Picasso源码解析
本来这一篇文章,早就应该写了,但是最近一直在研究项目的安全性,就一直耽搁了。研究了一段时间的安全性,收获颇丰,下一篇文章,将总结一下最近的收获。好了,先把Picasso捋一遍。
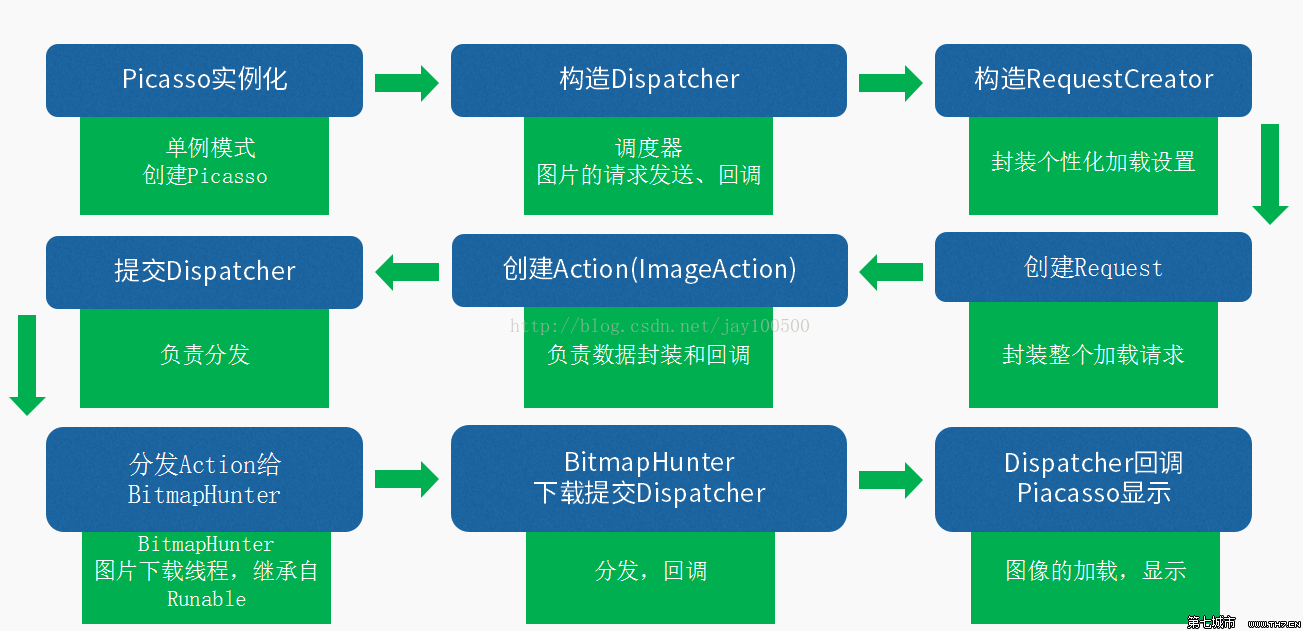
老规矩,先上流程图。这张图,从网上找来的。
Picasso的简单使用
build.gradle依赖
1 implementation 'com.squareup.picasso:picasso:2.71828'
加载图片
1 Picasso.get().load(url).into(imageView);
就一句代码,就实现了整个图片的加载。简单,明了。当然以前的版本是这样使用的 Picasso.with(this).load(url).into(imageView);
Picasso的源码解析
get()
我们先看看get()方法做了哪些操作
1 public static Picasso get() { 2 if (singleton == null) { 3 synchronized (Picasso.class) { 4 if (singleton == null) { 5 if (PicassoProvider.context == null) { 6 throw new IllegalStateException("context == null"); 7 } 8 singleton = new Builder(PicassoProvider.context).build(); 9 } 10 } 11 } 12 return singleton; 13 }
直接就通过一个双重判断形式的单例来获取到这个Picasso实例对象,我们看看singleton = new Builder(PicassoProvider.context).build();中的Builder做了什么。
1 /** Start building a new {@link Picasso} instance. */ 2 public Builder(@NonNull Context context) { 3 if (context == null) { 4 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Context must not be null."); 5 } 6 this.context = context.getApplicationContext(); 7 }
Building中所的操作不多,判断一下这个上下文环境,并且对上下文环境赋值为context.getApplicationContext();也就是说,Picasso的生命周期是和整个项目的生命周期是一致的,
当项目退出后,Picasso才会销毁。
build()
接着我们看看build()方法中做了哪些操作
1 /** Create the {@link Picasso} instance. */ 2 public Picasso build() { 3 Context context = this.context; 4 5 if (downloader == null) { 6 downloader = new OkHttp3Downloader(context); 7 } 8 if (cache == null) { 9 cache = new LruCache(context); 10 } 11 if (service == null) { 12 service = new PicassoExecutorService(); 13 } 14 if (transformer == null) { 15 transformer = RequestTransformer.IDENTITY; 16 } 17 18 Stats stats = new Stats(cache); 19 20 Dispatcher dispatcher = new Dispatcher(context, service, HANDLER, downloader, cache, stats); 21 22 return new Picasso(context, dispatcher, cache, listener, transformer, requestHandlers, stats, 23 defaultBitmapConfig, indicatorsEnabled, loggingEnabled); 24 } 25 }
build()方法中,主要是对这个下载器downloader,缓存cache,线程池PicassoExecutorService,事务分发器Dispatcher这几个对象的实例化。这几个对象,等会我们都会有介绍。
我们先看看Dispatcher这个事务分发器看看,先看看构造方法
1 Dispatcher(Context context, ExecutorService service, Handler mainThreadHandler, 2 Downloader downloader, Cache cache, Stats stats) { 3 this.dispatcherThread = new DispatcherThread(); 4 this.dispatcherThread.start(); 5 Utils.flushStackLocalLeaks(dispatcherThread.getLooper()); 6 this.context = context; 7 this.service = service; 8 this.hunterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); 9 this.failedActions = new WeakHashMap<>(); 10 this.pausedActions = new WeakHashMap<>(); 11 this.pausedTags = new LinkedHashSet<>(); 12 this.handler = new DispatcherHandler(dispatcherThread.getLooper(), this); 13 this.downloader = downloader; 14 this.mainThreadHandler = mainThreadHandler; 15 this.cache = cache; 16 this.stats = stats; 17 this.batch = new ArrayList<>(4); 18 this.airplaneMode = Utils.isAirplaneModeOn(this.context); 19 this.scansNetworkChanges = hasPermission(context, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE); 20 this.receiver = new NetworkBroadcastReceiver(this); 21 receiver.register(); 22 }
在构造方法中,除了将刚刚传入的下载器downloader,缓存cache,线程池PicassoExecutorService以外,还有几个比较重要的的一个是DispatcherHandler,NetworkBroadcastReceiver这两个对象
我们分别看看。
downloader下载器
1 if (downloader == null) { 2 downloader = new OkHttp3Downloader(context); 3 } 4 5 6 7 public OkHttpClient build() { 8 return new OkHttpClient(this); 9 }
我看了Picasso以前的版本,以前的版本下载器中,它会通过反射来获取OKhttp,如果项目中有使用OKhttp,则下载器就是使用OKhttp,否则的话,它会使用内嵌的UrlConnectionDownloader
下载器。但是新的版本以后(具体哪个版本开始,我没有深究)直接就是使用OKhttp了。
LruCache 缓存
1 /** Create a cache with a given maximum size in bytes. */ 2 public LruCache(int maxByteCount) { 3 cache = new android.util.LruCache<String, LruCache.BitmapAndSize>(maxByteCount) { 4 @Override protected int sizeOf(String key, BitmapAndSize value) { 5 return value.byteCount; 6 } 7 }; 8 }
这个缓存相当于给了一个具有给定最大字节大小的缓存。
PicassoExecutorService 线程池
1 class PicassoExecutorService extends ThreadPoolExecutor { 2 private static final int DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT = 3; 3 4 PicassoExecutorService() { 5 super(DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT, DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 6 new PriorityBlockingQueue<Runnable>(), new Utils.PicassoThreadFactory()); 7 } 8 9 void adjustThreadCount(NetworkInfo info) { 10 if (info == null || !info.isConnectedOrConnecting()) { 11 setThreadCount(DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT); 12 return; 13 } 14 switch (info.getType()) { 15 case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_WIFI: 16 case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_WIMAX: 17 case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_ETHERNET: 18 setThreadCount(4); 19 break; 20 case ConnectivityManager.TYPE_MOBILE: 21 switch (info.getSubtype()) { 22 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_LTE: // 4G 23 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_HSPAP: 24 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EHRPD: 25 setThreadCount(3); 26 break; 27 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_UMTS: // 3G 28 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_CDMA: 29 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EVDO_0: 30 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EVDO_A: 31 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EVDO_B: 32 setThreadCount(2); 33 break; 34 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_GPRS: // 2G 35 case TelephonyManager.NETWORK_TYPE_EDGE: 36 setThreadCount(1); 37 break; 38 default: 39 setThreadCount(DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT); 40 } 41 break; 42 default: 43 setThreadCount(DEFAULT_THREAD_COUNT); 44 } 45 }
这个线程池直接就继承ThreadPoolExecutor,默认的线程数是3个,而线程数的数量随着网络的变化而改变,WiFi的为4,4G的为3,3G的为2,2G的为1,其他情况都是使用默认的。
DispatcherHandler
1 private static class DispatcherHandler extends Handler { 2 private final Dispatcher dispatcher; 3 4 DispatcherHandler(Looper looper, Dispatcher dispatcher) { 5 super(looper); 6 this.dispatcher = dispatcher; 7 } 8 9 @Override public void handleMessage(final Message msg) { 10 switch (msg.what) { 11 case REQUEST_SUBMIT: { 12 Action action = (Action) msg.obj; 13 dispatcher.performSubmit(action); 14 break; 15 } 16 case REQUEST_CANCEL: { 17 Action action = (Action) msg.obj; 18 dispatcher.performCancel(action); 19 break; 20 } 21 case TAG_PAUSE: { 22 Object tag = msg.obj; 23 dispatcher.performPauseTag(tag); 24 break; 25 } 26 case TAG_RESUME: { 27 Object tag = msg.obj; 28 dispatcher.performResumeTag(tag); 29 break; 30 } 31 case HUNTER_COMPLETE: { 32 BitmapHunter hunter = (BitmapHunter) msg.obj; 33 dispatcher.performComplete(hunter); 34 break; 35 } 36 case HUNTER_RETRY: { 37 BitmapHunter hunter = (BitmapHunter) msg.obj; 38 dispatcher.performRetry(hunter); 39 break; 40 } 41 case HUNTER_DECODE_FAILED: { 42 BitmapHunter hunter = (BitmapHunter) msg.obj; 43 dispatcher.performError(hunter, false); 44 break; 45 } 46 case HUNTER_DELAY_NEXT_BATCH: { 47 dispatcher.performBatchComplete(); 48 break; 49 } 50 case NETWORK_STATE_CHANGE: { 51 NetworkInfo info = (NetworkInfo) msg.obj; 52 dispatcher.performNetworkStateChange(info); 53 break; 54 } 55 case AIRPLANE_MODE_CHANGE: { 56 dispatcher.performAirplaneModeChange(msg.arg1 == AIRPLANE_MODE_ON); 57 break; 58 } 59 default: 60 Picasso.HANDLER.post(new Runnable() { 61 @Override public void run() { 62 throw new AssertionError("Unknown handler message received: " + msg.what); 63 } 64 }); 65 } 66 } 67 }
这个DispatcherHandler直接Handler,并且是作用在dispatcherThread线程中的Handler,它用于把在dispatcherThread子线程的操作转到到Dispatcher中去,通过handleMessage()方法可以知道
如,请求取消,暂停,网络的变化,飞行模式的改变等等,都是通过Handler来切换处理的。
NetworkBroadcastReceiver
1 static class NetworkBroadcastReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver { 2 static final String EXTRA_AIRPLANE_STATE = "state"; 3 4 private final Dispatcher dispatcher; 5 6 NetworkBroadcastReceiver(Dispatcher dispatcher) { 7 this.dispatcher = dispatcher; 8 } 9 10 void register() { 11 IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(); 12 filter.addAction(ACTION_AIRPLANE_MODE_CHANGED); 13 if (dispatcher.scansNetworkChanges) { 14 filter.addAction(CONNECTIVITY_ACTION); 15 } 16 dispatcher.context.registerReceiver(this, filter); 17 } 18 19 void unregister() { 20 dispatcher.context.unregisterReceiver(this); 21 } 22 23 @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") 24 @Override public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) { 25 // On some versions of Android this may be called with a null Intent, 26 // also without extras (getExtras() == null), in such case we use defaults. 27 if (intent == null) { 28 return; 29 } 30 final String action = intent.getAction(); 31 if (ACTION_AIRPLANE_MODE_CHANGED.equals(action)) { 32 if (!intent.hasExtra(EXTRA_AIRPLANE_STATE)) { 33 return; // No airplane state, ignore it. Should we query Utils.isAirplaneModeOn? 34 } 35 dispatcher.dispatchAirplaneModeChange(intent.getBooleanExtra(EXTRA_AIRPLANE_STATE, false)); 36 } else if (CONNECTIVITY_ACTION.equals(action)) { 37 ConnectivityManager connectivityManager = getService(context, CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE); 38 dispatcher.dispatchNetworkStateChange(connectivityManager.getActiveNetworkInfo()); 39 } 40 } 41 }
这是一个广播,他的主要作用就是监听网络的变化,一旦网络发生了变化,则通过广播来接收到,并且通知相应的操作,比如更改线程的数量。
以上就是get()的所做的一些操作。
load()
1 public RequestCreator load(@Nullable String path) { 2 if (path == null) { 3 return new RequestCreator(this, null, 0); 4 } 5 if (path.trim().length() == 0) { 6 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Path must not be empty."); 7 } 8 return load(Uri.parse(path)); 9 } 10 11 RequestCreator(Picasso picasso, Uri uri, int resourceId) { 12 if (picasso.shutdown) { 13 throw new IllegalStateException( 14 "Picasso instance already shut down. Cannot submit new requests."); 15 } 16 this.picasso = picasso; 17 this.data = new Request.Builder(uri, resourceId, picasso.defaultBitmapConfig); 18 }
load()中所做的操作不多,主要通过path,来获得一个请求构造器RequestCreator
into()
public void into(ImageView target, Callback callback) { long started = System.nanoTime(); checkMain(); //判断是否在主线程 if (target == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target must not be null."); } if (!data.hasImage()) { //这里主要是判断uri是否为空,或者是resourceId是否为0,如果是的话,Picasso就会取消这个imageView的请求。并且将占位图显示 picasso.cancelRequest(target); if (setPlaceholder) { setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable()); } return; } if (deferred) { if (data.hasSize()) { //如果我们在代码中设置了fit()这个属性,也就是调整图像的大小,使其完全适合目标,但是又设置图片的宽高的话,就会抛异常了... throw new IllegalStateException("Fit cannot be used with resize."); } int width = target.getWidth(); int height = target.getHeight(); if (width == 0 || height == 0) { //如果我们设置的宽高中有一个为0的话,就会展示这个占位图 if (setPlaceholder) { setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable()); } picasso.defer(target, new DeferredRequestCreator(this, target, callback)); return; } data.resize(width, height); } Request request = createRequest(started); String requestKey = createKey(request); if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) { //先判断缓存中是否有数据,如果缓存中有数据的话则直接从缓存中取出来 Bitmap bitmap = picasso.quickMemoryCacheCheck(requestKey); if (bitmap != null) { picasso.cancelRequest(target); setBitmap(target, picasso.context, bitmap, MEMORY, noFade, picasso.indicatorsEnabled); if (picasso.loggingEnabled) { log(OWNER_MAIN, VERB_COMPLETED, request.plainId(), "from " + MEMORY); } if (callback != null) { callback.onSuccess(); } return; } } if (setPlaceholder) { //先展示占位图 setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable()); } Action action = new ImageViewAction(picasso, target, request, memoryPolicy, networkPolicy, errorResId, errorDrawable, requestKey, tag, callback, noFade); picasso.enqueueAndSubmit(action); //将请求事件添加到队列中,然后通过handler将请求事件发送出去。 }
基本Picasso的基本流程就是这样的了,如果有哪些错误,麻烦请指出,一起学习,一起进步




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号