从源码入门ThreadLocal
示例代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @ClassName ThreadLocalTest
* @Description TODO
* @Author heaboy@heaboy.com
* @Version 1.0.0
*/
public class ThreadTest{
private List<String> messages = new ArrayList<>();
public static final ThreadLocal<ThreadTest> holder = ThreadLocal.withInitial(ThreadTest::new);
public static void add(String msg){
holder.get().messages.add(msg);
}
public static List<String> clear(){
List<String> messages = holder.get().messages;
holder.remove();
System.out.println("size is" +messages.size());
return messages;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread [] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int j =i;
threads[i]=new Thread(()->{
ThreadTest.add("msg"+j);
List<String> messages = holder.get().messages;
System.out.println(messages);
});
threads[i].start();
}
}
}
查看ThreadLocal源码发现,可以通过无参构造和withInitial方法进行ThreadLocal实现,但不同的是无参构造,它只是一个空实现,不会做任何初始化工作,必须手动调用 set()
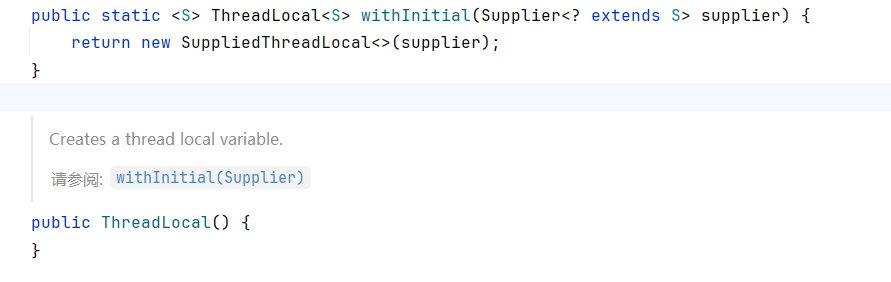
我们重点关注withInitial静态方法
withInitial返回的是一个SuppliedThreadLocal 实例,这是 ThreadLocal 的一个静态内部类并在后续进行赋值。

这里对关键方法进行了重写
ThreadLocal 的核心钩子方法:当某个线程第一次调用 get() 且之前未 set() 过值时,ThreadLocal 会回调 initialValue() 来生成“初始值”。
这里把生成逻辑委托给外部传入的 Supplier,实现“懒加载”初始值。

接下来我们关注holder.get()的逻辑及实现
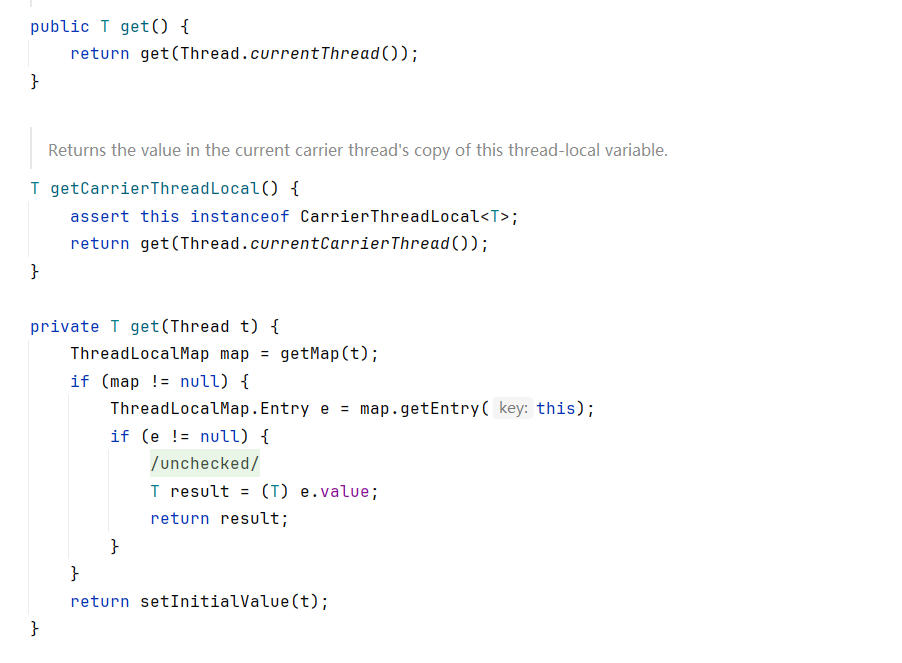
get()方法将当前线程作为参数传入了get(Thread t)方法
在get(Thread t)方法中
getMap(t)方法是:
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
而threadLocals是每个 Thread 对象内部都有一个字段,默认情况下
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
所以这一步就是:拿到当前线程的私有哈希表。
如果 map 存在,尝试取值
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
map.getEntry(this):用当前 ThreadLocal 实例作为 key,去哈希表中查找 Entry。
如果找到了
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T) e.value;
return result;
}
直接返回 value,结束。
如果 map 不存在,或没找到 Entry
return setInitialValue(t);
说明当前线程第一次访问这个 ThreadLocal,尚未存储值。
于是调用 setInitialValue(t):
private T setInitialValue(Thread t) {
T value = initialValue();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
map.set(this, value);
} else {
createMap(t, value);
}
if (this instanceof TerminatingThreadLocal<?> ttl) {
TerminatingThreadLocal.register(ttl);
}
if (TRACE_VTHREAD_LOCALS) {
dumpStackIfVirtualThread();
}
return value;
}
它会:
调用 initialValue() 生成初始值(可能是你通过 withInitial(...) 提供的)。
把值塞进当前线程的 ThreadLocalMap。
返回初始值。
其中
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
createMap 负责“从无到有”——当线程首次使用某个 ThreadLocal 时,把 ThreadLocalMap 实例化并挂到线程身上,从此该线程就有了自己的私有变量仓库。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号