03-Value-Based Reinforcement Learning
Value-Based Reinforcement Learning
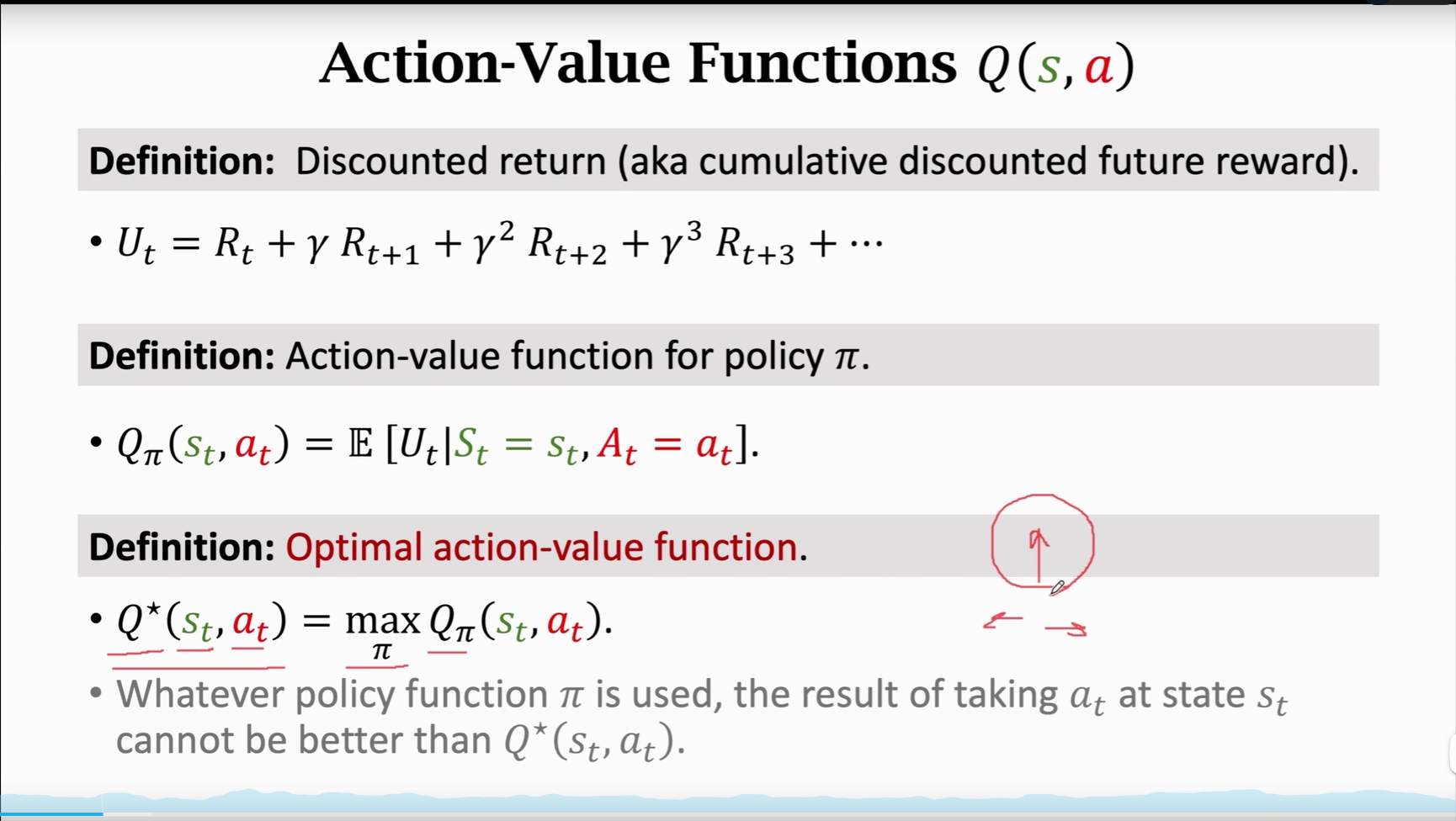
一、Deep Q-Network (DQN)
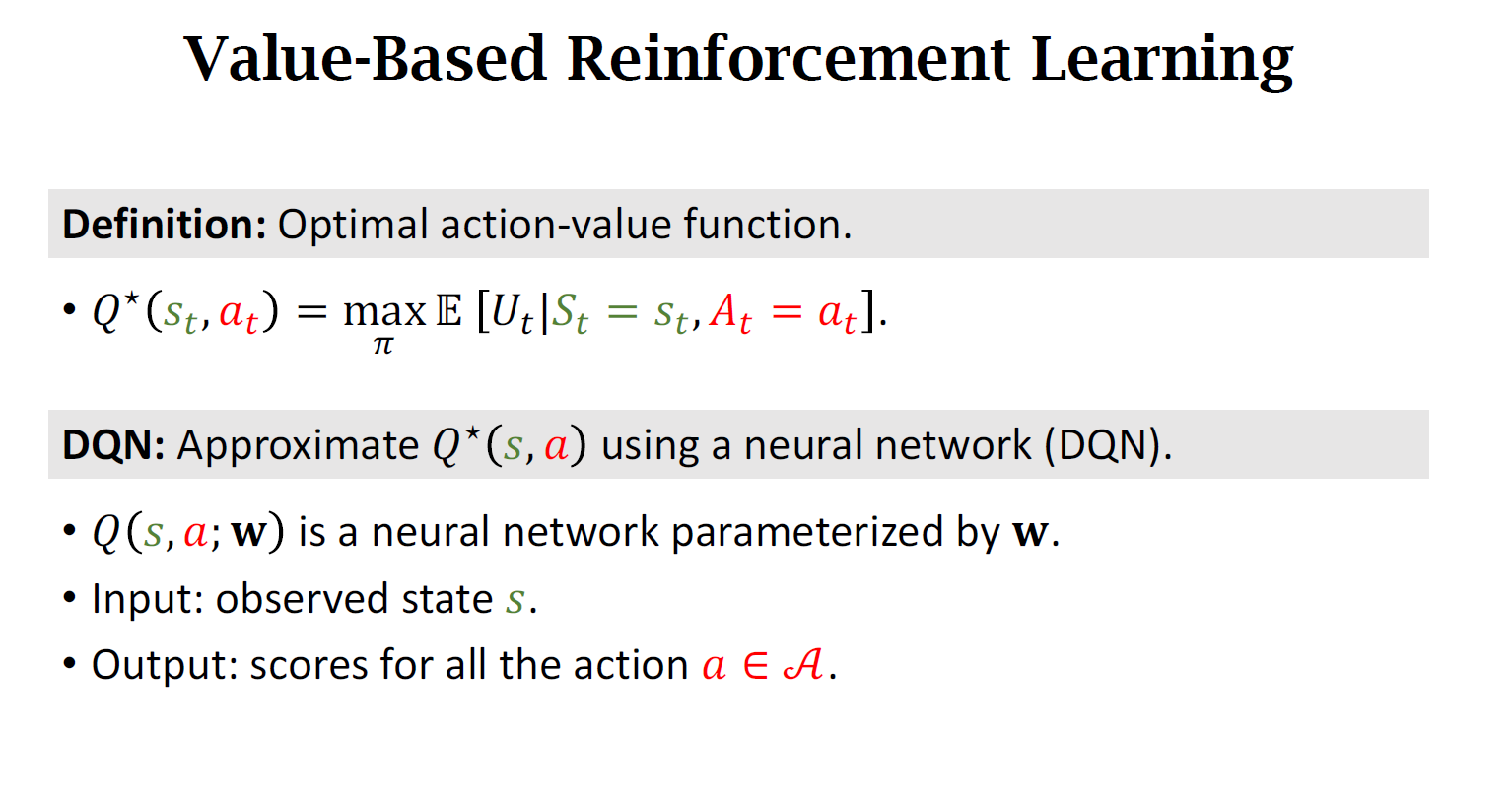
本质就是用神经网络近似\(Q^*\)函数,将 \(Q^{*}(s_t,a_t)\) 当作是一个先知,先知可以告诉你每个动作带来的平均回报,我们就应该听先知的话选平均回报最高的动作
-
Goal:
Win the game (≈ maximize the total reward.)
-
Question:
If we know $ Q^{*}(s_t,a_t) $ , what is the best action?

-
Challenge:
We do not know $ Q^{*}(s_t,a_t) $
价值学习的基本想法就是选择一个函数来近似 $ Q^{*}(s_t,a_t) $
比如超级玛丽玩个10w次,我们就基本上可以训练出一个先知了
-
Solution: Deep Q Network (DQN)
-
Use neural network \(𝑄(s,a;w)\) to approximate $ Q^{*}(s_t,a_t) $
-
w:神经网络的参数
-
s:状态s说神经网络的输入
-
神经网络的输出是很多数值,也就是对各个可能的数值的打分,每一个动作a对应一个分数。我们通过奖励来学习这个神经网络,这个神经网络的打分会越来越准。当神经网络玩了几百万次游戏后,神经网络将和先知一般
-
-
1.1 Apply DQN to Play Game
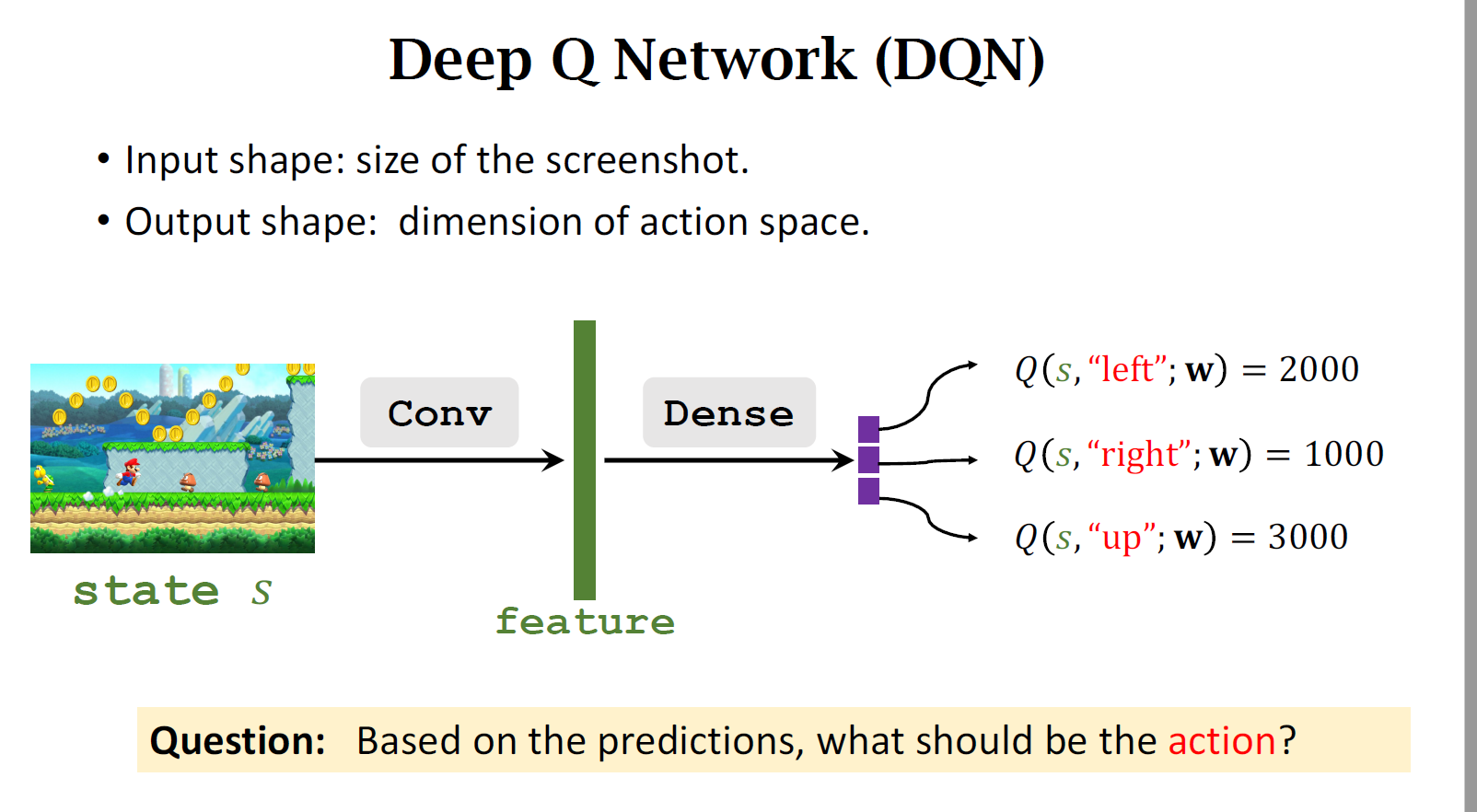
-
卷积层把图片变成特征向量,通过几个全链接层把特征映射到一个输出向量,输出向量也就是对动作打分,向量的每一个元素对应于一个动作,此情况有左右上三个动作所以是三维向量
-
所以只要把DQN训练好,就可以用DQN自动控制超级玛丽打赢游戏
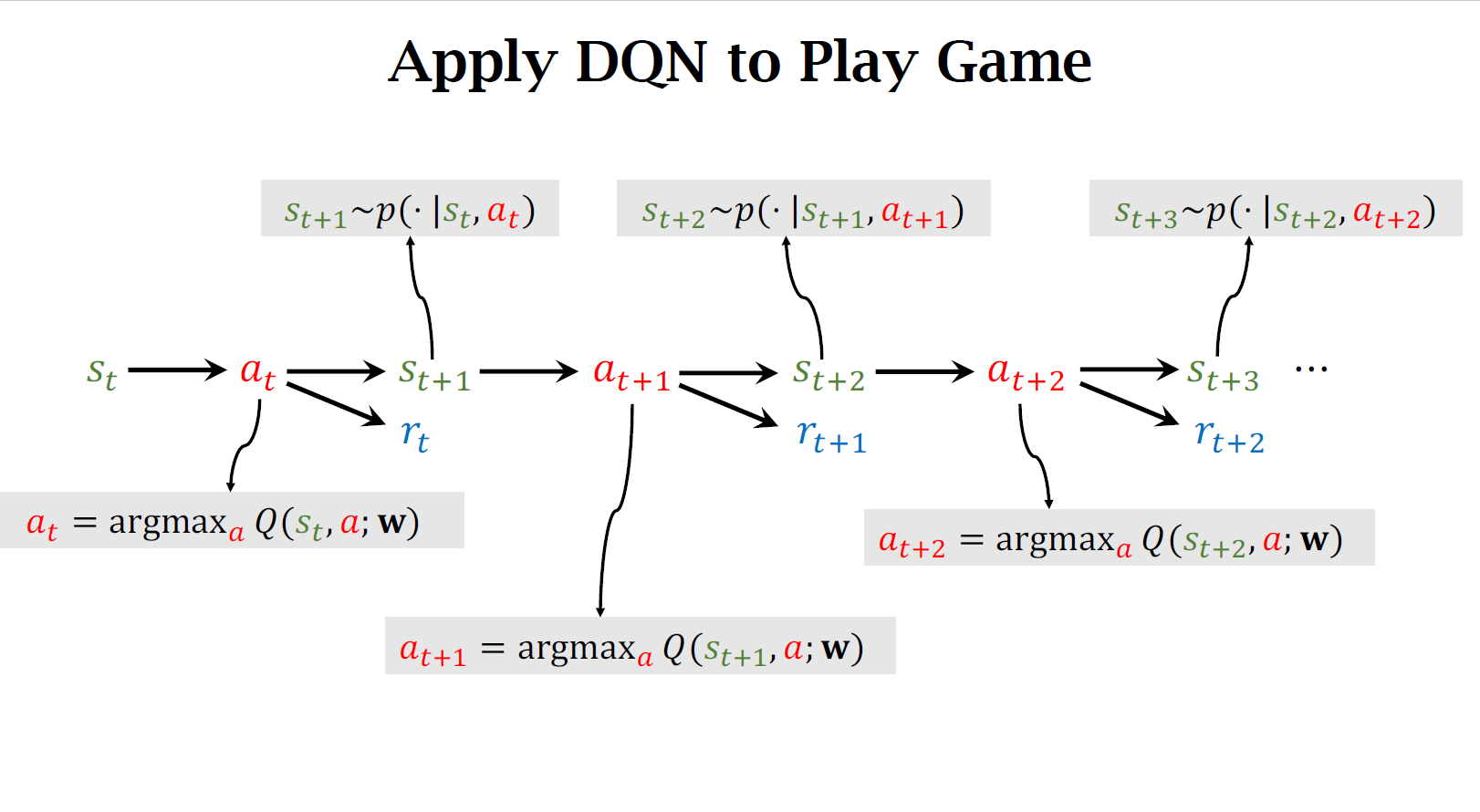
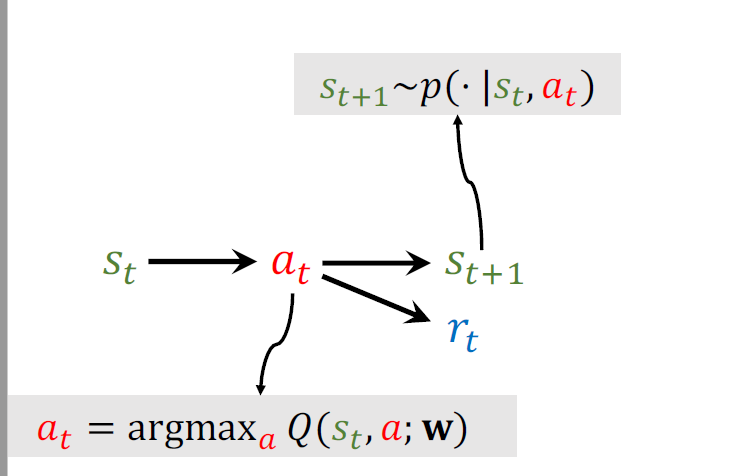
上图步骤:
-
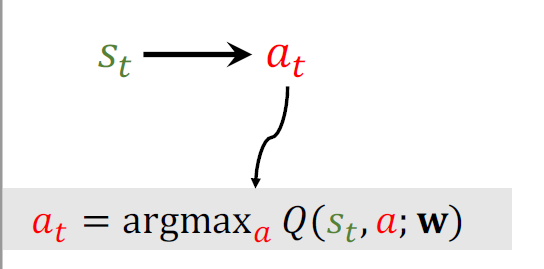
当前观测到状态\(s_t\)用DQN把状态\(s_t\)作为输入,给所有的动作打分,选出分数最高的动作,作为\(a_t\)
-
agent做出\(a_t\)这个动作后环境将会改变状态,用状态转移函数\(p\)来抽一个新的状态\(s_{t+1}\),环境将告诉我们这一步的奖励\(r_t\),奖励可以是+或-或0
-
有了新的状态\(s_{t+1}\),重复1和2,直到游戏结束
二、Temporal Difference (TD) Learning
2.1 Example
-
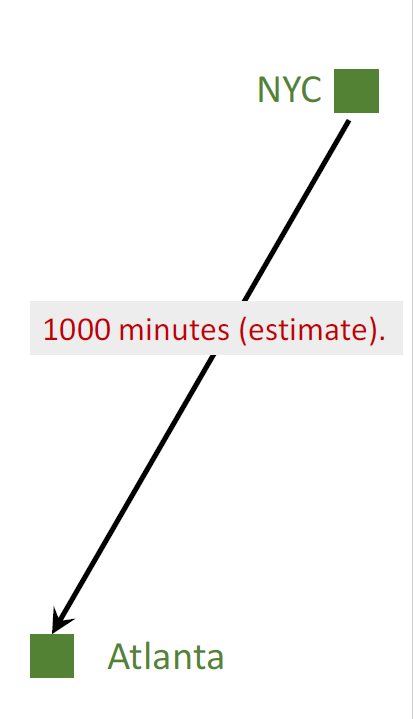
I want to drive from NYC to Atlanta.
-
Model \(Q(w)\) estimates the time cost, e.g., 1000 minutes.
模型 \(Q(w)\) 最开始并不准确,某种意义上可以说是纯随机的,但是随着更多人用这个模型得到更多数据,更多训练,这个模型就会越来越准,会像谷歌地图一样准确
-
Question1: How do I update the model?

我需要怎么样的数据,有了这些数据后我又该如何更新模型参数呢?
-
Make a prediction: \(𝑞 = Q(w)\) , e.g., 𝑞 = 1000
-
Finish the trip and get the target 𝑦, e.g., 𝑦 = 860.
-
Loss: \(L=\frac{1}{2} (q-y)^2\)
-

-
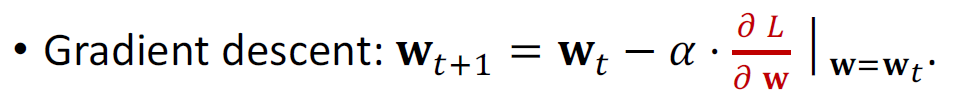
使用梯度下降更新模型参数,因为梯度下降减小了loss使得预测值和真实值更接近了
-
-
Can I update the model before finishing the trip?
在结束一次旅行前可以更新模型吗?
-
Can I get a better 𝐰 as soon as I arrived at DC?
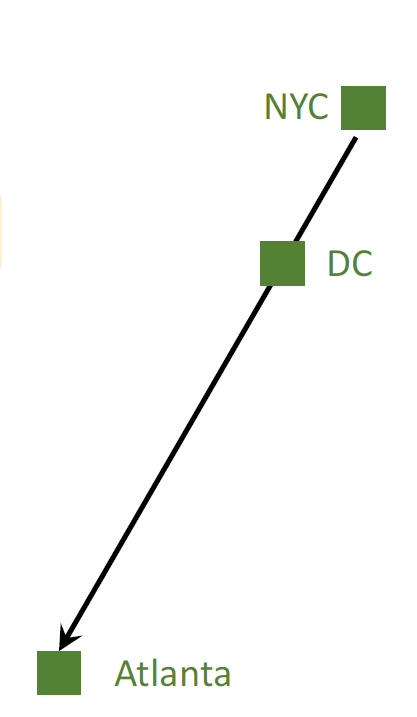
能否使用纽约到亚特兰大这一部分来更新模型呢?
可以的,我们可以使用TD算法来做这一件事
-
Model’s estimate:
NYC to Atlanta: 1000 minutes (estimate).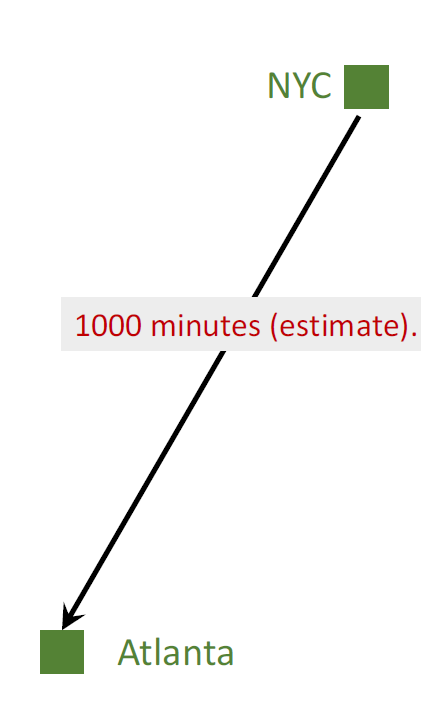
-
I arrived at DC; actual time cost:
NYC to DC: 300 minutes (actual).
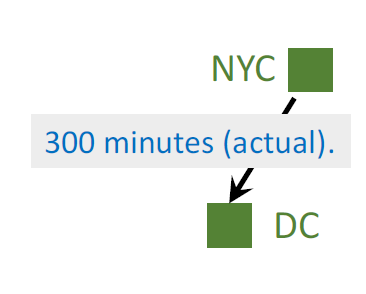
-
Model now updates its estimate:
DC to Atlanta: 600 minutes (estimate).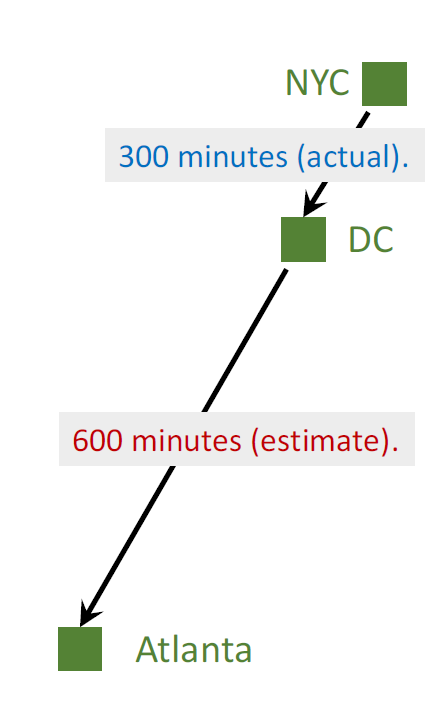
-
Model’s estimate: \(Q(w)\) = 1000 minutes.
-
Updated estimate: 300 + 600 = 900(TD target) minutes.
我越接近亚特兰大,TD target也就越准,用TD target的话我不需要跑完全部过程来直到真实的开销,随时可以更新TD target
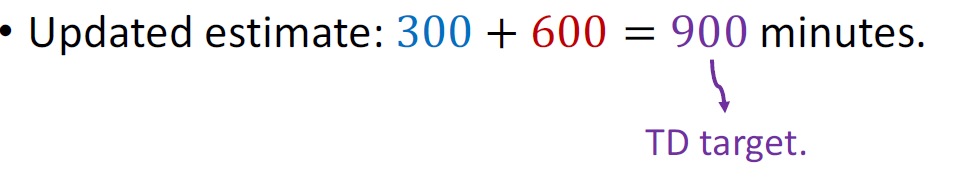
-
TD target y = 900 is a more reliable estimate than 1000.
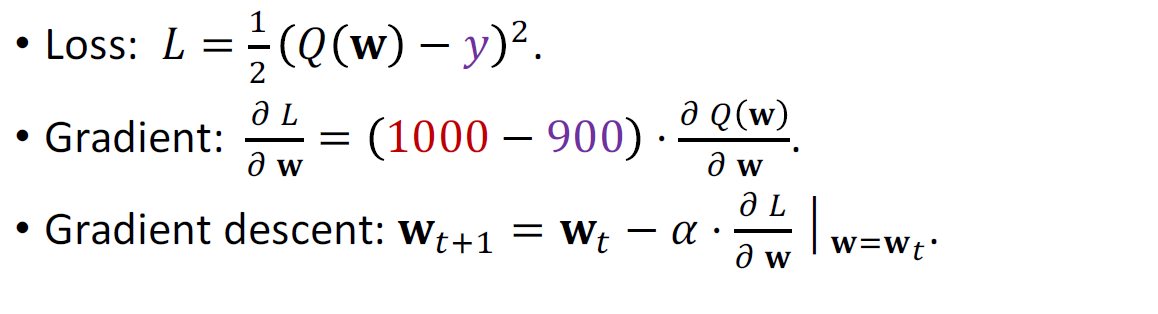
2.2 Why does TD learning work?
- Model’s estimates:
- NYC to Atlanta: 1000 minutes.
- DC to Atlanta: 600 minutes.
- NYC to DC: 400 minutes.
- Ground truth:
- NYC to DC: 300 minutes.
- TD error: \(𝛿 = 400 − 300 = 100\)
2.3 TD算法的目标
使得TD error尽可能接近0,也就是预计时间与实际时间相同,我们可以使用梯度下降来减少TD error
三、TD Learning for DQN
3.1 How to apply TD learning to DQN?
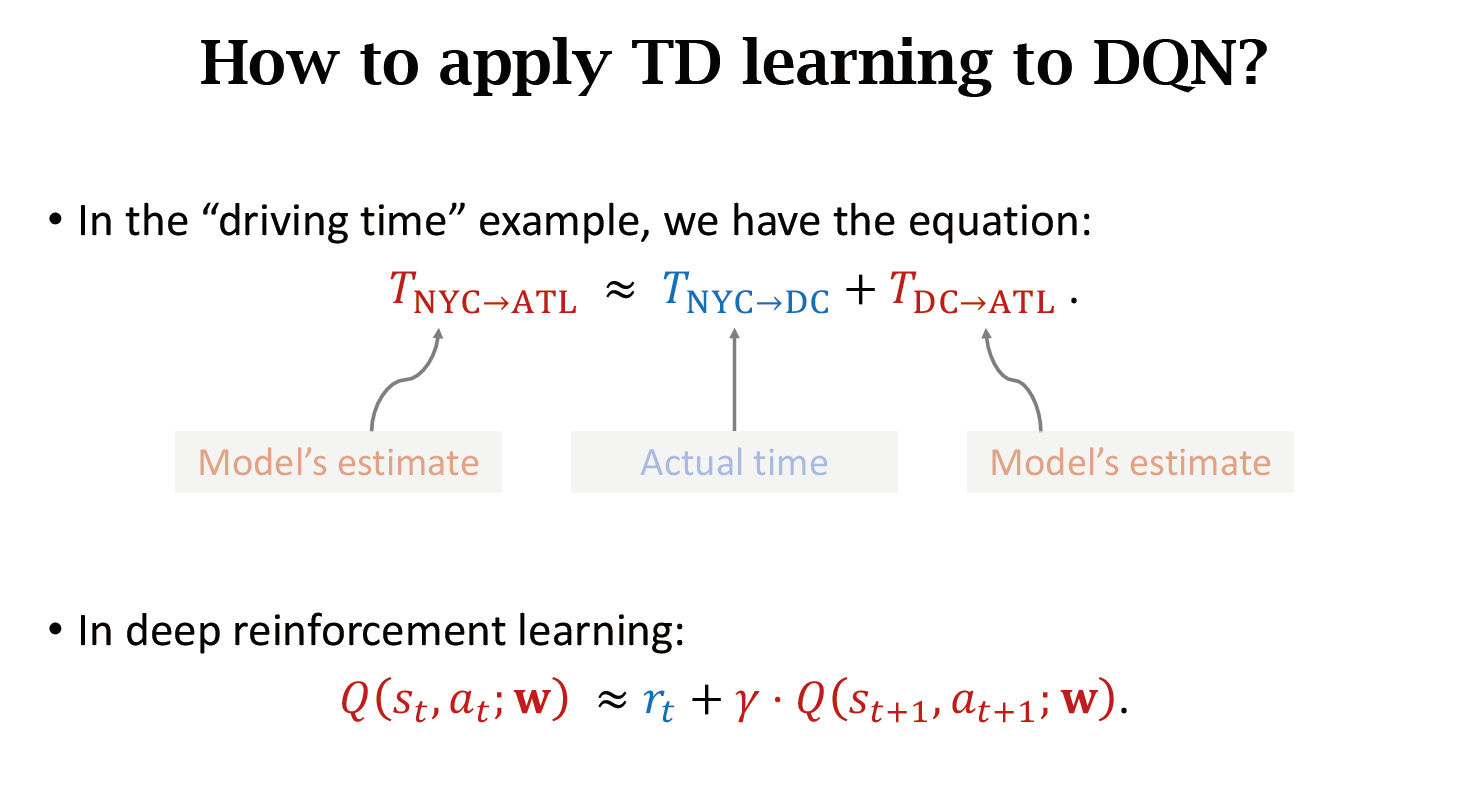
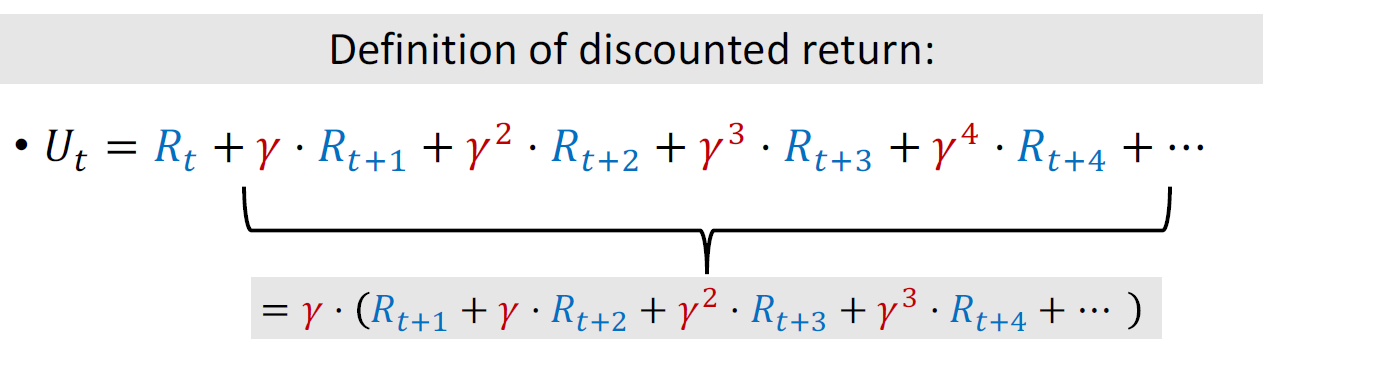
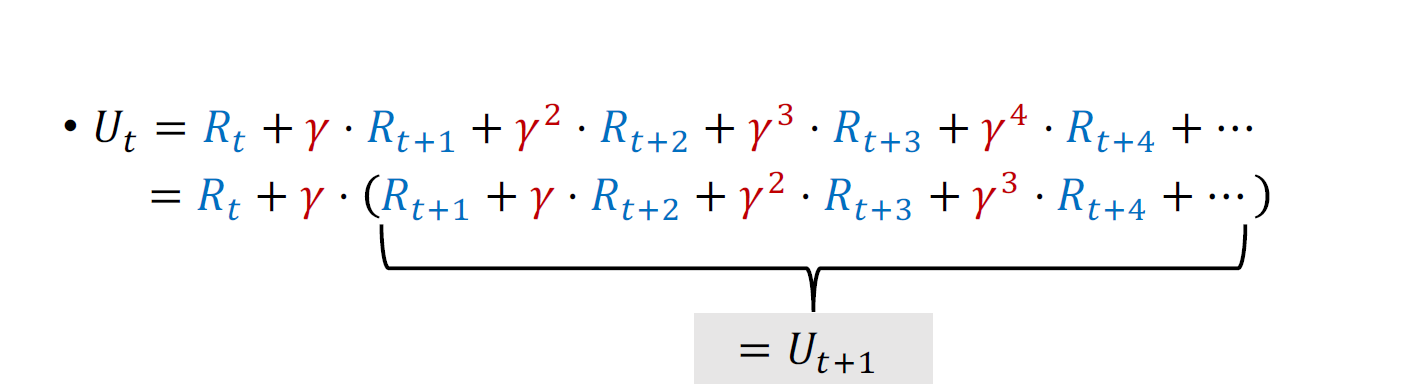

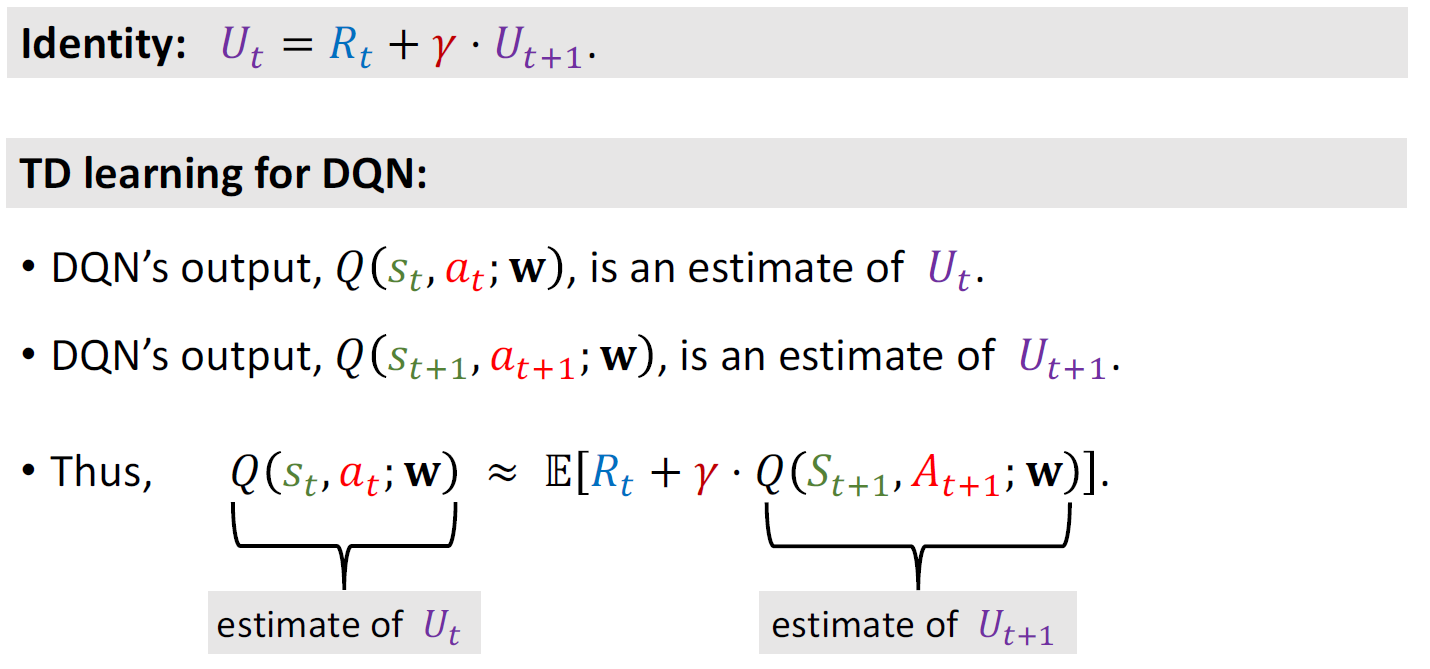
左边是对\(U_{t}\)的近似,右边是对\(U_{t+1}\)的近似,又因为:

所以左右大致相等
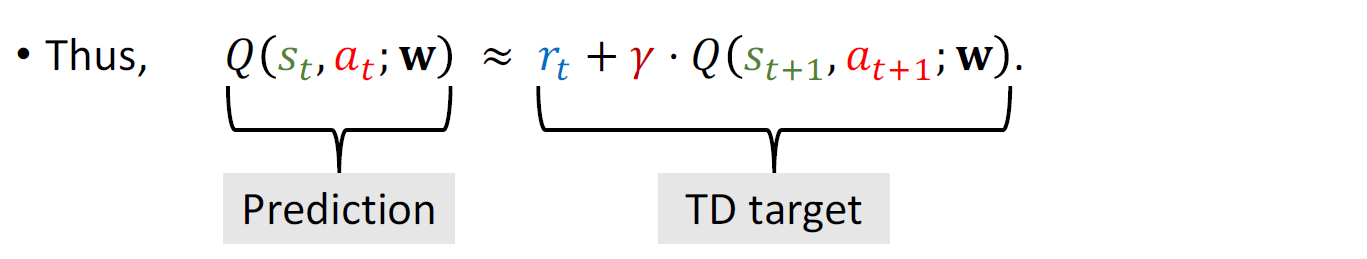
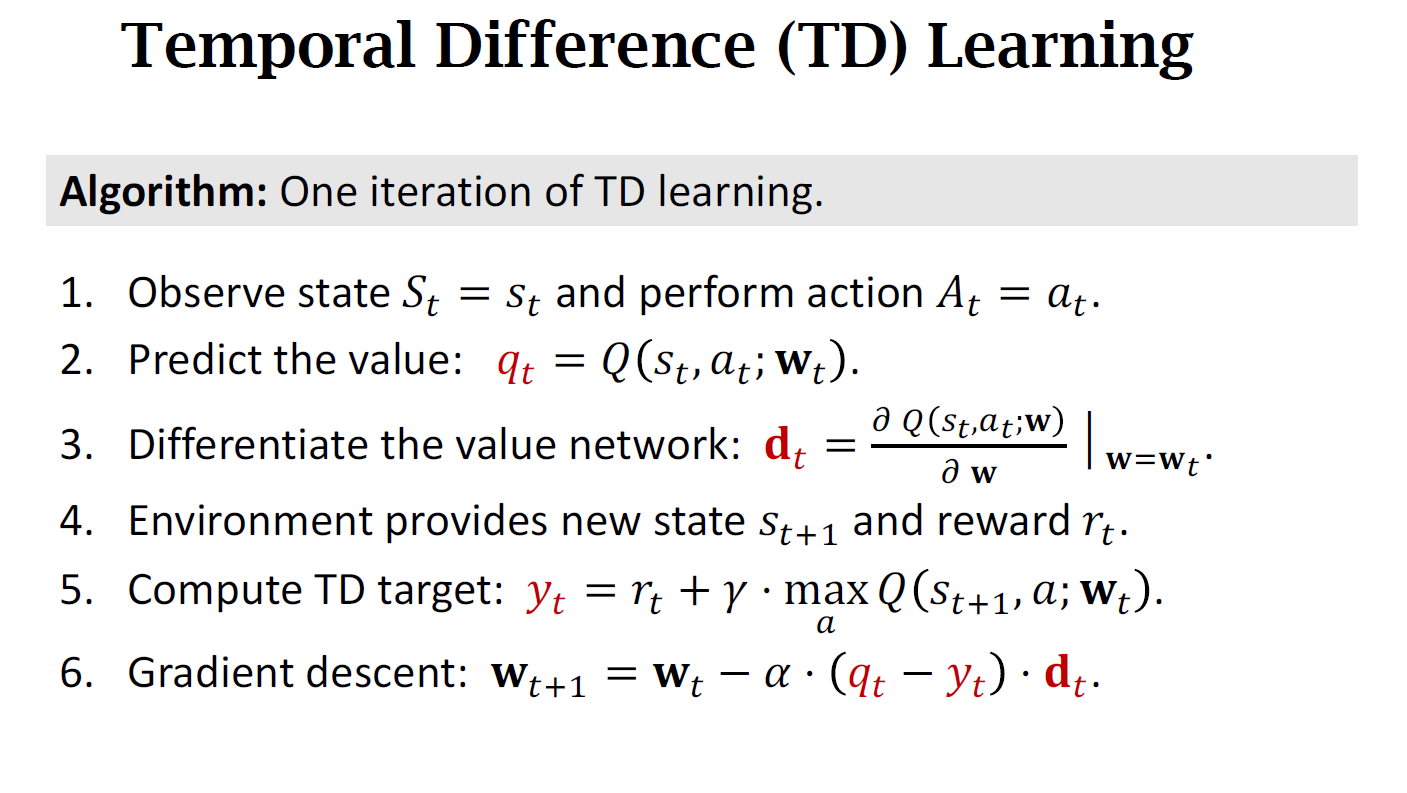
3.2 Train DQN using TD learning
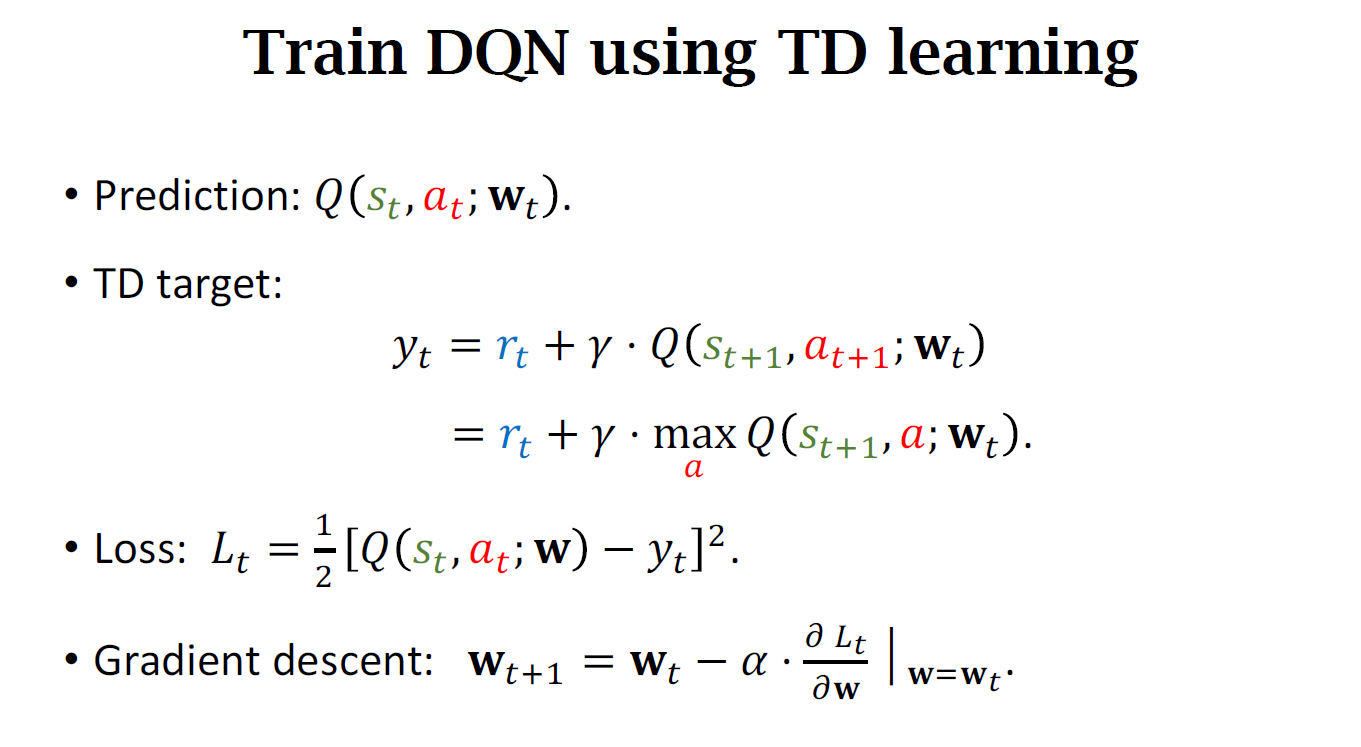
四、Summary



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号