1.4(JavaScript学习笔记) window对象的属性及方法
一、window对象
window对象代表当前窗口,所有全局对象都是windows的属性,
例如document是window的属性,window.document.writer("");
可以将window看做最外层的对象,其他一些了对象都是windows的属性。
window对象有很多属性,这些属性提供了对交互的支持(例如document、location...)
二、document对象
document是平时使用较多的对象,代表当前HTML文档.
window.document,前面的window可省略。
document也是window对象的一个属性。
每个载入浏览器的 HTML 文档都会成为 Document 对象。
Document 对象使我们可以从脚本中对 HTML 页面中的所有元素进行访问。
典型方法:document.getElementById(id);//返回指定id的HTML标签对象。
document.getElementByName();//返回指定名称的HTML对象集合。
document.write("");//向文档写入内容
document对象属性及方法可参阅:w3shcool document对象参考手册
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <input name="box" type = "checkbox" value = "1">1</input> <input name="box" type = "checkbox" value = "2">2</input> <input name="box" type = "checkbox" value = "3">3</input> <button onclick ="f()" >test</button> <p id = "content"></p> <script> function f(){ var i = 0; var boxs = document.getElementsByName("box"); var con = document.getElementById("content"); var info = "选择了"; for(var i = 0; i <boxs.length; i++){ if(boxs[i].checked == true){ info += boxs[i].value + ","; } } con.innerHTML = info; } </script> </body> </html>
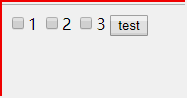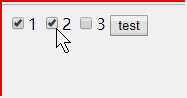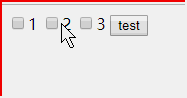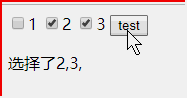
document.write()在文档加载完毕后再次调用会覆盖原有HTML文档内容。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <p id = "content">内容内容内容</p> <button onclick = "f()">test</button> <script> function f(){ document.write(""); alert("清除内容"); } </script> </body> </html>

HTML文档加载完毕后,关闭了输出流。
在输出流关闭后,重写调用document.write写入会先调用open方法,而open会先将页面清除。
如果是在输入流未结束的过程中,调用document.write写入则不会发生覆盖的情况。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <p id = "content">内容内容内容</p> <script> document.write("111"); alert("清除内容"); </script> </body> </html>

JavaScript代码执行时,文档尚未加载完毕,输出流没有关闭,
此时调用就不会重写打开输出流导致文档被覆盖。
不想被write覆盖可预先设置信息区块,后续通过innerHTM修改信息区块中内容,如第一个例子所示。
三、location对象
location对象主要提供获取当前url地址,设置页面url跳转等功能。
window.location前面的window可省略不写。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <button onclick = "f()">修改url为https://cn.bing.com/</button> <button onclick = "location.reload()">重新加载页面</button> <script> function f(){ location.href = "https://cn.bing.com/";//href代表完整的url路径 } </script> </body> </html>
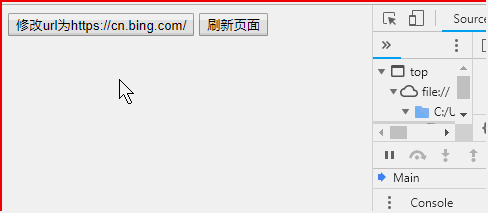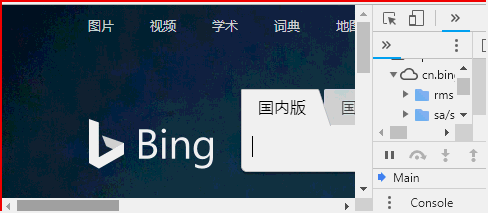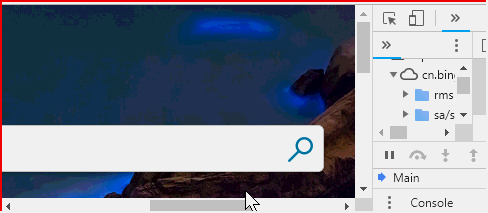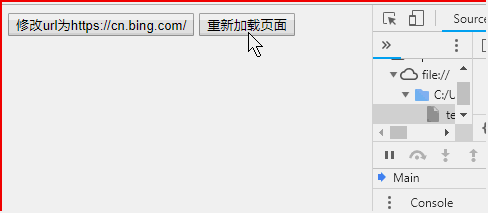
location其他属性及方法可参阅:w3school location对象参考手册
四、screen对象
screen对象主要包含当前浏览器的屏幕信息,例如可用的高、框为多少。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <script> document.write("屏幕高度" + screen.height + "<br>"); document.write("返回显示屏幕的高度 (除 Windows 任务栏之外)" + screen.availHeight); </script> </body> </html>

当前电脑分辨率为1366x768
screen其他属性及方法可参阅: w3school screen对象参考手册
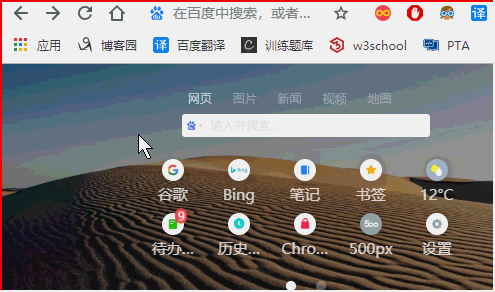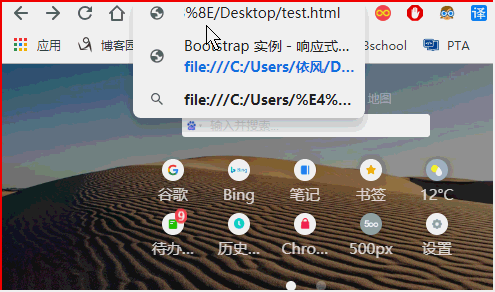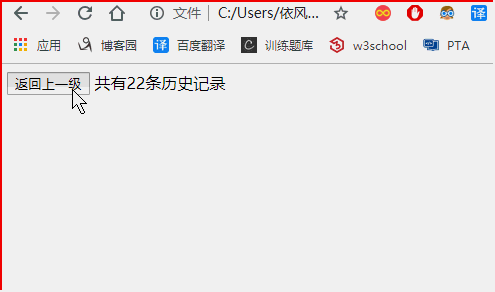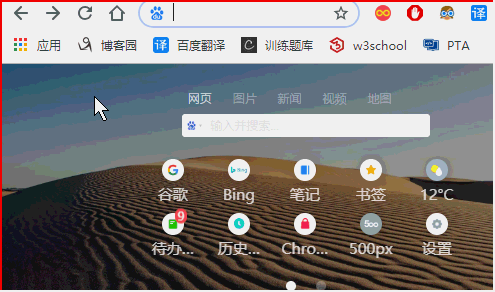
五、history对象
history代表浏览器的历史记录,可以进行回退等操作。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <button onclick = "history.back()">返回上一级</button> <script> document.write("共有" + history.length +"条历史记录") </script> </body> </html>
六、消息框
6.1警告框
window.alert(content);//window可省略。
content可为对象或字符串或数字,各个类型之间用‘+’连接。
支持转义字符,例如‘\n’代表换行。
警告框需点击确认后方可继续。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <script> var i = 3; window.alert("12" + '\n'+ i);//等价alert("12" + '\n' + i); </script> </body> </html>

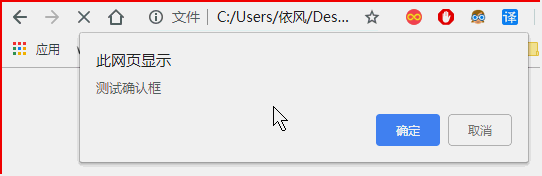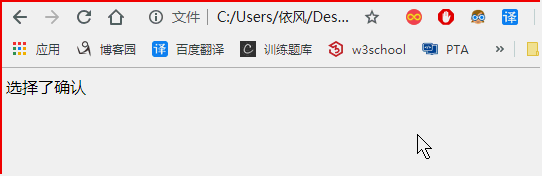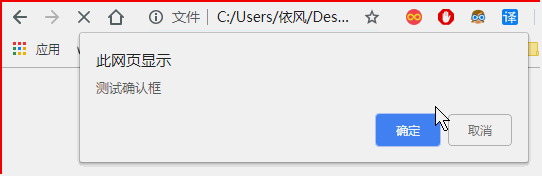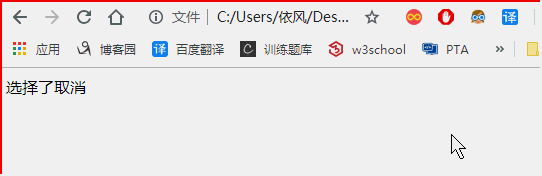
6.2确认框
确认框需等待用户点击确认或取消后方可继续。
点击确认返回true,点击取消返回false。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <script> var i = 3; var flag = window.confirm("测试确认框"); if(flag){ document.write("选择了确认"); }else{ document.write("选择了取消"); } </script> </body> </html>
6.3 提示框
提示框提供一个输入框,需点击确认或取消后方可继续。
如果点击确认返回的值为输入内容,如果点击取消返回null.
window.prompt("提示信息",默认值),默认值可不指定,不指定为空白。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> </head> <body > <script> var i = 3; var info = window.prompt("测试确认框", i);//window可省略 if(info == null){ document.write("没有输入"); }else{ document.write("输入了:" + info); } </script> </body> </html>

七、JavaScript计时
当需要在某一个固定时间后执行某一段代码或某个函数,可以采用JavaScript提供的计时函数。
window.setTimeout("执行的代码或函数名",多长时间后执行(单位毫秒ms)) 1000ms = 1s (秒)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script> function redirect(){ //获取<p>标签中的值,并将其-1,如果为0则跳转页面 if((document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML-=1) == 0){ location.href = "http://www.baidu.com"; } setTimeout("redirect()",1000);//每隔一秒调用redirect() window.setTimeout()等价 } </script> </head> <body onload = "redirect()"> <p id = "p1">5</p> </body> </html>

上例中页面加载及执行redirect函数,先将<p>内部的值-1,并判断是否大于0,大于0继续定时函数。
定时函数调用redirect函数(也可以使用循环调用)。知道时间为0跳转页面。
设置了定时函数,有时需要将其取消,可以使用clearTimeout()函数即可。
var a = setTimeout(xxxx); clearTimeout(a);
设置定时函数会返回一个对象,将这个对象作为clearTimeout()函数的参数,当执行clearTimeout时
就会取消执行参数对象所代表的定时函数。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script> var to; function redirect(){ //获取<p>标签中的值,并将其-1,如果为0则跳转页面 if((document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML-=1) == 0){ location.href = "http://www.baidu.com"; } to = window.setTimeout("redirect()",1000);//每隔一秒调用redirect() } function cancel(){ document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML += "停止成功"; window.clearTimeout(to);//停止执行 } </script> </head> <body onload = "redirect()"> <p id = "p1">5</p> <button onclick ="cancel()">停止跳转</button> </body> </html>

参考资料:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号