《c#10 in a nutshell》--- 读书随记(4)
Chaptor 4. Advanced C#
内容来自书籍《C# 10 in a Nutshell》
Author:Joseph Albahari
需要该电子书的小伙伴,可以留下邮箱,有空看到就会发送的
Delegates
委托是一种知道如何调用方法的对象。
delegate int Transformer (int x);
将一个适配的方法赋值给一个委托变量的时候,会创建一个委托实例:
int Square (int x) => x * x;
Transformer t = Square;
int answer = t(3); // answer is 9
Multicast Delegates
所有的委托实例都有广播的功能,这意味着,一个委托实例可以引用不止一个目标方法,可以是一个目标方法的集合,可以使用+或者+=来联合委托实例,也可以-或者-=来删减委托实例
SomeDelegate d = SomeMethod1;
d += SomeMethod2;
需要注意的是,委托是不可变的,所以上述的增删方法,其实是会创建一个新的实例,然后赋值到新的实例中
如果广播委托中,具有有返回值的方法,那么只会从最后一个方法中获取到返回值
The Func and Action Delegates
因为范型委托的缘故,我们可以写一些小型的,通用的委托类型集合。那就是Func and Action Delegates,它们定义在System命名空间。
delegate TResult Func <out TResult> ();
delegate TResult Func <in T, out TResult> (T arg);
delegate TResult Func <in T1, in T2, out TResult> (T1 arg1, T2 arg2);
... and so on, up to T16
delegate void Action ();
delegate void Action <in T> (T arg);
delegate void Action <in T1, in T2> (T1 arg1, T2 arg2);
... and so on, up to T16
Delegates Versus Interfaces
上面委托实现的功能,用接口也可以做到,但是相比委托,接口会比较麻烦
使用委托是一个更好的选择,如果以下的情况中出现一个或多个的时候
- 接口只定义了一个方法
- 广播功能
- 订阅者需要实现这个接口很多次
Delegate Compatibility
Type compatibility
委托类型之间是不兼容的,即使它们的签名都是一样的
Parameter compatibility
委托的参数支持逆变
delegate void StringAction (string s);
void ActOnObject (object o) => Console.WriteLine (o);
StringAction sa = new StringAction (ActOnObject);
sa ("hello");
Return type compatibility
委托返回值支持协变
delegate object ObjectRetriever();
string RetriveString() => "hello";
ObjectRetriever o = new ObjectRetriever (RetriveString);
object result = o();
Console.WriteLine (result);
Events
在使用委托的时候,会出现两种角色:广播器和订阅者
广播器就是一个类型包含着一个委托字段,广播器决定了什么时候广播,通过调用委托方法
订阅者是目标方法的接受者。订阅者决定了什么时候开始和结束监听,通过+=、-=操作符
事件是对这种模式的具象化成语言的特性。事件的主要目的是防止订阅者相互干扰
public delegate void PriceChangedHandler (decimal oldPrice, decimal newPrice);
public class Broadcaster
{
// Event declaration
public event PriceChangedHandler PriceChanged;
}
实际上,编译器会将上述代码翻译
PriceChangedHandler priceChanged;
// private delegate
public event PriceChangedHandler PriceChanged
{
add { priceChanged += value; }
remove { priceChanged -= value; }
}
Standard Event Pattern
using System;
Stock stock = new Stock ("THPW");
stock.Price = 27.10M;
// Register with the PriceChanged event
stock.PriceChanged += stock_PriceChanged;
stock.Price = 31.59M;
void stock_PriceChanged (object sender, PriceChangedEventArgs e)
{
if ((e.NewPrice - e.LastPrice) / e.LastPrice > 0.1M)
Console.WriteLine ("Alert, 10% stock price increase!");
}
public class PriceChangedEventArgs : EventArgs
{
public readonly decimal LastPrice;
public readonly decimal NewPrice;
public PriceChangedEventArgs (decimal lastPrice, decimal newPrice)
{
LastPrice = lastPrice; NewPrice = newPrice;
}
}
public class Stock
{
string symbol;
decimal price;
public Stock (string symbol) => this.symbol = symbol;
public event EventHandler<PriceChangedEventArgs> PriceChanged;
protected virtual void OnPriceChanged (PriceChangedEventArgs e)
{
PriceChanged?.Invoke (this, e);
}
public decimal Price
{
get => price;
set
{
if (price == value) return;
decimal oldPrice = price;
price = value;
OnPriceChanged (new PriceChangedEventArgs (oldPrice, price));
}
}
}
Lambda Expressions
一个lambda表达式是替代委托实例的一个匿名方法。编译器马上将lambda表达式转换为下面两个:
- 委托实例
- 表达式树,
Expression<TDelegate>
Capturing Outer Variables
lambda可以捕捉外部的参数,也就叫做闭包
int factor = 2;
Func<int, int> multiplier = n => n * factor;
Console.WriteLine (multiplier (3));
捕捉的参数的值,是在这个委托或者lambda表达式被使用的时候计算得到的,不是在捕捉的瞬间得到的。
int factor = 2;
Func<int, int> multiplier = n => n * factor;
factor = 10;
Console.WriteLine (multiplier (3));
如果闭包的内部修改了捕捉的变量,被捕捉的变量在外围也会被改变
int seed = 0;
Func<int> natural = () => seed++;
Console.WriteLine (natural()); // 0
Console.WriteLine (natural()); // 1
Console.WriteLine (seed); // 2
而且,如果被捕捉的变量的生命周期已经结束了,但是由于闭包捕捉了,那它的生命周期会被延长。
static Func<int> Natural()
{
int seed = 0;
return () => seed++;
}
static void Main()
{
Func<int> natural = Natural();
Console.WriteLine (natural()); // 0
Console.WriteLine (natural()); // 1
}
还有就是,一个在lambda中的本地变量是独一无二的,每次执行委托实例的时候,都是新的本地变量
static Func<int> Natural()
{
return() => { int seed = 0; return seed++; };
}
static void Main()
{
Func<int> natural = Natural();
Console.WriteLine (natural()); // 0
Console.WriteLine (natural()); // 0
}
Static lambdas
当你捕捉了本地变量、参数、实例字段或者this引用的时候,编译器可能会需要去创建并实例化一个私有类,去存储一个引用到被捕捉的数据,这会产生一个比较小的性能损耗,因为需要申请内存。如果在一个对性能要求比较高的场景下,可以用一个微调优化策略来让这个损耗降低到最小
在C# 9 中,如果确定了不需要捕捉外部变量,那么可以使用static关键字,这对优化有帮助。
Func<int, int> multiplier = static n => n * 2;
这对本地方法也是一样的
Capturing iteration variables
如果捕捉的变量,是循环的迭代变量,那么情况就相当于引用了一个循环外部的变量,然后循环每次都会修改同一个变量,而lambda内部引用的这个变量只会看到最后的变化的值
Action[] actions = new Action[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
actions [i] = () => Console.Write (i);
foreach (Action a in actions) a(); // 333
Lambda Expressions Versus Local Methods
Local method有几个比lambda更有优势的地方:
- 可以优雅地递归调用
- 避免了指定委托类型的混乱
- 开销稍微小一点
Local method更有效是因为,它避免了委托的间接性(委托消耗了CPU时钟和申请内存),它也可以访问在外围方法的本地变量,但是不需要编译器保持一个隐藏的类来捕捉变量,但其实很多时候,需要用到的是delegate
try Statements and Exceptions
try
{
... // exception may get thrown within execution of this block
}
catch (ExceptionA ex)
{
... // handle exception of type ExceptionA
}
catch (ExceptionB ex)
{
... // handle exception of type ExceptionB
}
finally
{
... // cleanup code
}
The catch Clause
可以捕捉后,没有生成变量
try
{
byte b = byte.Parse (args[0]);
Console.WriteLine (b);
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
Console.WriteLine ("Please provide at least one argument");
}
catch (FormatException)
{
Console.WriteLine ("That's not a number!");
}
catch (OverflowException)
{
Console.WriteLine ("You've given me more than a byte!");
}
Exception filters
类似于switch,可以添加守卫
catch (WebException ex) when (ex.Status == WebExceptionStatus.Timeout)
{
...
}
The finally Block
void ReadFile()
{
StreamReader reader = null;
// In System.IO namespace
try
{
reader = File.OpenText ("file.txt");
if (reader.EndOfStream) return;
Console.WriteLine (reader.ReadToEnd());
}
finally
{
if (reader != null) reader.Dispose();
}
}
一般在这个模块,会释放资源,这是一个标准的打开关闭文件资源的方法,但是使用using关键字会更好
The using statement
和上面的代码有相同的效果,资源的使用后,会自己释放
using (StreamReader reader = File.OpenText ("file.txt"))
{
...
}
// 在C# 8 中更进一步,在离开if这个block之后,资源会被释放
if (File.Exists ("file.txt"))
{
using var reader = File.OpenText ("file.txt");
Console.WriteLine (reader.ReadLine());
...
}
Throwing Exceptions
手动抛出异常
throw new ArgumentNullException (nameof (name));
Rethrowing an exception
try { ... }
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log error
...
throw; // Rethrow same exception
}
Key Properties of System.Exception
异常类型的最重要的几个属性:
- StackTrace,一个字符串,表示从异常的原点调用到 catch 块的所有方法。
- Message,一个字符串,描述error
- InnerException,导致外部异常的内部异常(如果有的话)本身可以有另一个内部异常。
Common Exception Types
以下几种异常在CLR和.NET库中用的非常广泛:
- System.ArgumentException,调用方法的时候,使用错误的参数
- System.ArgumentNullException,不希望函数的参数是null
- System.ArgumentOutOfRangeException,参数太大
- System.InvalidOperationException,非法操作
- System.NotSupportedException,对调用某个函数不支持
- System.NotImplementedException,表明这个方法没有实现
- System.ObjectDisposedException,调用
disposed方法的时候出错了
Enumeration and Iterators
Enumeration
一个enumerator是只读的。
foreach语句就是对一个enumerable对象进行迭代。一个enumerable对象在逻辑上代表一个序列。它自身不是一个游标,而是产生一个游标对象在它之上。
class Enumerator // Typically implements IEnumerator or IEnumerator<T>
{
public IteratorVariableType Current { get {...} }
public bool MoveNext() {...}
}
class Enumerable // Typically implements IEnumerable or IEnumerable<T>
{
public Enumerator GetEnumerator() {...}
}
高层次抽象中使用:
foreach (char c in "beer")
Console.WriteLine (c);
在低层次抽象中使用:
using (var enumerator = "beer".GetEnumerator())
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
var element = enumerator.Current;
Console.WriteLine (element);
}
如果enumerator实现了IDisposable,那么foreach语句也会和using语句一样,隐式调用释放方法
Collection Initializers
一些集合初始化方法
List<int> list = new List<int> {1, 2, 3};
var dict = new Dictionary<int, string>()
{
{ 5, "five" },
{ 10, "ten" }
};
var dict = new Dictionary<int, string>()
{
[3] = "three",
[10] = "ten"
};
Iterators
如果说foreach是enumerator的消费者,那么Iterators就是enumerator的生产者
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
foreach (int fib in Fibs(6))
Console.Write (fib + " ");
IEnumerable<int> Fibs (int fibCount)
{
for (int i = 0, prevFib = 1, curFib = 1; i < fibCount; i++)
{
yield return prevFib;
int newFib = prevFib+curFib;
prevFib = curFib;
curFib = newFib;
}
}
// OUTPUT: 1 1 2 3 5 8
需要注意的是,编译器会把iterator方法转换为一个实现了IEnumerable<T>和或者IEnumerator<T>的私有类。
Iterator Semantics
一个迭代器可以是一个方法、属性或者索引器,关键的是要包含yield语句
迭代器必须要返回四个接口的其中一个:
- System.Collections.IEnumerable
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<T>- System.Collections.IEnumerator
System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerator<T>
迭代器的语义是根据它的返回值决定它的语义的
多个yield语句是允许的
foreach (string s in Foo())
Console.WriteLine(s); // Prints "One","Two","Three"
IEnumerable<string> Foo()
{
yield return "One";
yield return "Two";
yield return "Three";
}
yield break
return语句在迭代器中是不合法的,如果需要提前结束方法,可以用yield break
Iterators and try/catch/finally blocks
yield return是不可以出现在try-catch块中的
但是可以出现在try-finally块中
Composing Sequences
迭代器是高度可组合的。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
foreach (int fib in EvenNumbersOnly (Fibs(6)))
Console.WriteLine (fib);
IEnumerable<int> Fibs (int fibCount)
{
for (int i = 0, prevFib = 1, curFib = 1; i < fibCount; i++)
{
yield return prevFib;
int newFib = prevFib+curFib;
prevFib = curFib;
curFib = newFib;
}
}
IEnumerable<int> EvenNumbersOnly (IEnumerable<int> sequence)
{
foreach (int x in sequence)
if ((x % 2) == 0)
yield return x;
}
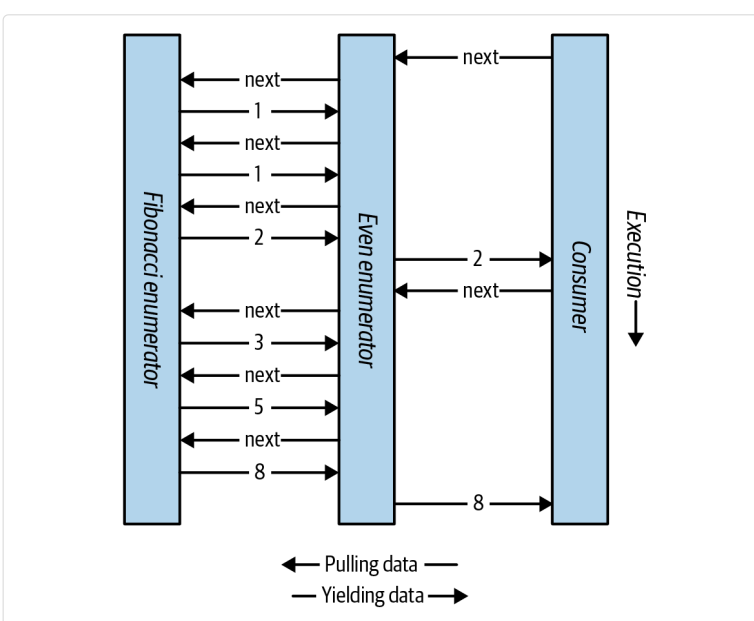
真正的计算推迟到了第一次调用MoveNext方法,所以是延迟求值,懒加载
Nullable Value Types
一个引用类型,可以用null来代表这个实例不存在,但是一个值类型就不行,为了表示值类型不存在,必须使用一个指定的结构,那就是nullable类型。一个可空类型用值类型后跟?表示
int? i = null;
Nullable Struct
T?会翻译为System.Nullable<T>类型,是一个轻量的不可变结构体,只有两个字段,代表了Value和HasValue
public struct Nullable<T> where T : struct
{
public T Value {get;}
public bool HasValue {get;}
public T GetValueOrDefault();
public T GetValueOrDefault (T defaultValue);
...
}
代码int? i = null;会被翻译为Nullable<int> i = new Nullable<int>();
Implicit and Explicit Nullable Conversions
int? x = 5; // implicit
int y = (int)x; // explicit
如果nullable没有值,那么强转会抛异常InvalidOperationException
Operator Lifting
Nullable<T>类型没有定义一些操作符的操作,比如<,>,==等,但是,下面的代码是正确的
int? x = 5;
int? y = 10;
bool b = x < y; // true
这是因为编译器在基础值类型那里借用或者提升了<这个操作,在语义上,相当于将前面的代码转换了
bool b = (x.HasValue && y.HasValue) ? (x.Value < y.Value) : false;
Operator lifting意味着,你可以在T?上隐式使用T的操作。
Nullable Reference Types
可空值类型为值类型带来可空性,而可空引用类型(C # 8)则相反
当开启这个特性之后,它为引用类型带来了非空性,目的是避免NullReferenceException
Nullable引用类型引入了纯粹由编译器强制执行的安全级别,当它检测到有生成NullReferenceException风险的代码时,以警告的形式提示
在开启之后,编译器会认为非空性是默认的,如果一个引用类型希望接受null而不会被编译器警告,那么必须在类型后面标记?,以此表明这个类型是可空引用类型
需要注意的是,因为可空引用类型是编译时构造,所以string和string?在运行时没有区别,相反,可空值类型在类型系统中引入了一些具体的东西,即Nullable<T>
The Null-Forgiving Operator
在解引用一个可空引用类型的时候,编译器会警告,因为可能会引发NullReferenceException
void Foo (string? s) => Console.Write (s.Length);
也可以使用null-forgiving operator(!),消除警告
void Foo (string? s) => Console.Write (s!.Length);
但是这样很危险,因为我们只是消除警告,这个异常还是有可能引发的,所以可以检查
void Foo (string? s)
{
if (s != null) Console.Write (s.Length);
}
Extension Methods
扩展方法允许一个已经存在的类型被扩展一个新的方法,但是不需要更改类型的原定义
扩展方法必须是静态的类下的静态方法,而且方法的第一个参数必须是this修饰,而且第一个参数的类型必须是被扩展的类型
public static class StringHelper
{
public static bool IsCapitalized (this string s)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(s)) return false;
return char.IsUpper (s[0]);
}
}
Console.WriteLine ("Perth".IsCapitalized());
在经过编译器之后,会被翻译成
Console.WriteLine (StringHelper.IsCapitalized ("Perth"));
接口也可以被扩展
public static T First<T> (this IEnumerable<T> sequence)
{
foreach (T element in sequence)
return element;
throw new InvalidOperationException ("No elements!");
}
...
Console.WriteLine ("Seattle".First()); // S
Extension Method Chaining
还可以链式调用
public static class StringHelper
{
public static string Pluralize (this string s) {...}
public static string Capitalize (this string s) {...}
}
string x = "sausage".Pluralize().Capitalize();
Ambiguity and Resolution
Namespaces
除非扩展方法的类在作用域内,否则无法访问该方法,通常是通过导入该方法的命名空间访问该方法
using System;
namespace Utils
{
public static class StringHelper
{
public static bool IsCapitalized (this string s)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(s)) return false;
return char.IsUpper (s[0]);
}
}
}
namespace MyApp
{
using Utils;
class Test
{
static void Main() => Console.WriteLine ("Perth".IsCapitalized());
}
}
Extension methods versus instance methods
任何兼容的实例方法总是优先于扩展方法
Extension methods versus extension methods
如果两个扩展方法具有相同的签名,则必须将扩展方法作为普通静态方法调用,以消除要调用的方法的歧义。
但是,如果一个扩展方法具有更具体的参数,则更具体的方法优先。
Demoting an extension method
当 Microso 将扩展方法添加到。NET 运行时库中与某些现有第三方库中的扩展方法冲突的。作为第三方库的作者,您可能希望“撤回”您的扩展方法,但不会删除它,也不会破坏与现有使用者的二进制兼容性。
幸运的是,这很容易实现,只需从扩展方法的定义中删除 this 关键字即可。将扩展方法降级为普通静态方法。这个解决方案的美妙之处在于,针对旧库编译的任何程序集都将继续工作(并像以前一样绑定到您的方法)。是因为扩展方法调用在编译期间被转换为静态方法调用。
消费者只有在重新编译时才会受到降级的影响,此时对以前扩展方法的调用现在将绑定到 Microsoft 版本(如果已导入名称空间)。如果使用者仍然想要调用您的方法,他们可以通过将其作为静态方法调用来实现。
Anonymous Types
匿名类型是编译器动态创建的一个简单类,用于存储一组值。若要创建匿名类型,请使用新关键字后跟对象初始值设定项,指定该类型将包含的属性和值
var dude = new { Name = "Bob", Age = 23 };
如果在同一程序集中声明的两个匿名类型实例的元素的命名和类型相同,则它们将具有相同的基础类型
var a1 = new { X = 2, Y = 4 };
var a2 = new { X = 2, Y = 4 };
Console.WriteLine (a1.GetType() == a2.GetType()); // True
还可以创建匿名类型的数组
var dudes = new[]
{
new { Name = "Bob", Age = 30 },
new { Name = "Tom", Age = 40 }
};
一个方法不能返回匿名类型对象,除非用dynamic关键字修饰方法
匿名类型是不可变的,所以不能修改,但是在C# 10中,可以通过with关键字,从旧的对象中创建新的对象
var a1 = new { A = 1, B = 2, C = 3, D = 4, E = 5 };
var a2 = a1 with { E = 10 };
Console.WriteLine (a2); // { A = 1, B = 2, C = 3, D = 4, E = 10 }
Tuples
元组提供了一种简单存储多个值的类型。主要目的是方法可以返回多个值,而不需要使用out关键字,元组是值类型
var bob = ("Bob", 23);
Naming Tuple Elements
可以给元组中的元素命名
var tuple = (name:"Bob", age:23);
Console.WriteLine (tuple.name);
Console.WriteLine (tuple.age);
Type erasure
我们之前说过,编译器通过为每个元素构建具有命名属性的自定义类来处理匿名类型。对于元组,C#的工作方式不同,它使用一系列已有的泛型结构:
public struct ValueTuple<T1>
public struct ValueTuple<T1,T2>
public struct ValueTuple<T1,T2,T3>
...
每个ValueTuple<>结构体都有字段名字为Item1, Item2,以此类推
所以,(string,int)是类型ValueTuple<string,int>的别名,这意味着命名的元组元素在基础类型中没有对应的属性名。相反,名称只存在于源代码中,以及编译器的想象中。在运行时,名称大多会消失,因此如果反编译引用命名元组元素的程序,您将看到仅引用 Item1、 Item2等。此外,当您在调试器中检查一个元组变量(它被赋予了一个对象)时(或者在 LINQPad 中转储它) ,元素名称不在其中。而且在大多数情况下,您不能在运行时使用反射来确定元组的元素名称。
Records
record是设计用来处理不可变数据的类型。它最有用的特性是nondestructive mutation,在只是结合或者拥有数据的地方,也很有用。而且record只存在于编译时,在运行时,CLR将它们看作类或者结构体
record和class有着一样的成员,也可以实现接口和继承基类
Defining a Record
record可以像class一样定义
Parameter lists
特殊的是
record Point (double X, double Y);
参数列表可以包括in和params修饰符,不能有out和ref修饰符。
如果指定了参数列表,编译器将执行下列额外步骤:
- 参数都会有init-only属性
- 编写一个主构造函数来填充属性
- 会有一个解构函数
Nondestructive Mutation
非破坏性突变(直译)
编译器对所有record执行的最重要的一步是编写一个复制构造函数(和一个隐藏的克隆方法)
通过with关键字实现Nondestructive Mutation(非破坏性变异)
Point p1 = new Point (3, 3);
Point p2 = p1 with { Y = 4 };
Console.WriteLine (p2); // Point { X = 3, Y = 4 }
record Point (double X, double Y);
Property Validation
可以在init访问器中编写验证逻辑
record Point
{
// Notice that we assign x to the X property (and not the _x field):
public Point (double x, double y) => (X, Y) = (x, y);
double _x;
public double X
{
get => _x;
init
{
if (double.IsNaN (value))
throw new ArgumentException ("X Cannot be NaN");
_x = value;
}
}
public double Y { get; init; }
}
Patterns
type pattern:
if (obj is string { Length:4 })
Console.WriteLine ("A string with 4 characters");
这个模式同样适用于is操作符,switch语句和表达式
var Pattern
var Pattern是type pattern的一种变体,您可以用var关键字替换类型名称。转换总是成功的,所以它的目的仅仅是让您重用下面的变量:
bool IsJanetOrJohn (string name) =>
name.ToUpper() is var upper && (upper == "JANET" || upper == "JOHN");
Constant Pattern
void Foo (object obj)
{
if (obj is 3) ...
}
Relational Patterns
在C# 9中,可以使用比较操作符
if (x is > 100) Console.WriteLine ("x is greater than 100");
// 在switch中很有用
string GetWeightCategory (decimal bmi) => bmi switch
{
< 18.5m => "underweight",
< 25m => "normal",
< 30m => "overweight",
_ => "obese"
};
Pattern Combinators
在C# 9中,可以使用and、or和not关键字,组合匹配模式
bool IsJanetOrJohn (string name) => name.ToUpper() is "JANET" or "JOHN";
bool IsVowel (char c) => c is 'a' or 'e' or 'i' or 'o' or 'u';
bool Between1And9 (int n) => n is >= 1 and <= 9;
bool IsLetter (char c) => c is >= 'a' and <= 'z'
or >= 'A' and <= 'Z';
if (obj is not string) ...
and的优先级比or高
Tuple and Positional Patterns
在C# 8中,可以匹配元组
var p = (2, 3);
Console.WriteLine (p is (2, 3)); // True
int AverageCelsiusTemperature (Season season, bool daytime) =>
(season, daytime) switch
{
(Season.Spring, true) => 20,
(Season.Spring, false) => 16,
(Season.Summer, true) => 27,
(Season.Summer, false) => 22,
(Season.Fall, true) => 18,
(Season.Fall, false) => 12,
(Season.Winter, true) => 10,
(Season.Winter, false) => -2,
_ => throw new Exception ("Unexpected combination")
};
enum Season { Spring, Summer, Fall, Winter };
record Point (int X, int Y);
Console.WriteLine (p is (var x, var y) && x == y); // True
Property Patterns
在C# 8中,可以匹配对象的一个或多个属性值
if (obj is string { Length:4 }) ...
可以嵌套属性
{ Scheme: { Length: 4 }, Port: 80 } => true,
// C# 10
{ Scheme.Length: 4, Port: 80 } => true,
还可以结合其他的模式
// 结合比较操作符
{ Host: { Length: < 1000 }, Port: > 0 } => true,
// 结合when
{ Scheme: "http" } when string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace (uri.Query) => true,
// 结合type pattern
bool ShouldAllow (object uri) => uri switch
{
Uri { Scheme: "http", Port: 80 } => true,
Uri { Scheme: "https", Port: 443 } => true,
...
}
// 新增一个变量在匹配成功后
Uri { Scheme: "http", Port: 80 } httpUri => httpUri.Host.Length < 1000,
// 在属性的级别插入变量
{ Scheme: "http", Port: 80, Host: string host } => host.Length < 1000,
{ Scheme: "http", Port: 80, Host: var host } => host.Length < 1000,
Operator Overloading
可以重载的操作符

Operator Functions
重载的函数需要符合一些要求:
- 函数的名字就是需要重载的操作符
- 函数必须是
static和public的 - 参数列表代表操作数
- 返回值代表表达式的返回值
- 最少需要一个操作数,而且类型是声明函数的类型
public struct Note
{
}
public static Note operator + (Note x, int semitones)
{
return new Note (x.value + semitones);
}
Custom Implicit and Explicit Conversions
public static implicit operator double (Note x)
=> 440 * Math.Pow (2, (double) x.value / 12 );
public static explicit operator Note (double x)
=> new Note ((int) (0.5 + 12 * (Math.Log (x/440) / Math.Log(2) ) ));
Note n = (Note)554.37; // explicit conversion
double x = n; // implicit conversion
XML Documentation
Standard XML Documentation Tags
<summary>摘要<remarks>描述<param>参数列表描述<returns>返回值描述<exception>可能抛出异常描述<example>示例代码<c>代码片段<see>插入对其他类型或成员的内联交叉引用<list>指示文档生成器发出项目符号、编号或表格样式的列表<para>指示文档生成器将内容格式化为单独的段落





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号