TensorFlow作业
TensorFlowd学习报告:
Tensor(张量)意味着N维数组,Flow(流)意味着基于数据流图的计算.数据流图中的图就是我们所说的有向图,我们知道,在图这种数据结构中包含两种基本元素:节点和边.这两种元素在数据流图中有自己各自的作用。节点用来表示要进行的数学操作,另外,任何一种操作都有输入/输出,因此它也可以表示数据的输入的起点/输出的终点。边表示节点与节点之间的输入/输出关系,一种特殊类型的数据沿着这些边传递.这种特殊类型的数据在TensorFlow被称之为tensor,即张量,所谓的张量通俗点说就是多维数组.当我们向这种图中输入张量后,节点所代表的操作就会被分配到计算设备完成计算。此外,TensorFlowd还分别具有一以下四个特性:灵活性、可移植性、多语言支持和高效性。
实验:
# TensorFlow and tf.keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
# Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(tf.__version__)
fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
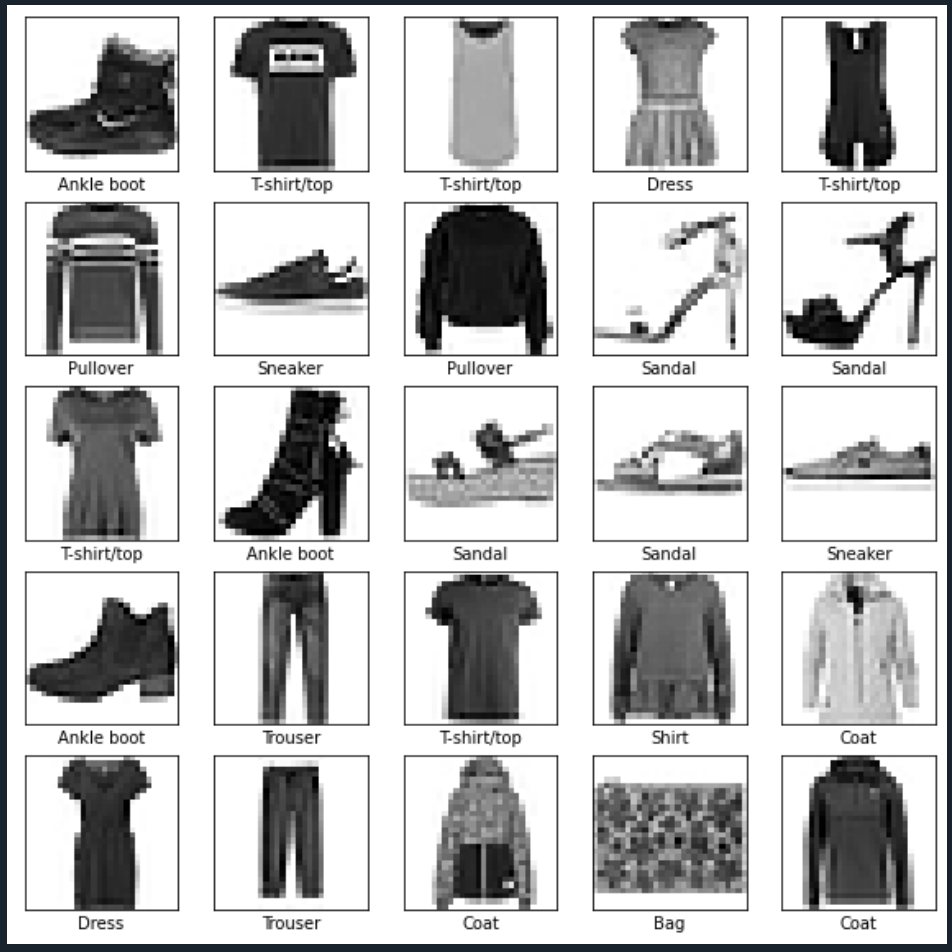
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
train_images.shape
len(train_labels)
train_labels
test_images.shape
len(test_labels)
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(train_images[0])
plt.colorbar()
plt.grid(False)
plt.show()
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5,5,i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]])
plt.show()
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(10)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2)
print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc)
probability_model = tf.keras.Sequential([model,
tf.keras.layers.Softmax()])
predictions = probability_model.predict(test_images)
predictions[0]
np.argmax(predictions[0])
test_labels[0]
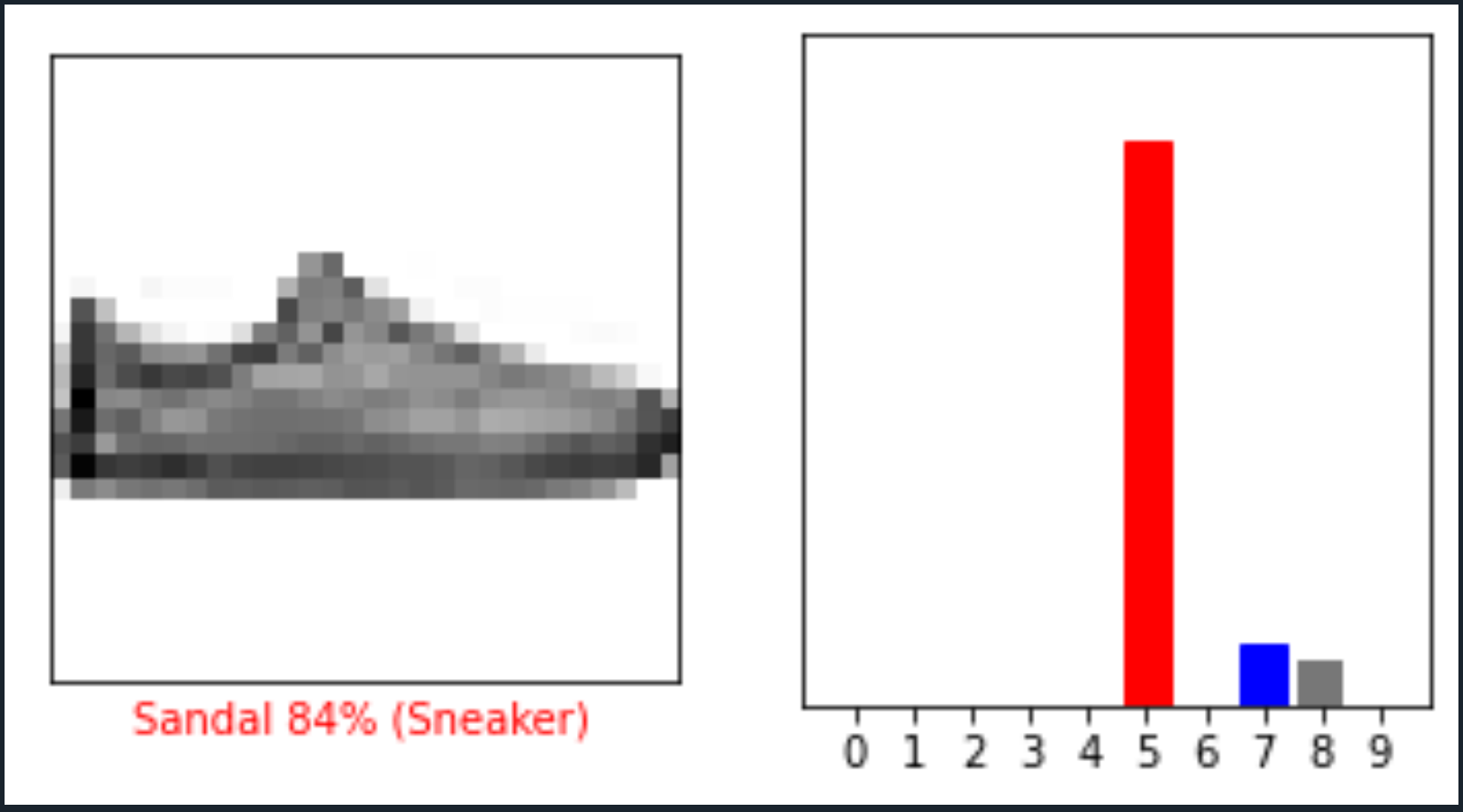
def plot_image(i, predictions_array, true_label, img):
predictions_array, true_label, img = predictions_array, true_label[i], img[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
if predicted_label == true_label:
color = 'blue'
else:
color = 'red'
plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label],
100*np.max(predictions_array),
class_names[true_label]),
color=color)
def plot_value_array(i, predictions_array, true_label):
predictions_array, true_label = predictions_array, true_label[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks(range(10))
plt.yticks([])
thisplot = plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array, color="#777777")
plt.ylim([0, 1])
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
thisplot[predicted_label].set_color('red')
thisplot[true_label].set_color('blue')
i = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
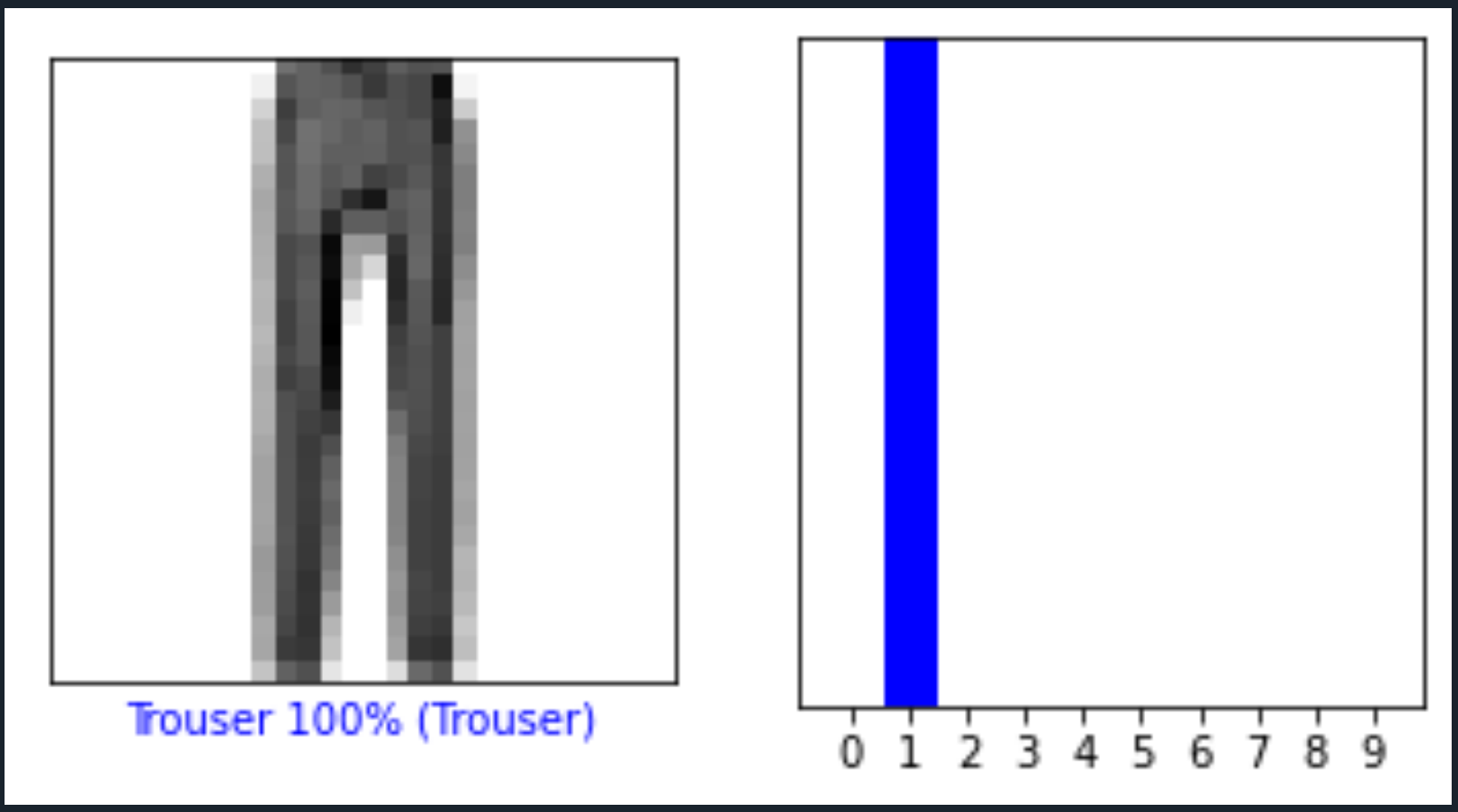
i = 12
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
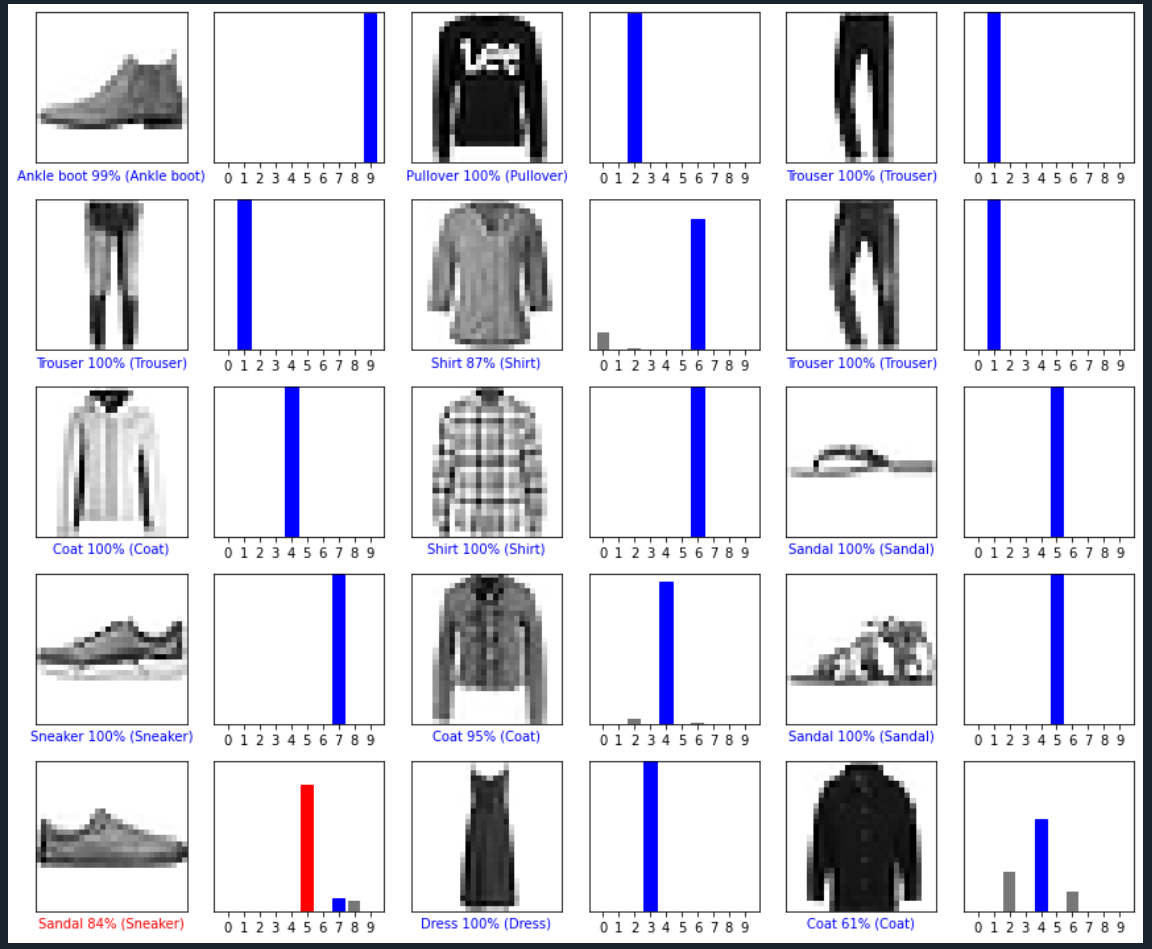
num_rows = 5
num_cols = 3
num_images = num_rows*num_cols
plt.figure(figsize=(2*2*num_cols, 2*num_rows))
for i in range(num_images):
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
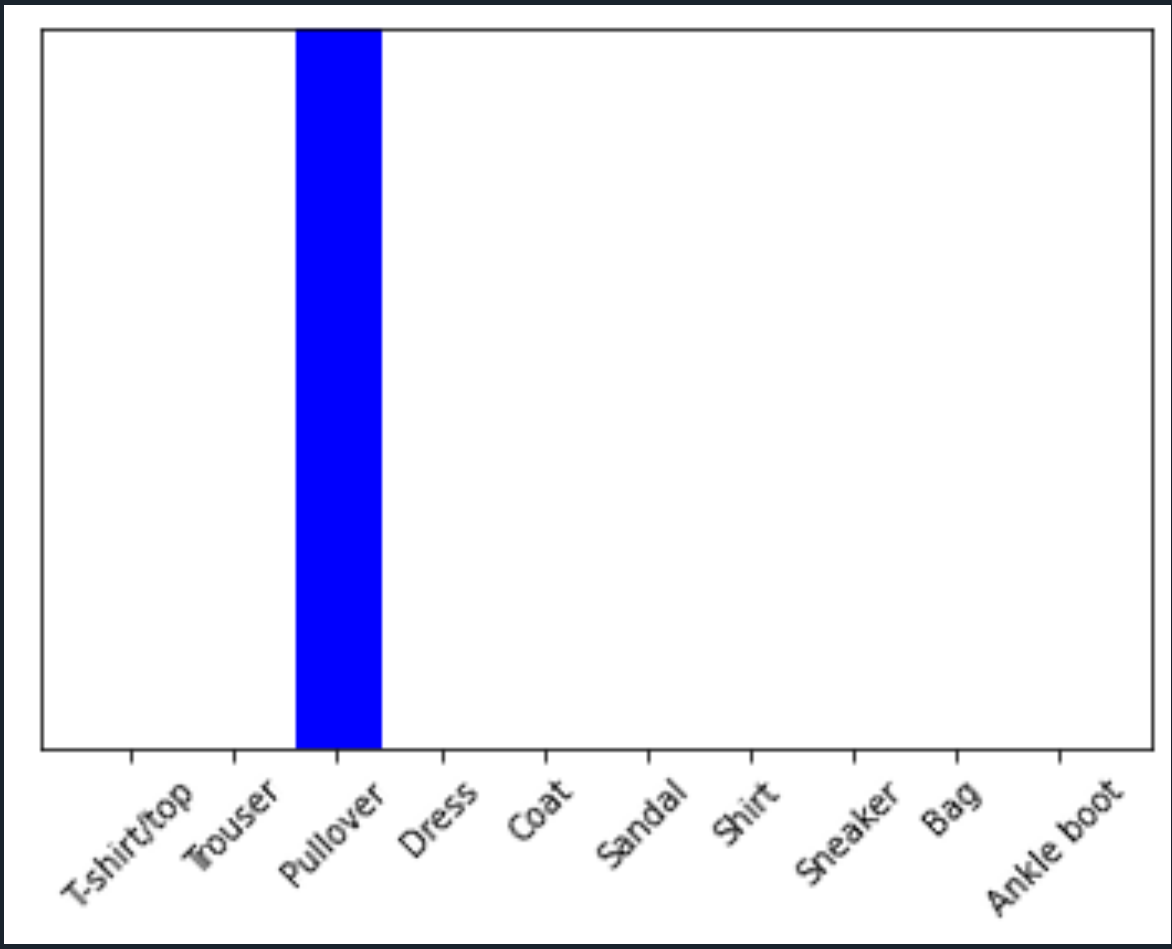
img = test_images[1]
print(img.shape)
img = (np.expand_dims(img,0))
print(img.shape)
predictions_single = probability_model.predict(img)
print(predictions_single)
plot_value_array(1, predictions_single[0], test_labels)
_ = plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45)
np.argmax(predictions_single[0])
结果:


课后作业:
1,卷积中的局部连接:层间神经只有局部范围内的连接,在这个范围内采用全连接的方式,超过这个范围的神经元则没有连接;连接与连接之间独立参数,相比于去全连接减少了感受域外的连接,有效减少参数规模。全连接:层间神经元完全连接,每个输出神经元可以获取到所有神经元的信息,有利于信息汇总,常置于网络末尾;连接与连接之间独立参数,大量的连接大大增加模型的参数规模。
2,利用快速傅里叶变换把图片和卷积核变换到频域,频域把两者相乘,把结果利用傅里叶逆变换得到特征图。
3,池化操作的作用:对输入的特征图进行压缩,一方面使特征图变小,简化网络计算复杂度;一方面进行特征压缩,提取主要特征。激活函数的作用:用来加入非线性因素的,解决线性模型所不能解决的问题。
4,消除数据之间的量纲差异,便于数据利用与快速计算。
5,寻找损失函数的最低点,就像我们在山谷里行走,希望找到山谷里最低的地方。那么如何寻找损失函数的最低点呢?在这里,我们使用了微积分里导数,通过求出函数导数的值,从而找到函数下降的方向或者是最低点(极值点)。损失函数里一般有两种参数,一种是控制输入信号量的权重(Weight, 简称 ),另一种是调整函数与真实值距离的偏差(Bias,简称
)。我们所要做的工作,就是通过梯度下降方法,不断地调整权重
和偏差b,使得损失函数的值变得越来越小。而随机梯度下降算法只随机抽取一个样本进行梯度计算。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号