《c#10 in a nutshell》--- 读书随记(6)
Chaptor 7. Collections
内容来自书籍《C# 10 in a Nutshell》
Author:Joseph Albahari
需要该电子书的小伙伴,可以留下邮箱,有空看到就会发送的
Enumeration
IEnumerable and IEnumerator
public interface IEnumerator
{
bool MoveNext();
object Current { get; }
void Reset();
}
public interface IEnumerable
{
IEnumerator GetEnumerator();
}
IEnumerable<T> and IEnumerator<T>
public interface IEnumerator<T> : IEnumerator, IDisposable
{
T Current { get; }
}
public interface IEnumerable<T> : IEnumerable
{
IEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator();
}
IEnumerable<T> and IDisposable
IEnumerable<T>继承了IDisposable接口,这允许了enumerators持有资源的引用,比如数据库的连接,并确保这些资源在enumeration完成之后被释放
The ICollection and IList Interfaces
虽然enumeration接口提供对集合向前迭代的协议,但是它们没有提供检测集合大小、通过索引访问成员、查询或者修改集合的机制。所以.NET 定义了ICollection, IList,IDictionary接口。
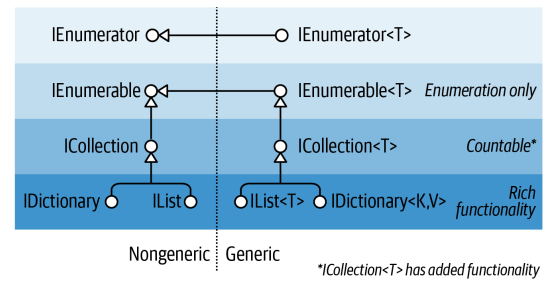
IEnumerable<T> (and IEnumerable)提供的最小的功能
ICollection<T> (and ICollection)提供中等的功能
IList<T>/IDictionary<K,V>提供最丰富的功能
ICollection<T> and ICollection
public interface ICollection<T> : IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable
{
int Count { get; }
bool Contains (T item);
void CopyTo (T[] array, int arrayIndex);
bool IsReadOnly { get; }
void Add(T item);
bool Remove (T item);
void Clear();
}
ICollection<T>提供了集合的大小、判断元素是否存在、转换为数组、判断是不是只读、添加、删除、清空功能。
IList<T> and IList
IList接口提供对集合元素做索引定位的功能
public interface IList<T> : ICollection<T>, IEnumerable<T>, IEnumerable
{
T this [int index] { get; set; }
int IndexOf (T item);
void Insert (int index, T item);
void RemoveAt (int index);
}
IReadOnlyCollection<T> and IReadOnlyList<T>
提供了只读功能的操作
Lists, Queues, Stacks, and Sets
List<T> and ArrayList
提供了一种动态扩张的数组对象,几乎是最常用的集合类。
ArrayList实现了IList,List<T> 实现了IList和IList<T>
实际上,List<T>和ArrayList的内部实现是维持一个数组对象。追加对象非常高效,但是插入和删除元素比较慢。用二分查找用在一个已经排序的列表查找元素很快
public class List<T> : IList<T>, IReadOnlyList<T>
{
public List ();
public List (IEnumerable<T> collection);
public List (int capacity);
// Add+Insert
public void Add(T item);
public void AddRange(IEnumerable<T> collection);
public void Insert(int index, T item);
public void InsertRange (int index, IEnumerable<T> collection);
// Remove
public bool Remove(T item);
public void RemoveAt(int index);
public void RemoveRange (int index, int count);
public int RemoveAll(Predicate<T> match);
// Indexing
public T this [int index] { get; set; }
public List<T> GetRange (int index, int count);
public Enumerator<T> GetEnumerator();
// Exporting, copying and converting:
public T[] ToArray();
public void CopyTo (T[] array);
public void CopyTo (T[] array, int arrayIndex);
public void CopyTo (int index, T[] array, int arrayIndex, int count);
public ReadOnlyCollection<T> AsReadOnly();
public List<TOutput> ConvertAll<TOutput> (Converter <T,TOutput> converter);
// Other:
public void Reverse(); // Reverses order of elements in list.
public int Capacity { get;set; } // Forces expansion of internal array.
public void TrimExcess(); // Trims internal array back to size.
public void Clear(); // Removes all elements, so Count=0.
}
如果导入System.Linq,那么ArrayList就有扩展方法转换为List
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.AddRange (new[] { 1, 5, 9 } );
List<int> list = al.Cast<int>().ToList();
LinkedList<T>
双向链表,主要的好处是,它可以非常快速地在任意位置插入或删除一个元素,因为只需要更新node的指针。但是在查找一个元素的时候,就比较慢了,因为链表没有索引机制,必须访问每个元素,直到找到需要的元素
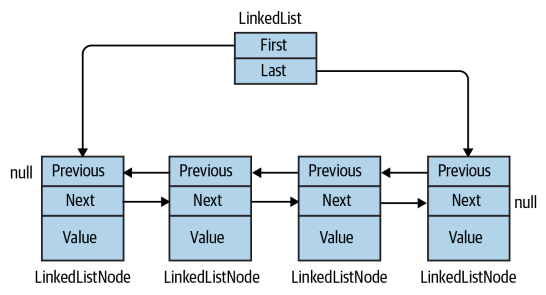
LinkedList<T>实现了IEnumerable<T>和ICollection<T>,但是没有实现IList<T>,因为链表没有索引
Queue<T> and Queue
队列,是一个先进先出的数据结构。有Enqueue插入元素到队尾和Dequeue从队头删除元素方法。还有一个Peek方法,查看队头元素,但是没有删除。而且没有实现IList<T>/IList,因为队列不可以使用索引随意访问。本质是使用数组对象实现的,更像是一个范型List。
Stack<T> and Stack
栈,是后进先出的数据结构。有Push方法插入元素到栈底和Pop方法从栈顶弹出元素,还有一个非破坏性的Peek方法查看栈顶元素。内部实现也是一个数组对象。
BitArray
BitArray是一个动态增长的集合,用来存储压缩的bool值。在内存效率上,它比简单的bool数组或者bool列表要更加高效,因为它只用了1bit来存储一个值,而正常bool值是占1byte
var bits = new BitArray(2);
bits[1] = true;
有位运算操作:And, Or, Xor, and Not
HashSet<T> and SortedSet<T>
有几种显著特征:
Contains方法非常快速,因为是使用基于hash的查找- 不可以存储重复值
- 不可以定位访问
它们都实现了ISet<T>,ICollection<T>接口,在.NET 5,还实现了IReadOnlySet<T>接口
HashSet<T>是用hashtable只存储key实现的
SortedSet<T>是用红黑树实现的
对于Set来说,真正感兴趣的方法是集合的操作,以下操作是破坏性的
public void UnionWith(IEnumerable<T> other); // Adds
public void IntersectWith(IEnumerable<T> other); // Removes
public void ExceptWith(IEnumerable<T> other); // Removes
public void SymmetricExceptWith (IEnumerable<T> other); // Removes
然后下面的方法不是破坏性的
public bool IsSubsetOf(IEnumerable<T> other);
public bool IsProperSubsetOf(IEnumerable<T> other);
public bool IsSupersetOf(IEnumerable<T> other);
public bool IsProperSupersetOf (IEnumerable<T> other);
public bool Overlaps(IEnumerable<T> other);
public bool SetEquals(IEnumerable<T> other);
SortedSet<T>除了以上的方法,还额外有特色的方法:
public virtual SortedSet<T> GetViewBetween (T lowerValue, T upperValue)
public IEnumerable<T> Reverse()
public T Min { get; }
public T Max { get; }
还可以在构造时,传入一个IComparer<T>来为元素排序
Dictionaries
字典是键值对的集合,最常用于查找和排序列表
实现的接口是IDictionary和IDictionary<TKey,TValue>
每种实现的字典,在不同场景有不同的效率
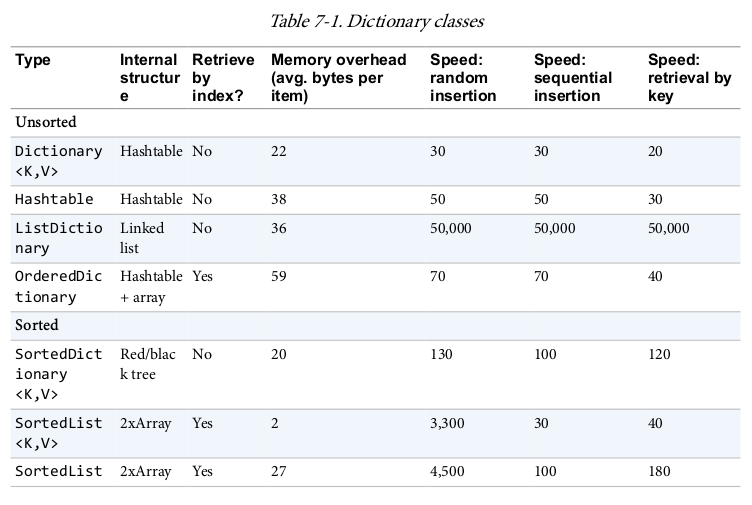
用大O符号表示,通过key检索的时间复杂度:
- O(1):
Hashtable、Dictionary和OrderedDictionary - O(log n):
SortedDictionary和SortedList - O(n):
ListDictionary
IDictionary<TKey,TValue>
public interface IDictionary <TKey, TValue> :
ICollection <KeyValuePair <TKey, TValue>>, IEnumerable
{
bool ContainsKey (TKey key);
bool TryGetValue (TKey key, out TValue value);
void Add(TKey key, TValue value);
bool Remove(TKey key);
TValue this [TKey key]{ get; set; }
ICollection <TKey> Keys{ get; }
ICollection <TValue> Values { get; }
}
public struct KeyValuePair <TKey, TValue>
{
public TKey Key{ get; }
public TValue Value { get; }
}
Immutable Collections
ReadOnlyCollection<T>创建了一个集合的视图。限制了集合写入的能力
immutable collections扩展了这个原理,当一个集合初始化之后,就不能被修改了,如果需要增加一个元素到集合中,需要新建一个集合,保持旧的不变
immutable collections是.NET的一部分,所有的集合定义在System.Collections.Immutable
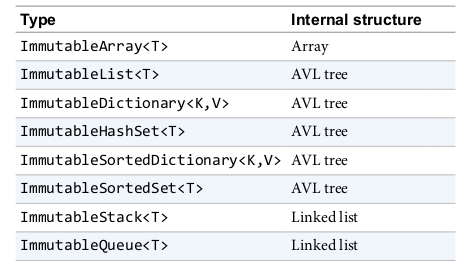
immutable collections暴露了一些和mutable功能相似的接口。不同的是,如果一些方法是需要修改集合的,则不会出现修改原有集合,而是返回一个新的集合
Creating Immutable Collections
ImmutableArray<int> array = ImmutableArray.Create<int> (1, 2, 3);
// IEnumerable<T>可以转换为不可变
var list = new[] { 1, 2, 3 }.ToImmutableList();
Builders
ImmutableArray<int>.Builder builder = ImmutableArray.CreateBuilder<int>();
builder.Add (1);
builder.Add (2);
builder.Add (3);
builder.RemoveAt (0);
ImmutableArray<int> myImmutable = builder.ToImmutable();
Immutable Collections and Performance
大多数的immutable collections使用AVL树作为底层数据结构,这允许添加/删除操作重用原始内部结构的某些部分,而不必从头开始重新创建整个集合。这减少了添加/删除操作的开销,从潜在的大型(大型集合)到适度的大型,但它的代价是使读取操作变慢。最终的结果是,大多数不可变集合在读写方面都比可变集合慢。
受影响最严重的是 ImmutableList < T > ,它对于读操作和添加操作都比 List < T > 慢10到200倍(取决于列表的大小)。所以出现了ImmutableArray< T >,通过使用数组,避免了读取操作的损耗,它的读取性能和可变类型的相差无几,但是代价就是写入的速度比 ImmutableList < T > 还要慢,因为没有原来的结构可以重用了
尽管不可变集合作为一个整体会带来潜在的巨大性能开销,但是保持对总体规模的正确认识非常重要。在一台典型的笔记本电脑上,具有100万个元素的 ImmutableList 上的 Add 操作仍然可能在不到1微秒的时间内发生,而读操作则可能在不到100纳秒的时间内发生。而且,如果需要在循环中执行写操作,则可以通过构建器避免累计成本。
-
不可变性允许轻松的并发性和并行性,因此您可以使用所有可用的内核。与可变状态并行很容易导致错误,并且需要使用锁或并发集合,这两者都会损害性能。
-
使用不可变性,您不需要“防御性地复制”集合或数据结构来防止意外的更改。这是在编写 VisualStudio 的最新部分时有利于使用不可变集合的一个因素。
-
在大多数典型的程序中,很少有集合具有足够的元素来对差异产生影响。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号