59.二叉树的深度
输入一棵二叉树的根结点,求该树的深度。
从根结点到叶结点依次经过的结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
数据范围:
树中节点数量 [0,500]。
样例:
输入:二叉树[8, 12, 2, null, null, 6, 4, null, null, null, null]如下图所示:
输出:3
代码:
dfs解法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int treeDepth(TreeNode root) {
//递归终止条件:当前节点为空时,深度为0
if(root == null)return 0;
//递归计算左子树的最大深度
//递归计算右子树的最大深度
//当前树的最大深度 = 左右子树深度的较大值 + 1(当前节点)
return Math.max(treeDepth(root.left),treeDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
bfs解法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int treeDepth(TreeNode root) {
//处理空树情况
if(root == null)return 0;
//创建队列用于BFS遍历
Queue<TreeNode>q = new LinkedList<>();
//将根节点入队
q.offer(root);
//记录树的深度
int res = 0;
//开始层序遍历
while(!q.isEmpty()){
//当前层的节点数
int k = q.size();
//深度+1
res++;
//遍历当前层的所有节点
for(int i = 0;i<k;i++){
//取出队首节点
TreeNode t = q.poll();
//将左子节点入队(如果存在)
if(t.left!=null)q.offer(t.left);
//将右子节点入队(如果存在)
if(t.right!=null)q.offer(t.right);
}
}
//返回树的深度
return res;
}
}

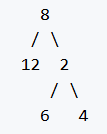

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号