量旋转 + 染色) |
| 应用 | 学习用途多 | 对实时性要求高的场景(例如数据库内存索引) | 大多数通用库(C++ STL、Java) |
5. 在脑海中的映射
- BST = 最基础的“左<根<右”结构,最坏退化最严重。
- AVL = 给 BST 装上“严格平衡”引擎,查询最快但插入/删除稍重。
- 红黑树 = 给 BST 装上“染色+旋转”引擎,查询略慢于 AVL,但插入/删除最轻量,工业界首选。
理解了这三者的平衡策略和权衡后,看到 std::map 或数据库索引,用红黑树就会更有感:它用颜色松散地维护平衡,保证高度对数级,同时把“每次插入/删除的旋转成本”控制在最低。
6. zig-zig / zig-zag
在红黑树的插入修正中,我们要分两种结构形态来处理——“外侧插入”(zig-zig)和“内侧插入”(zig-zag)。它们的区别就在于,新节点相对于它的父亲和祖父,是“沿着同一条边”下去,还是“先沿一边再折回来”:
-
外侧插入(zig-zig):父和新节点都在祖父的同一侧
-
例子:祖父
g的左子树里有父p,p的左子树里又插入了新节点z。 -
形状:
g / p / z -
之所以叫“外侧”,是因为
z“贴着”同一条从g→p的边往外延伸,就像一直沿左边往下走。 -
处理:只需对
g做一次 右旋,并交换g/p的颜色,就能一举恢复平衡。
-
-
内侧插入(zig-zag):父和新节点在祖父的相反侧上折回来
-
例子:祖父
g的左子树里有父p,p的右子树里插入了新节点z。 -
形状:
g / p \ z -
叫“内侧”,是因为
z先从g→p的同一侧下来,又在p上折向另一侧,形成一个“之”字折回的结构。 -
处理:先对
p做一次左旋,把它变成“外侧插入”的形态(把z挪到g的左边一条直线上),然后再像外侧插入那样对g做一次右旋。
-
所以,“外侧插入” 之所以得名,就是因为新节点 z 沿着祖父 g 和父 p 的同一侧一条直线“向外”延伸(zig-zig),可以用一次旋转解决;而**“内侧插入”**(zig-zag)则是“先向外再向内”或“先向内再向外”的折回结构,需要先做一次小旋转把它变成外侧,再做一次大旋转。
libcxx源码
代码使用release/15.x, commit id:8dfdcc7b7bf6
cpp学习
先以set为入口,因为set使用红黑树存储.
// include/set
template <class _Key, class _Compare = less<_Key>,
class _Allocator = allocator<_Key> >
class _LIBCPP_TEMPLATE_VIS set
{
public:
// types:
typedef _Key key_type;
typedef key_type value_type;
typedef __type_identity_t<_Compare> key_compare;
typedef key_compare value_compare;
typedef __type_identity_t<_Allocator> allocator_type;
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef const value_type& const_reference;
static_assert((is_same<typename allocator_type::value_type, value_type>::value),
"Allocator::value_type must be same type as value_type");
private:
typedef __tree<value_type, value_compare, allocator_type> __base;
typedef allocator_traits<allocator_type> __alloc_traits;
__base __tree_;
/*omitted part of code*/
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
iterator begin() _NOEXCEPT {return __tree_.begin();}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
const_iterator begin() const _NOEXCEPT {return __tree_.begin();}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
iterator end() _NOEXCEPT {return __tree_.end();}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
const_iterator end() const _NOEXCEPT {return __tree_.end();}
例如常用的insert
// include/set
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const value_type& __v)
{return __tree_.__insert_unique(__v);}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
iterator insert(const_iterator __p, const value_type& __v)
{return __tree_.__insert_unique(__p, __v);}
template <class _InputIterator>
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
void insert(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l)
{
for (const_iterator __e = cend(); __f != __l; ++__f)
__tree_.__insert_unique(__e, *__f);
}
#ifndef _LIBCPP_CXX03_LANG
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pair<iterator,bool> insert(value_type&& __v)
{return __tree_.__insert_unique(_VSTD::move(__v));}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
iterator insert(const_iterator __p, value_type&& __v)
{return __tree_.__insert_unique(__p, _VSTD::move(__v));}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
void insert(initializer_list<value_type> __il)
{insert(__il.begin(), __il.end());}
#endif // _LIBCPP_CXX03_LANG
两个重载,对应左值、右值。还有一个sfinae重载,面对参数类型与容器存储的类型不匹配的情况,例如set
__enable_if_t<!is_same<…>::value> 就是一个 SFINAE 限制:
__unconstref<_Vp>::type 会去掉 _Vp 的 const& 或者引用修饰,得到纯粹的类型。
如果这个纯类型 不等于 容器的元素类型 __container_value_type,那么 enable_if_t存在,模板 有效;
如果它恰好等于元素类型(比如你传入了一个 value_type&&),那么 enable_if_t不存在,模板被 SFINAE 掉,不参与重载。
// include/__tree
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pair<iterator, bool> __insert_unique(const __container_value_type& __v) {
return __emplace_unique_key_args(_NodeTypes::__get_key(__v), __v);
}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pair<iterator, bool> __insert_unique(__container_value_type&& __v) {
return __emplace_unique_key_args(_NodeTypes::__get_key(__v), _VSTD::move(__v));
}
template <class _Vp,
class = __enable_if_t<!is_same<typename __unconstref<_Vp>::type, __container_value_type>::value> >
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pair<iterator, bool> __insert_unique(_Vp&& __v) {
return __emplace_unique(_VSTD::forward<_Vp>(__v));
}
以常见的insert右值为例,__emplace_unique_key_args的函数签名为
// include/__tree
template <class _Key, class ..._Args>
pair<iterator, bool>
__emplace_unique_key_args(_Key const&, _Args&&... __args);
定义
// include/__tree
template <class _Tp, class _Compare, class _Allocator> // 类模板的参数
template <class _Key, class... _Args> // 类模板的模板成员函数的参数
pair<typename __tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::iterator, bool>
__tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::__emplace_unique_key_args(_Key const& __k, _Args&&... __args)
{
__parent_pointer __parent;
__node_base_pointer& __child = __find_equal(__parent, __k);
__node_pointer __r = static_cast<__node_pointer>(__child);
bool __inserted = false;
if (__child == nullptr)
{
__node_holder __h = __construct_node(_VSTD::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
__insert_node_at(__parent, __child, static_cast<__node_base_pointer>(__h.get()));
__r = __h.release();
__inserted = true;
}
return pair<iterator, bool>(iterator(__r), __inserted);
}
这里就是如何在rbtree上插入一个新的节点,那么首先来看__tree的定义,了解一些类型和成员的定义
// include/__tree
template <class _Tp, class _Compare, class _Allocator>
class __tree
{
public:
// 注入三个类型
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef _Compare value_compare;
typedef _Allocator allocator_type;
private:
typedef allocator_traits<allocator_type> __alloc_traits;
typedef typename __make_tree_node_types<value_type, // !
typename __alloc_traits::void_pointer>::type
_NodeTypes;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::key_type key_type;
public:
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__node_value_type __node_value_type;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__container_value_type __container_value_type;
typedef typename __alloc_traits::pointer pointer;
typedef typename __alloc_traits::const_pointer const_pointer;
typedef typename __alloc_traits::size_type size_type;
typedef typename __alloc_traits::difference_type difference_type;
public:
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__void_pointer __void_pointer;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__node_type __node;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__node_pointer __node_pointer;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__node_base_type __node_base;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__node_base_pointer __node_base_pointer;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__end_node_type __end_node_t;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__end_node_pointer __end_node_ptr;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__parent_pointer __parent_pointer;
typedef typename _NodeTypes::__iter_pointer __iter_pointer;
typedef typename __rebind_alloc_helper<__alloc_traits, __node>::type __node_allocator;
typedef allocator_traits<__node_allocator> __node_traits;
注意_NodeTypes,他是__make_tree_node_types<value_type, typename __alloc_traits::void_pointer>导出的类型.
// include/__tree
template <class _ValueTp, class _VoidPtr>
struct __make_tree_node_types {
typedef typename __rebind_pointer<_VoidPtr, __tree_node<_ValueTp, _VoidPtr> >::type
_NodePtr;
typedef __tree_node_types<_NodePtr> type;
};
这里_NodePtr就是指向__tree_node<T1,T2>的指针
pointer_traits/rebind_pointer: https://www.cnblogs.com/ijpq/p/18916711
allocator见https://www.cnblogs.com/ijpq/p/18916673
partial spec的匹配:https://github.com/ijpq/Templates-ISO-IEC/commit/7ac66dcc09052edf38d4c30c80bf56b55a4fe8a1
// include/__tree
template <class _NodePtr, class _NodeT = typename pointer_traits<_NodePtr>::element_type>
struct __tree_node_types;
template <class _NodePtr, class _Tp, class _VoidPtr>
struct __tree_node_types<_NodePtr, __tree_node<_Tp, _VoidPtr> >
: public __tree_node_base_types<_VoidPtr>,
__tree_key_value_types<_Tp>,
__tree_map_pointer_types<_Tp, _VoidPtr>
{
typedef __tree_node_base_types<_VoidPtr> __base;
typedef __tree_key_value_types<_Tp> __key_base;
typedef __tree_map_pointer_types<_Tp, _VoidPtr> __map_pointer_base;
public:
typedef typename pointer_traits<_NodePtr>::element_type __node_type;
typedef _NodePtr __node_pointer;
typedef _Tp __node_value_type;
typedef typename __rebind_pointer<_VoidPtr, __node_value_type>::type
__node_value_type_pointer;
typedef typename __rebind_pointer<_VoidPtr, const __node_value_type>::type
__const_node_value_type_pointer;
#if defined(_LIBCPP_ABI_TREE_REMOVE_NODE_POINTER_UB)
typedef typename __base::__end_node_pointer __iter_pointer;
#else
typedef typename conditional<
is_pointer<__node_pointer>::value,
typename __base::__end_node_pointer,
__node_pointer>::type __iter_pointer;
#endif
private:
static_assert(!is_const<__node_type>::value,
"_NodePtr should never be a pointer to const");
static_assert((is_same<typename __rebind_pointer<_VoidPtr, __node_type>::type,
_NodePtr>::value), "_VoidPtr does not rebind to _NodePtr.");
};
因此,__tree中的Nodeypes就是_tree_node_types
保存了数节点的值类型,值.
指向右孩子、父节点的指针和红黑标记放在另一个基类
template <class _VoidPtr>
class _LIBCPP_STANDALONE_DEBUG __tree_node_base
: public __tree_node_base_types<_VoidPtr>::__end_node_type
{
typedef __tree_node_base_types<_VoidPtr> _NodeBaseTypes;
public:
typedef typename _NodeBaseTypes::__node_base_pointer pointer;
typedef typename _NodeBaseTypes::__parent_pointer __parent_pointer;
pointer __right_;
__parent_pointer __parent_;
bool __is_black_;
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pointer __parent_unsafe() const { return static_cast<pointer>(__parent_);}
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
void __set_parent(pointer __p) {
__parent_ = static_cast<__parent_pointer>(__p);
}
private:
~__tree_node_base() = delete;
__tree_node_base(__tree_node_base const&) = delete;
__tree_node_base& operator=(__tree_node_base const&) = delete;
};
rbtree具体操作的代码
set的insert
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const value_type& __v)
{return __tree_.__insert_unique(__v);}
// set
template <class _Key, class _Compare = less<_Key>,
class _Allocator = allocator<_Key> >
class _LIBCPP_TEMPLATE_VIS set
{
public:
// types:
typedef _Key key_type;
typedef key_type value_type;
typedef __type_identity_t<_Compare> key_compare;
typedef key_compare value_compare;
typedef __type_identity_t<_Allocator> allocator_type;
typedef __tree<value_type, value_compare, allocator_type> __base;
__base __tree_;
};
_LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
pair<iterator, bool> __insert_unique(const __container_value_type& __v) {
return __emplace_unique_key_args(_NodeTypes::__get_key(__v), __v);
}
声明父节点指针parent,k为待插入的值
template <class _Tp, class _Compare, class _Allocator>
template <class _Key, class... _Args>
pair<typename __tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::iterator, bool>
__tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::__emplace_unique_key_args(_Key const& __k, _Args&&... __args)
{
__parent_pointer __parent;
__node_base_pointer& __child = __find_equal(__parent, __k);
__node_pointer __r = static_cast<__node_pointer>(__child);
bool __inserted = false;
if (__child == nullptr)
{
__node_holder __h = __construct_node(_VSTD::forward<_Args>(__args)...);
__insert_node_at(__parent, __child, static_cast<__node_base_pointer>(__h.get()));
__r = __h.release();
__inserted = true;
}
return pair<iterator, bool>(iterator(__r), __inserted);
}
到这里,就是rbtree插入节点的具体实现
可以先看这个代码,相对好理解
- 创建一个空节点用于插入数值
- 从根节点开始遍历,依次判断插入位置
/**
* An RBTree-based set implementation
*
* @tparam key_t key type
* @tparam compare_t compare function
*/
template <typename key_t, typename compare_t = std::less<key_t>>
struct rb_tree {
/**
* Tree node
*/
struct node_t {
node_t *fa; // == nullptr if root of the tree, otherwise parent
node_t *ch[2]; // == nullptr if child is empty
// ch[0]: left child, ch[1]: right child
key_t data;
size_t sz; // Size of subtree
bool red; // == true if node is red, otherwise black
/**
* Get child direction of current non-null node
*
* @return true if this node is right child of its parent, otherwise false
*/
auto child_dir() const -> bool { return this == fa->ch[1]; }
};
using pointer = node_t *;
using const_pointer = const node_t *;
using pointer_const = node_t *const;
const compare_t compare;
pointer root;
rb_tree() : compare{}, root{nullptr} {}
// ...
};
/**
* @return nullptr if insert failed, otherwise pointer of inserted node
*/
auto insert(const key_t &data) -> const_pointer {
pointer n = new node_t;
n->fa = n->ch[0] = n->ch[1] = nullptr;
n->data = data, n->sz = 1;
pointer now = root, p = nullptr;
bool dir = 0;
while (now) {
p = now;
dir = compare(now->data, data);
now = now->ch[dir];
}
insert_fixup_leaf(p, n, dir);
return n;
}
/**
* Insert leaf node {@code n} to {@code p}
*
* @param p parent of node which will be inserted
* @param n leaf node which will be inserted
* @param dir direction of n, 0: left; 1: right
*/
void insert_leaf(pointer_const p, pointer_const n, bool dir) {
if (!p) {
root = n;
return;
}
p->ch[dir] = n, n->fa = p;
auto now = p;
while (now) now->sz++, now = now->fa;
}
/**
* Insert leaf node {@code n} to {@code p}, then fixup
*
* @param p parent of node which will be inserted
* @param n node which will be inserted
* @param dir direction of n, 0: left; 1: right
*/
void insert_fixup_leaf(pointer p, pointer n, bool dir) {
n->red = p;
insert_leaf(p, n, dir);
// Fix double red
// ...
// Post process: color root black
root->red = false;
}
// Find place to insert if __v doesn't exist
// Set __parent to parent of null leaf
// Return reference to null leaf
// If __v exists, set parent to node of __v and return reference to node of __v
template <class _Tp, class _Compare, class _Allocator>
template <class _Key>
typename __tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::__node_base_pointer&
__tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::__find_equal(__parent_pointer& __parent,
const _Key& __v)
{
__node_pointer __nd = __root();
__node_base_pointer* __nd_ptr = __root_ptr();
if (__nd != nullptr)
{
while (true)
{
if (value_comp()(__v, __nd->__value_)) // 如果插入值在排序上,位于当前节点的前面 return true if __v comp nd->value
{
if (__nd->__left_ != nullptr) {
__nd_ptr = _VSTD::addressof(__nd->__left_);
__nd = static_cast<__node_pointer>(__nd->__left_); // 移动到left节点
} else {
__parent = static_cast<__parent_pointer>(__nd);
return __parent->__left_; // nd->left为空,返回该节点的ref
}
}
else if (value_comp()(__nd->__value_, __v))
{
if (__nd->__right_ != nullptr) {
__nd_ptr = _VSTD::addressof(__nd->__right_);
__nd = static_cast<__node_pointer>(__nd->__right_);
} else {
__parent = static_cast<__parent_pointer>(__nd);
return __nd->__right_;
}
}
else
{
__parent = static_cast<__parent_pointer>(__nd); // 如果待插入值已存在,返回该节点。
return *__nd_ptr;
}
}
}
__parent = static_cast<__parent_pointer>(__end_node());
return __parent->__left_;
}
继续看插入操作
在找完插入位置之后,如果值已存在,直接返回存在的节点。
符合cppreference中的语义
Return value
1,2) A pair consisting of an iterator to the inserted element (or to the element that prevented the insertion) and a bool value set to true if and only if the insertion took place.
template <class _Tp, class _Compare, class _Allocator>
template <class _Key, class... _Args>
pair<typename __tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::iterator, bool>
__tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::__emplace_unique_key_args(_Key const& __k, _Args&&... __args)
{
__parent_pointer __parent;
__node_base_pointer& __child = __find_equal(__parent, __k);
__node_pointer __r = static_cast<__node_pointer>(__child);
bool __inserted = false;
if (__child == nullptr)
{
__node_holder __h = __construct_node(_VSTD::forward<_Args>(__args)...); // 用参数构建新节点
__insert_node_at(__parent, __child, static_cast<__node_base_pointer>(__h.get()));
__r = __h.release();
__inserted = true;
}
return pair<iterator, bool>(iterator(__r), __inserted); // 这是一路返回的
}
进行插入
template <class _Tp, class _Compare, class _Allocator>
void __tree<_Tp, _Compare, _Allocator>::__insert_node_at(
__parent_pointer __parent, __node_base_pointer& __child,
__node_base_pointer __new_node) _NOEXCEPT
{
__new_node->__left_ = nullptr;
__new_node->__right_ = nullptr;
__new_node->__parent_ = __parent; // 挂父节点
// __new_node->__is_black_ is initialized in __tree_balance_after_insert
__child = __new_node;
if (__begin_node()->__left_ != nullptr)
__begin_node() = static_cast<__iter_pointer>(__begin_node()->__left_);
_VSTD::__tree_balance_after_insert(__end_node()->__left_, __child);
++size();
}
平衡操作
// Returns: true if __x is a left child of its parent, else false
// Precondition: __x != nullptr.
template <class _NodePtr>
inline _LIBCPP_INLINE_VISIBILITY
bool
__tree_is_left_child(_NodePtr __x) _NOEXCEPT
{
return __x == __x->__parent_->__left_;
}
// Effects: Rebalances __root after attaching __x to a leaf.
// Precondition: __x has no children.
// __x == __root or == a direct or indirect child of __root.
// If __x were to be unlinked from __root (setting __root to
// nullptr if __root == __x), __tree_invariant(__root) == true.
// Postcondition: __tree_invariant(end_node->__left_) == true. end_node->__left_
// may be different than the value passed in as __root.
template <class _NodePtr>
void
__tree_balance_after_insert(_NodePtr __root, _NodePtr __x) _NOEXCEPT
{
_LIBCPP_ASSERT(__root != nullptr, "Root of the tree shouldn't be null"); // 根节点
_LIBCPP_ASSERT(__x != nullptr, "Can't attach null node to a leaf"); // 待插入的新节点
__x->__is_black_ = __x == __root; // 新插入节点染色(非根节点时红色)
while (__x != __root && !__x->__parent_unsafe()->__is_black_) // 父节点是红色时需要进行调整
{
// __x->__parent_ != __root because __x->__parent_->__is_black == false
if (_VSTD::__tree_is_left_child(__x->__parent_unsafe())) // 父节点是祖父的左孩子时
{
_NodePtr __y = __x->__parent_unsafe()->__parent_unsafe()->__right_; // 找叔节点
if (__y != nullptr && !__y->__is_black_) // 叔节点是红色 // case 1
{
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe(); // 移动到父节点
__x->__is_black_ = true; // 父节点染黑
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe(); // 移动到祖父节点
__x->__is_black_ = __x == __root; // 不到根节点时祖父节点染红
__y->__is_black_ = true; // 叔节点染黑
}
else // 叔节点是黑色 //
{
if (!_VSTD::__tree_is_left_child(__x)) // case2‘
{
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe();
_VSTD::__tree_left_rotate(__x);
}
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe(); // case2
__x->__is_black_ = true;
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe();
__x->__is_black_ = false;
_VSTD::__tree_right_rotate(__x);
break;
}
}
else
{
_NodePtr __y = __x->__parent_unsafe()->__parent_->__left_;
if (__y != nullptr && !__y->__is_black_)
{
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe();
__x->__is_black_ = true;
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe();
__x->__is_black_ = __x == __root;
__y->__is_black_ = true;
}
else
{
if (_VSTD::__tree_is_left_child(__x))
{
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe();
_VSTD::__tree_right_rotate(__x);
}
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe();
__x->__is_black_ = true;
__x = __x->__parent_unsafe();
__x->__is_black_ = false;
_VSTD::__tree_left_rotate(__x);
break;
}
}
}
}
左旋、右旋
// Effects: Makes __x->__right_ the subtree root with __x as its left child
// while preserving in-order order.
template <class _NodePtr>
void
__tree_left_rotate(_NodePtr __x) _NOEXCEPT
{
_LIBCPP_ASSERT(__x != nullptr, "node shouldn't be null");
_LIBCPP_ASSERT(__x->__right_ != nullptr, "node should have a right child");
_NodePtr __y = __x->__right_;
__x->__right_ = __y->__left_;
if (__x->__right_ != nullptr)
__x->__right_->__set_parent(__x);
__y->__parent_ = __x->__parent_;
if (_VSTD::__tree_is_left_child(__x))
__x->__parent_->__left_ = __y;
else
__x->__parent_unsafe()->__right_ = __y;
__y->__left_ = __x;
__x->__set_parent(__y);
}
// Effects: Makes __x->__left_ the subtree root with __x as its right child
// while preserving in-order order.
template <class _NodePtr>
void
__tree_right_rotate(_NodePtr __x) _NOEXCEPT
{
_LIBCPP_ASSERT(__x != nullptr, "node shouldn't be null");
_LIBCPP_ASSERT(__x->__left_ != nullptr, "node should have a left child");
_NodePtr __y = __x->__left_;
__x->__left_ = __y->__right_;
if (__x->__left_ != nullptr)
__x->__left_->__set_parent(__x);
__y->__parent_ = __x->__parent_;
if (_VSTD::__tree_is_left_child(__x))
__x->__parent_->__left_ = __y;
else
__x->__parent_unsafe()->__right_ = __y;
__y->__right_ = __x;
__x->__set_parent(__y);
}
解释
以左侧的zigzag为例
case1(父红且叔红):没有结构性失衡,只要染色再上溯。
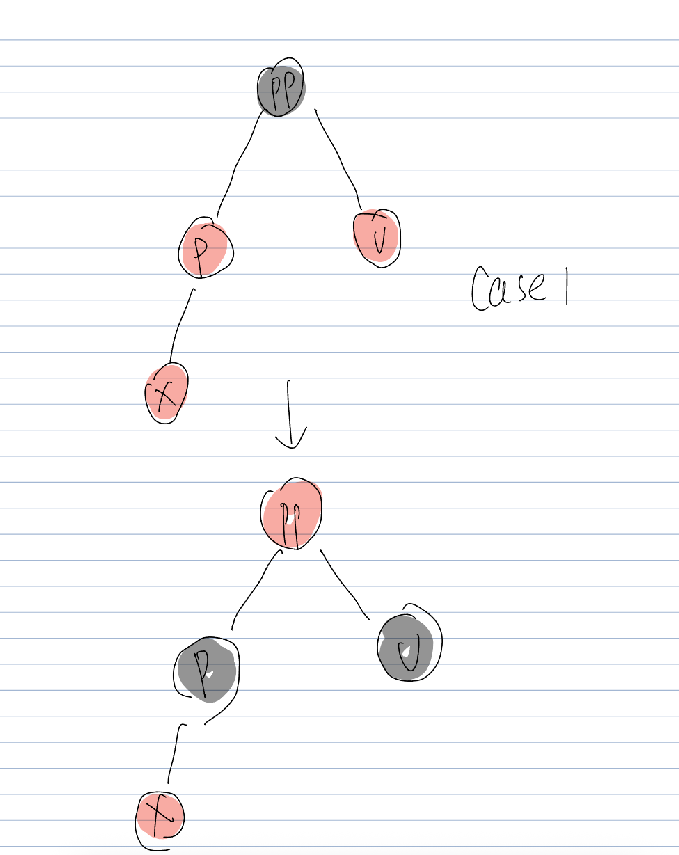
case2' 父红叔黑, 如果是zigzag,先调整为zigzig
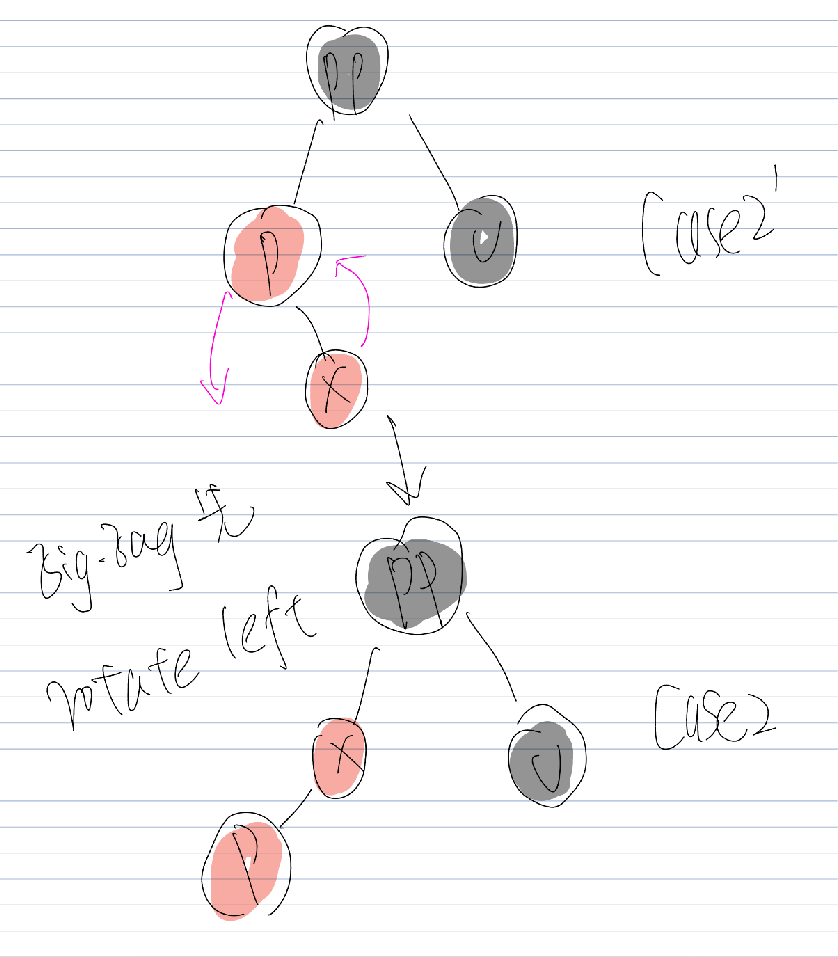
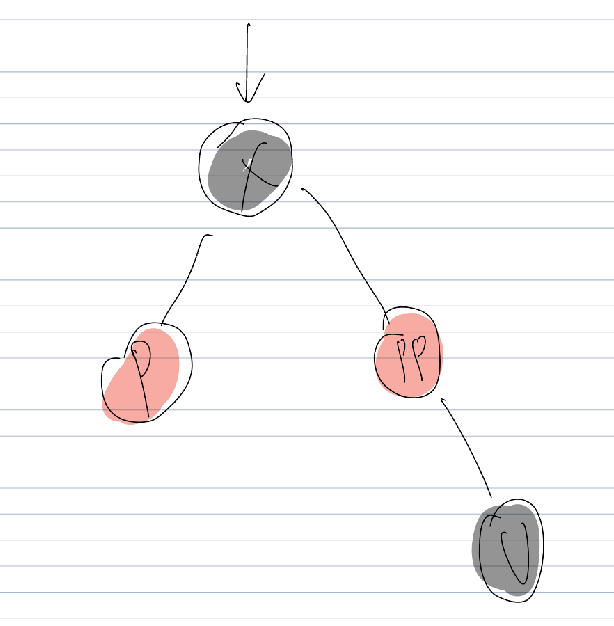
case2 在完成case2‘操作后

本文来自博客园,作者:ijpq,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ijpq/p/18903437




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号