编译运行附件中的代码,提交运行结果截图
理解代码,特别是相关系统调用的使用。
- testmf.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
int res = mkfifo("/tmp/myfifo", 0777);
if (res == 0) {
printf("FIFO created \n");
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
- consumer.c
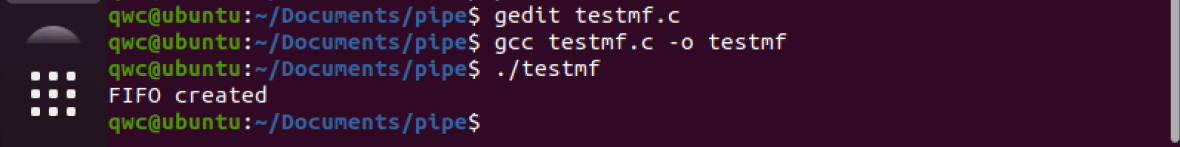
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/myfifo"
#define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF
int main()
{
int pipe_fd;
int res;
int open_mode = O_RDONLY;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];
int bytes = 0;
memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));
printf("Process %d opeining FIFO O_RDONLY \n", getpid());
pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode);
printf("Process %d result %d\n", getpid(), pipe_fd);
if (pipe_fd != -1) {
do {
res = read(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
bytes += res;
} while (res > 0);
close(pipe_fd);
} else {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Process %d finished, %d bytes read\n", getpid(), bytes);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
- producer.c
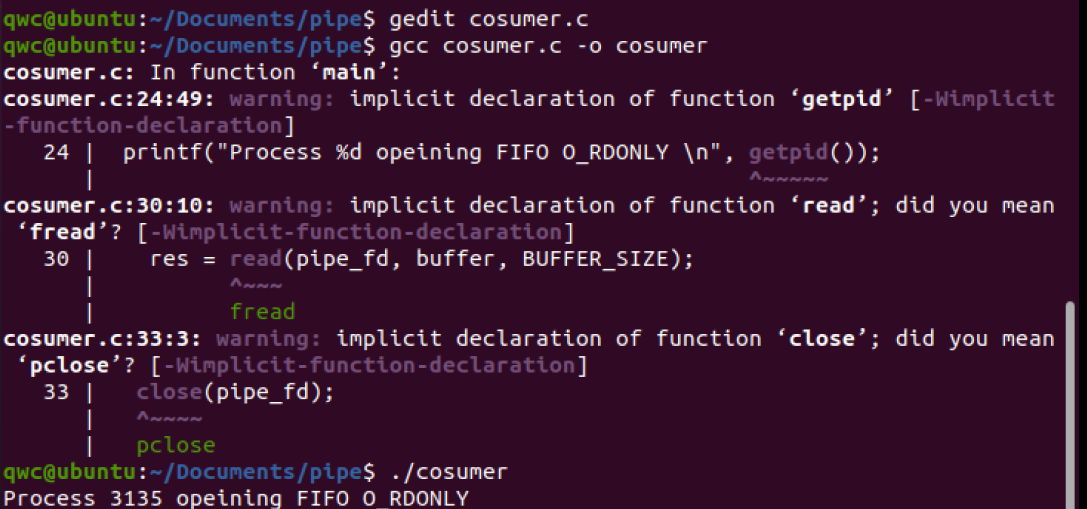
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define FIFO_NAME "/tmp/myfifo"
#define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF
#define TEN_MEG (1024 * 1024 * 10)
int main()
{
int pipe_fd;
int res;
int open_mode = O_WRONLY;
int bytes = 0;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1];
if (access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) == -1) {
res = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, 0777);
if (res != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Could not create fifo %s \n",
FIFO_NAME);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
printf("Process %d opening FIFO O_WRONLY\n", getpid());
pipe_fd = open(FIFO_NAME, open_mode);
printf("Process %d result %d\n", getpid(), pipe_fd);
if (pipe_fd != -1) {
while (bytes < TEN_MEG) {
res = write(pipe_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
if (res == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Write error on pipe\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
bytes += res;
}
close(pipe_fd);
} else {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Process %d finish\n", getpid());
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
- listargs.c
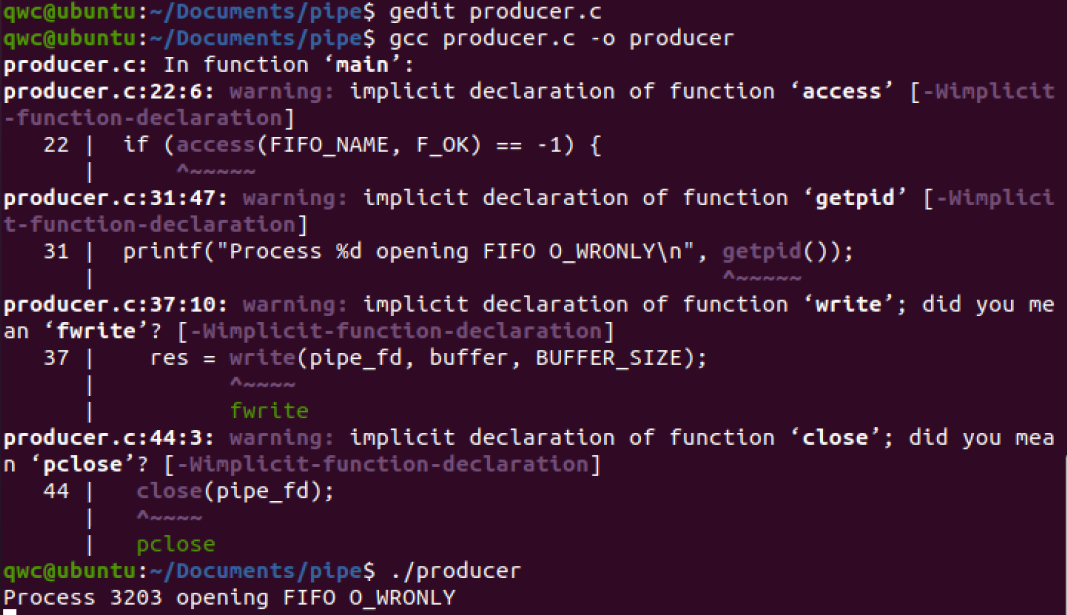
#include<stdio.h>
main( int ac, char *av[] )
{
int i;
printf("Number of args: %d, Args are:\n", ac);
for(i=0;i<ac;i++)
printf("args[%d] %s\n", i, av[i]);
fprintf(stderr,"This message is sent to stderr.\n");
}
- pipe.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define oops(m,x) { perror(m); exit(x); }
int main(int ac, char **av)
{
int thepipe[2],
newfd,
pid;
if ( ac != 3 ){
fprintf(stderr, "usage: pipe cmd1 cmd2\n");
exit(1);
}
if ( pipe( thepipe ) == -1 )
oops("Cannot get a pipe", 1);
if ( (pid = fork()) == -1 )
oops("Cannot fork", 2);
if ( pid > 0 ){
close(thepipe[1]);
if ( dup2(thepipe[0], 0) == -1 )
oops("could not redirect stdin",3);
close(thepipe[0]);
execlp( av[2], av[2], NULL);
oops(av[2], 4);
}
close(thepipe[0]);
if ( dup2(thepipe[1], 1) == -1 )
oops("could not redirect stdout", 4);
close(thepipe[1]);
execlp( av[1], av[1], NULL);
oops(av[1], 5);
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号