线程安全、同步与异步
线程安全、同步与异步 首先,如果在多线程并发的环境下,有共享数据会被修改,此时可能出现安全问题。
怎么解决线程安全问题?
可以让线程排队一个一个执行,不能并发,即线程同步机制,效率低一些。
其次,异步就是并发,同步即为排队。
Java中有实例变量(堆)、静态变量(方法区)、局部变量(栈)。其中局部变量永远不会存在线程安全问题,因为它不共享。
synchronized三种用法
1.同步代码块
2.实例方法上用synchronized
3.静态方法上使用,表示找类锁。类锁只有一把,100个对象1个类锁。//synchronized出现在静态方法,类锁,见文末
Account 类
package com.javastudy.example11;
public class Account {
private String acount;
private double money;
public Account(String acount, double money) {
this.acount = acount;
this.money = money;
}
public String getAcount() {
return acount;
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setAcount(String acount) {
this.acount = acount;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
//取款操作
//synchronized void getMoney(double money){
void getMoney(double money){
// synchronized (this)
// {
double before=this.getMoney();
double after=before-money;
//模拟延迟,并发可能出问题!!!
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
this.setMoney(after);
// }
}
}
AccountThread类
package com.javastudy.example11;
public class AccountThread extends Thread{
private Account zhanghu;
public AccountThread(Account zhanghu) {
this.zhanghu = zhanghu;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized(zhanghu){
double money=500;
zhanghu.getMoney(money);
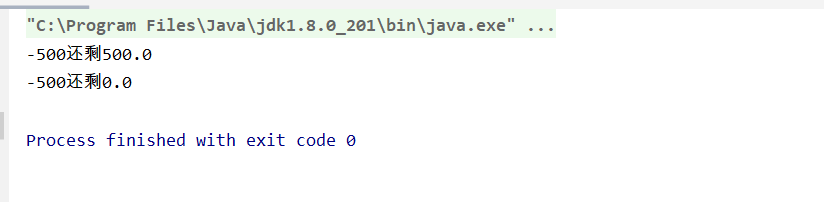
System.out.println("-500"+"还剩"+zhanghu.getMoney());
}
}}
Test类
package com.javastudy.example11;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account act=new Account("1",1000);
Thread t1= new AccountThread(act);
Thread t2= new AccountThread(act);
t1.setName("t1");
t2.setName("t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
运行截图
synchronized多种情况与类锁问题
package com.javastudy.example11;
public class StaticTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Myclass mc = new Myclass();
Myclass mc2 = new Myclass();
Thread t1=new MyThread01(mc);
Thread t2=new MyThread01(mc2);//不同对象,注意多种情况,有时是一个对象。
t1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
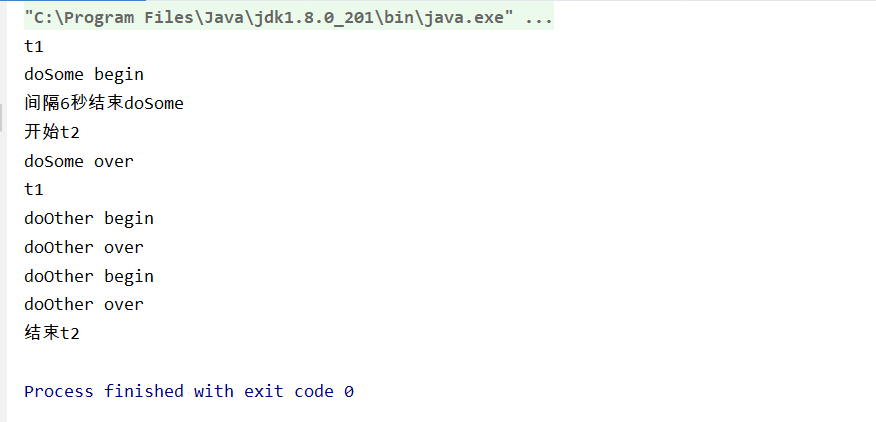
System.out.println("开始t2");
t2.start();
}
}
class MyThread01 extends Thread{
Myclass mc;
static int x=1;
public MyThread01(Myclass mc) {
this.mc = mc;
}
public void run() {
if(x==1){
x++;
System.out.println("t1");
mc.doSome();
System.out.println("t1");
mc.doOther();
}
else{
mc.doOther();
System.out.println("结束t2");}
}
}
class Myclass{
public synchronized static void doSome(){ //synchronized出现在静态方法,类锁
System.out.println("doSome begin");
System.out.println("间隔6秒结束doSome");
try {
Thread.sleep(6000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("doSome over");
}
//public synchronized void doOther(){ //只有一个对象时,需要等待
public synchronized static void doOther(){ //synchronized出现在静态方法,类锁
System.out.println("doOther begin");
System.out.println("doOther over");
}
}
运行截图



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号