Atcoder Beginner Contest 423 A-E
A
CODE
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define usetime() (double)clock () / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000.0
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
void read(int& x){
char c;
bool f=0;
while((c=getchar())<48) f|=(c==45);
x=c-48;
while((c=getchar())>47) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-48;
x=(f ? -x : x);
}
int x,c;
int main(){
read(x),read(c);
int ans=x/(1+c*1.0/1000);
printf("%d",ans/1000*1000);
return 0;
}
//^o^
B
CODE
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define usetime() (double)clock () / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000.0
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn=1e6+5;
void read(int& x){
char c;
bool f=0;
while((c=getchar())<48) f|=(c==45);
x=c-48;
while((c=getchar())>47) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-48;
x=(f ? -x : x);
}
int n;
int a[maxn];
int main(){
read(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) read(a[i]);
int l=0,r=n+1;
while(l<=n&&a[++l]==0);
while(r>0&&a[--r]==0);
if(l>r) printf("0");
else printf("%d",r-l);
return 0;
}
//^o^
C
也是简单的一道题,但是由于着急\(A\)掉,首 \(wa\) 以后尝试乱改 \(AC\)
于是————

告诫我们不能着急

大致结构是这样的,想必大家在 \(B\) 中有所了解
如果他在第 \(i\) 个房间,那么他就在 \(i\) 和 \(i+1\) 号门之间
如果发现此时左边全是锁上的门,就不用继续向左处理门,右边同理
否则他所需要操作门的区间内,每个开着的门要操作两次,关着的门操作一次
CODE
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define usetime() (double)clock () / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000.0
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn=2e5+5;
void read(int& x){
char c;
bool f=0;
while((c=getchar())<48) f|=(c==45);
x=c-48;
while((c=getchar())>47) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-48;
x=(f ? -x : x);
}
int n,x;
int a[maxn];
int main(){
read(n),read(x);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) read(a[i]);
int ans=0;
int l=0,r=n;
while(a[l]&&l<x) ++l;
while(a[r-1]&&r>x) --r;
for(int i=l;i<r;i++) ans+=a[i]+1;
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}
//^o^
D
每一个团进入餐厅时,会产生一个截止时间点,其他团进入餐厅肯定会在这些时间点上
考虑把所有时间点都放到优先队列中,一个一个处理即可
CODE
注:代码中将值变为负数是为了直接适配小根堆,避免定义结构体或重载运算符
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define fst first
#define sec second
#define mkp(a,b) make_pair(a,b)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
const int maxn=3e5+5;
void read(int& x){
char c;
bool f=0;
while((c=getchar())<48) f|=(c==45);
x=c-48;
while((c=getchar())>47) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-48;
x=(f ? -x : x);
}
int a[maxn],b[maxn],c[maxn];
LL ans[maxn];
priority_queue<pair<LL,pii> > p;
int n,k;
int main(){
read(n),read(k);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
read(a[i]),read(b[i]),read(c[i]);
p.push(mkp(-a[i],mkp(-c[i],i)));
}
queue<int> l;
LL sum=0;
while(!p.empty()){
pair<LL,pii> i=p.top();
p.pop(),i.fst=-i.fst,i.sec.fst=-i.sec.fst;
if(i.sec.fst<0) sum+=i.sec.fst;
else l.push(i.sec.sec);
while((!l.empty())&&sum+c[l.front()]<=k){
int j=l.front();
l.pop(),sum+=c[j],ans[j]=i.fst;
p.push(mkp(-(i.fst+b[j]),mkp(c[j],j)));
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
printf("%lld\n",ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}
//^o^
E
提供一种线段树做法,下面有官解写法
考虑如何计算合并两个区间所产生的新价值
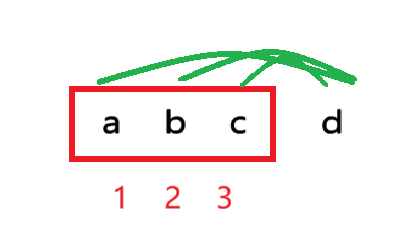
如图,假设现将区间 \(abc\) 与区间 \(d\) 合并,新的价值中,每个数的系数分别是 \(1,2,3\)
同理,手推一下包含三个数的右边区间,每个数的系数分别是 \(3,2,1\)
怎么和并这样的阶梯状带权区间和呢?

如图,对于这样的由高到低的阶梯状系数和,其中 \(k\) 表示区间的阶梯状系数和,\(sum\) 表示区间和,\(p\) 表示区间包含的数字数量
得出 \(k[u]=k[l]+p[r]*sum[l]+k[r]\)
由于要一个系数由高到低,一个系数由低到高的带权区间和,所以分别表示为 \(k1,k2\)
则合并一个区间的价值为 \(t[u]=k1[l]*p[r]+k2[r]*p[l]+t[l]+t[r]\)
这样就有了区间和并操作,这样线段树就可以实现了,时间复杂度为 \(O(q\,\,log\,\,n)\)
CODE
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define usetime() (double)clock () / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000.0
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn=2e5+5;
void read(int& x){
char c;
bool f=0;
while((c=getchar())<48) f|=(c==45);
x=c-48;
while((c=getchar())>47) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-48;
x=(f ? -x : x);
}
struct node{
LL t,sum;
int p;
LL k1,k2;
};
int n,q;
int a[maxn];
LL t[maxn<<2];
LL sum[maxn<<2];
LL k1[maxn<<2],k2[maxn<<2];
int p[maxn<<2];
void push_up(int u){
sum[u]=sum[u<<1]+sum[u<<1|1];
k1[u]=k1[u<<1]+p[u<<1]*sum[u<<1|1]+k1[u<<1|1];
k2[u]=k2[u<<1]+p[u<<1|1]*sum[u<<1]+k2[u<<1|1];
t[u]=k1[u<<1]*p[u<<1|1]+k2[u<<1|1]*p[u<<1]+t[u<<1]+t[u<<1|1];
p[u]=p[u<<1]+p[u<<1|1];
}
void build(int l=1,int r=n,int u=1){
if(l==r){
p[u]=1;
sum[u]=t[u]=k1[u]=k2[u]=a[l];
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(l,mid,u<<1),build(mid+1,r,u<<1|1);
push_up(u);
}
node query(int L,int R,int l=1,int r=n,int u=1){
if(l>R||r<L) return (node){0,0,0,0,0};
if(l>=L&&r<=R) return (node){t[u],sum[u],p[u],k1[u],k2[u]};
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
node a=query(L,R,l,mid,u<<1),b=query(L,R,mid+1,r,u<<1|1);
return (node){a.k1*b.p+b.k2*a.p+a.t+b.t,a.sum+b.sum,a.p+b.p,a.k1+a.p*b.sum+b.k1,a.k2+b.p*a.sum+b.k2};
}
int main(){
read(n),read(q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) read(a[i]);
build();
int l,r;
while(q--){
read(l),read(r);
printf("%lld\n",query(l,r).t);
}
return 0;
}
//^o^
\(upd\,\,on\,\,2025.9.18\)
为了不造成误解,说一下官解做法
题目让我们求这个:
拆开来,整理一下:
然后提前做一下 \(A_i \times i^2 \,,\, A_i \times i \,,\, A_i\) 的前缀和即可
CODE
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define usetime() (double)clock () / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000.0
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn=3e5+5;
void read(int& x){
char c;
bool f=0;
while((c=getchar())<48) f|=(c==45);
x=c-48;
while((c=getchar())>47) x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+c-48;
x=(f ? -x : x);
}
int a[maxn],n,q;
LL s0[maxn],s1[maxn],s2[maxn];
int main(){
read(n),read(q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
read(a[i]);
s0[i]=s0[i-1]+a[i],s1[i]=s1[i-1]+a[i]*i,s2[i]=s2[i-1]+1ll*a[i]*i*i;
}
int l,r;
while(q--){
read(l),read(r);
LL ans=-(s2[r]-s2[l-1])+1ll*(l+r)*(s1[r]-s1[l-1])+1ll*(r-l-1ll*l*r+1)*(s0[r]-s0[l-1]);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
//^o^


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号