kaggle地理空间分析-manipulating geospatial data(处理地理空间数据)<iv>
介绍
在本教程中,您将学习有关地理空间数据的两种常见操作:地理编码和表联接。
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
import numpy as np
import folium
from folium import Marker
Geocoding(地理编码)
地理编码是将地点或地址的名称转换为地图上的位置的过程。 例如,如果您曾经使用Google Maps,Bing Maps或Baidu Maps根据地标描述查找地理位置,那么您已经使用了地理编码器!
我们将使用geopandas进行所有的地理编码。
from geopandas.tools import geocode
要使用地理编码器,我们只需要提供:
- 名称或地址为Python字符串,以及
- 提供者的名称;为避免必须提供API密钥,我们将使用OpenStreetMap Nominatim geocoder(地理编码器)。
如果地理编码成功,则会返回包含两列的GeoDataFrame:
- “几何”列包含(纬度,经度)位置,以及
- “地址”列包含完整地址。
result = geocode("The Great Pyramid of Giza", provider="nominatim")
result
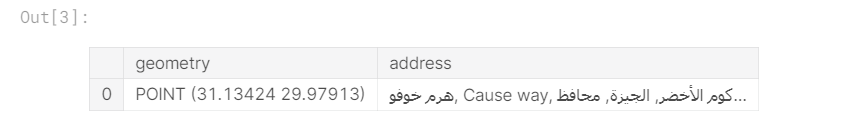
“geometry(几何)”列中的条目是一个Point对象,我们可以分别从y和x属性获得纬度和经度。
point = result.geometry.iloc[0]
print("Latitude:", point.y)
print("Longitude:", point.x)
Latitude: 29.9791264
Longitude: 31.13423837510151
通常,我们需要对许多不同的地址进行地理编码。 例如,假设我们想获得欧洲100所顶尖大学的位置。
universities = pd.read_csv("../input/geospatial-learn-course-data/top_universities.csv")
universities.head()

然后,我们可以使用lambda函数将地址解析器应用于DataFrame中的每一行。 (我们使用try / except语句来说明地理编码失败的情况。)
def my_geocoder(row):
try:
point = geocode(row, provider='nominatim').geometry.iloc[0]
return pd.Series({'Latitude': point.y, 'Longitude': point.x, 'geometry': point})
except:
return None
universities[['Latitude', 'Longitude', 'geometry']] = universities.apply(lambda x: my_geocoder(x['Name']), axis=1)
print("{}% of addresses were geocoded!".format(
(1 - sum(np.isnan(universities["Latitude"])) / len(universities)) * 100))
# Drop universities that were not successfully geocoded
universities = universities.loc[~np.isnan(universities["Latitude"])]
universities = gpd.GeoDataFrame(universities, geometry=universities.geometry)
universities.crs = {'init': 'epsg:4326'}
universities.head()
90.0% of addresses were geocoded!
接下来,我们将地理编码器返回的所有位置可视化。 请注意,其中一些位置肯定不准确,因为它们不在欧洲!
# Create a map
m = folium.Map(location=[54, 15], tiles='openstreetmap', zoom_start=2)
# Add points to the map
for idx, row in universities.iterrows():
Marker([row['Latitude'], row['Longitude']], popup=row['Name']).add_to(m)
# Display the map
m
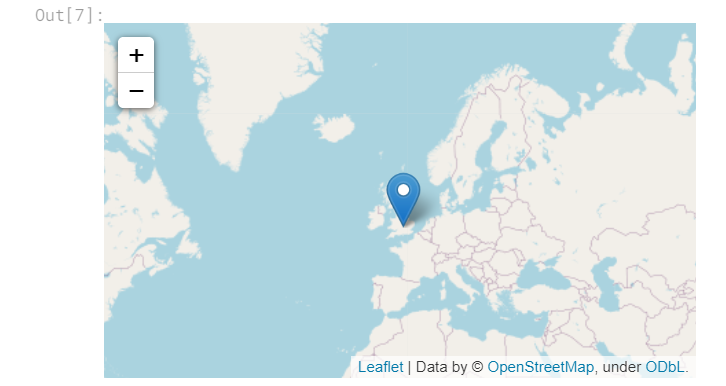
Table joins(表联接)
现在,我们将切换主题,并考虑如何合并来自不同来源的数据。
Attribute join(属性联接)
您已经知道如何使用pd.DataFrame.join()将来自多个DataFrame的信息与共享索引组合在一起。我们将这种联接数据的方式(通过简化索引中的匹配值)称为属性联接。
使用GeoDataFrame执行属性联接时,最好使用gpd.GeoDataFrame.merge()。 为了说明这一点,我们将使用一个包含欧洲每个国家边界的GeoDataFrame europe_boundaries。 此GeoDataFrame的前五行打印如下。
world = gpd.read_file(gpd.datasets.get_path('naturalearth_lowres'))
europe = world.loc[world.continent == 'Europe'].reset_index(drop=True)
europe_stats = europe[["name", "pop_est", "gdp_md_est"]]
europe_boundaries = europe[["name", "geometry"]]
europe_boundaries.head()

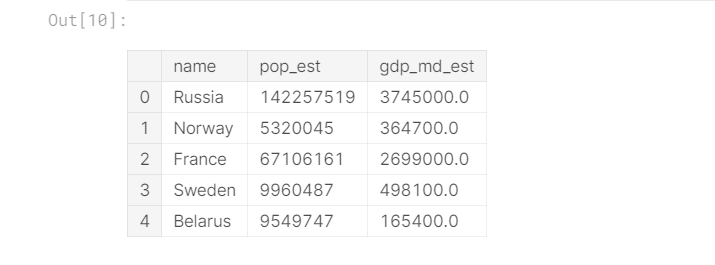
我们将其与一个DataFrame europe_stats一起加入,其中包含每个国家/地区的估计人口和国内生产总值(GDP)。
europe_stats.head()
我们在下面的代码单元中进行属性联接。on参数设置为列名,该列名用于将europe_boundaries中的行与europe_stats中的行进行匹配。
# Use an attribute join to merge data about countries in Europe
europe = europe_boundaries.merge(europe_stats, on="name")
europe.head()

Spatial join(空间连接)
连接的另一种类型是**spqtial join。通过空间连接,我们根据“几何”列中对象之间的空间关系来组合GeoDataFrame。 例如,我们已经有一个GeoDataFrameuniversities,其中包含欧洲大学的地理编码地址。
然后,我们可以使用空间连接将每所大学与其对应的国家/地区进行匹配。 我们使用gpd.sjoin()完成此操作。
# Use spatial join to match universities to countries in Europe
european_universities = gpd.sjoin(universities, europe)
# Investigate the result
print("We located {} universities.".format(len(universities)))
print("Only {} of the universities were located in Europe (in {} different countries).".format(
len(european_universities), len(european_universities.name.unique())))
european_universities.head()
We located 90 universities.
Only 85 of the universities were located in Europe (in 15 different countries).

上方的空间连接着眼于两个GeoDataFrames中的“geometry”列。 如果来自universitiesGeoDataFrame的Point对象与来自europe DataFrame的Polygon对象相交,则将相应的行合并并添加为europe_universitiesDataFrame的单行。否则,结果中将省略没有匹配大学的国家(和没有匹配国家的大学)。
可通过how和op参数为不同类型的联接定制gpd.sjoin()方法。 例如,您可以通过设置how ='left'(或how ='right')来进行SQL左(或右)联接的等效操作。 我们不会在此微型课程中进行详细介绍,但是您可以在文档中了解更多信息。
Your turn
使用地理编码和表联接来确定下一个星巴克储备烘焙所的合适位置。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号