24.回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例1:
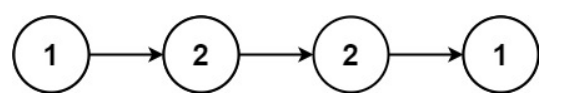
输入:head = [1,2,2,1]
输出:true
示例2:
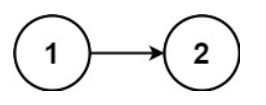
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:false
提示:
- 链表中节点数目在范围[1, 105] 内
- 0 <= Node.val <= 9
代码:
借助额外数组
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//定义一个列表
List<Integer>list = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历链表,将链表元素存储到列表中
while(head!=null){
list.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
//使用双指针,一个从头开始遍历,一个从尾到头遍历,判断是否满足回文
for(int i = 0,j = list.size()-1;i<j;i++,j--){
if(list.get(i) != list.get(j))return false;
}
return true;
}
}
不借助额外数组
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//如果链表为空,直接返回true
if(head == null)return true;
//定义一个快指针
ListNode fast = head;
//定义一个慢指针
ListNode slow = head;
//快指针每次移动两个单位,慢指针每次移动一个单位
//当快指针不能移动了,说明慢指针恰好走到链表中间,通过慢指针可以将链表分为两部分
while(fast.next != null&&fast.next.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
//翻转后半部分链表
ListNode cur = slow.next;
ListNode pre = null;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
//遍历判断是否满足回文链表条件
while(pre!=null){
if(pre.val!=head.val)return false;
pre = pre.next;
head = head.next;
}
return true;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号