6.重建二叉树
输入一棵二叉树前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建该二叉树。
注意:
- 二叉树中每个节点的值都互不相同;
- 输入的前序遍历和中序遍历一定合法;
数据范围:
树中节点数量范围 [0,100]。
样例:
给定:
前序遍历是:[3, 9, 20, 15, 7]
中序遍历是:[9, 3, 15, 20, 7]
返回:[3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7, null, null, null, null]
返回的二叉树如下所示:
代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//构造中序遍历值和数组下标的映射,帮助我们快速根据中序遍历数组的值定位对应的下标,主要是为了根据根节点的值找到其在中序遍历数组中的下标
Map<Integer,Integer>mp = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
//n为先序遍历数组的长度
int n = inorder.length;
//如果n为零直接返回null
if(n == 0)return null;
//遍历中序遍历数组,构造映射
for(int i = 0;i<n;i++)mp.put(inorder[i],i);
//递归构造二叉树
return build(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int pl,int pr,int il,int ir){
//前序遍历中的第一个节点就是根节点,root_val即为根节点的值
int root_val = preorder[pl];
//在中序遍历中定位根节点,root_idx即为根节点在中序遍历数组中的下标
int root_idx = mp.get(root_val);
//根据根节点的值root_val构造根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(root_val);
//如果il<root_idx表示中序遍历数组左边还有值,说明还有左子树,递归遍历构造左子树
//此时先序遍历数组的左右下标进行更新,左下标向右移动一位,变为pl+1,右下标更新为pl+1+左子树节点个数-1,由于左子树节点个数为root_idx-il,所以右下标更新为pl+root_idx-il
//同理中序遍历数组的左右下标进行更新,左下标仍为il,右下标更新为root_idx-1
if(il<root_idx)root.left = build(preorder,inorder,pl+1,pl+root_idx-il,il,root_idx-1);
//如果ir>root_idx表示中序遍历数组右边还有值,说明还有右子树,递归遍历构造右子树
//此时先序遍历数组的左右下标进行更新,左下标变为pl+root_idx-il+1,右下标仍为pr
//同理中序遍历数组的左右下标进行更新,左下标仍为root_idx+1,右下标仍为ir
if(ir>root_idx)root.right = build(preorder,inorder,pl+root_idx-il+1,pr,root_idx+1,ir);
//返回根节点
return root;
}
}

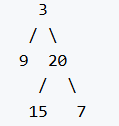

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号