Django-简单使用和生命周期
Django的简单使用和生命周期
-
创建Django工程
django-admin startproject 工程名 -
创建APP
cd 工程名
python manage.py startapp cmdb -
配置静态文件
project.settings.pySTATICFILES_DIRS = ( os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static"), ) -
模板路径
DIRS ==> [os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'templates'),] -
settings中
middlerware # 注释 csrf -
定义路由规则
url.py"login" --> 函数名 -
定义视图函数
app下views.pydef func(request): # request.method GET / POST # http://127.0.0.1:8009/home?nid=123&name=alex # request.GET.get('',None) # 获取请求发来的而数据 # request.POST.get('',None) # return HttpResponse("字符串") # return render(request, "HTML模板的路径") # return redirect('/只能填URL') -
特殊的模板语言
-- {{ 变量名 }}
def func(request): return render(request, "index.html", {'current_user': "alex"})
index.html <html> .. <body> <div>{{current_user}}</div> </body> </html> ====> 最后生成的字符串 <html> .. <body> <div>alex</div> </body> </html> -- For循环 def func(request): return render(request, "index.html", {'current_user': "alex", 'user_list': ['alex','eric']})
index.html <html> .. <body> <div>{{current_user}}</div> <ul> {% for row in user_list %} {% if row == "alex" %} <li>{{ row }}</li> {% endif %} {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html> #####索引################# def func(request): return render(request, "index.html", { 'current_user': "alex", 'user_list': ['alex','eric'], 'user_dict': {'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'}})
index.html <html> .. <body> <div>{{current_user}}</div> <a> {{ user_list.1 }} </a> <a> {{ user_dict.k1 }} </a> <a> {{ user_dict.k2 }} </a> </body> </html> ###### 条件 def func(request): return render(request, "index.html", { 'current_user': "alex", "age": 18, 'user_list': ['alex','eric'], 'user_dict': {'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'}})
index.html <html> .. <body> <div>{{current_user}}</div> <a> {{ user_list.1 }} </a> <a> {{ user_dict.k1 }} </a> <a> {{ user_dict.k2 }} </a> {% if age %} <a>有年龄</a> {% if age > 16 %} <a>老男人</a> {% else %} <a>小鲜肉</a> {% endif %} {% else %} <a>无年龄</a> {% endif %} </body> -
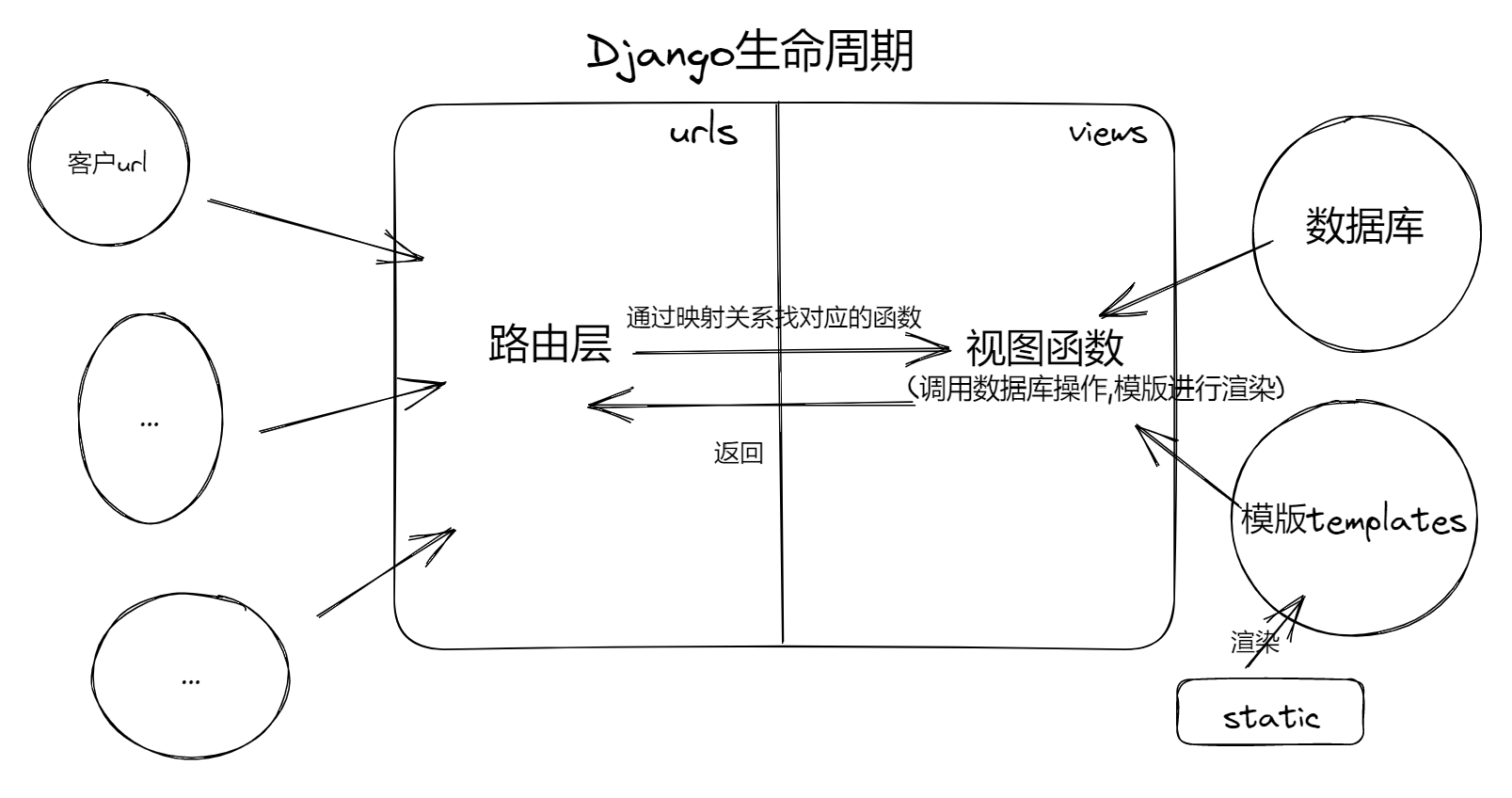
Django生命周期
![]()
本文来自博客园,作者:{Max},仅供学习和参考
posted on 2023-03-01 22:52 huxiaofeng 阅读(24) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号