数据基本类型---字符串
字符串的定义与创建
字符串是一个有序的字符的集合,用于存储和表示基本的文本信息,' '或'' ''或''' '''中间包含的内容称之为字符串
创建:
>>> s = "Hello, World!!" >>> s 'Hello, World!!'
字符串的特性与常用操作
特性:
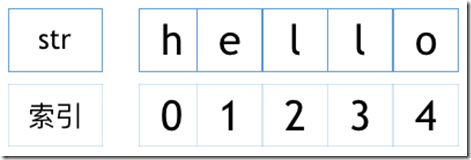
1.按照从左到右的顺序定义字符集合,下标从0开始顺序访问,有序。
2.修改时会开辟一块新的内存空间,内存地址会发生变化,不可变。
补充:
1.字符串的单引号和双引号都无法取消特殊字符的含义,如果想让引号内所有字符均取消特殊意义,在引号前面加r,如name=r'l\thf'
2.unicode字符串与r连用必需在r前面,如name=ur'l\thf'
常用操作:
# 索引 >>> s = "Hello" >>> s[1] 'e' >>> s[-1] 'o' >>> s[-2] 'l' >>> s3 = "hello, world!" >>> s3.strip() 'hello, world!' # 长度 >>> s = "hello,world!" >>> len(s) 12 # 切片 >>> s = '0123456789' >>> s[0:7] '0123456' >>> s[7:9] '78' >>> s[:7] '0123456' >>> s[7:] '789' >>> s[:] '0123456789' >>> s[0:7:2] '0246' >>> s[0:7:3] '036' >>> s[::2] '02468' >>> s[::-1] '9876543210' >>> s[-1:] '9' >>> s[-5:] '56789' >>> s[-5::-1] '543210' >>>
操作函数:
# 首字母大写,其它小写 >>> s = 'hello World!' >>> s.capitalize() 'Hello world!' # 大写字母变小写,小写字母变大写 >>> s = "lFiAaBu" >>> s.swapcase() 'LfIaAbU' # 所有写字母转换成大写 >>> s = 'hello World!' >>> s.upper() 'HELLO WORLD!' # 所有大写字母转换成小写 >>> s = "HEllo World!" >>> s.lower() 'hello world!' # 居中并插入填充 >>> s = 'Hello world!' >>> s.center(50,'*') '*******************Hello world!*******************' >>> s.center(50) ' Hello world! ' # 统计字符个数 >>> s = 'hello world!' >>> s.count('o') 2 >>> s.count('o', 0 , 5) # 规定统计为哪部分中的字符,数字为索引值 1 >>> # 判断用什么开头和结尾 >>> s = 'hello world!' >>> s.endswith('!') True >>> s.endswith('o') False >>> s.startswith('h') True >>> s.startswith('o') False # 扩展tab键,改变tab键的长度,tab键默认为4 >>> s2 = 'a\tb' >>> s2 'a\tb' >>> print(s2) a b >>> s2.expandtabs() 'a b' >>> s2.expandtabs(20) 'a b' # 查找 >>> s = 'hello world!' >>> s.find('o') # 返回的值为字符串的索引 4 >>> s.find('o', 0, 5) # 可以规定查找范围 4 >>> s.find('o', 0, 3) -1 >>> s.rfind('o') # 从左边开始查找 7 # 字符串格式化,同%s格式化类似 >>> s3 = 'my name is {0}, i am {1} years old' >>> s3 'my name is {0}, i am {1} years old' >>> s3.format('houxingbin',18) 'my name is houxingbin, i am 18 years old' >>> >>> s3 = 'my name is {name}, i am {age} years old' >>> s3.format(name = 'houxingbin', age = 18) 'my name is houxingbin, i am 18 years old' >>> # 返回索引 s = 'hello world!' >>> s.index('o') 4 >>> s.index('o', 5, 6) # 如果没有会返回异常信息 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> ValueError: substring not found >>> s.index('o', 5) 7 # 是否是一个整数 >>> ' s'.isdecimal() False >>> '22'.isdecimal() True >>> '22.2'.isdecimal() False >>> >>> '22.2'.isdigit() False >>> '22'.isdigit() True >>> '22s'.isdigit() False # 是否是一个合法的变量名 >>> '333ab'.isidentifier() False >>> 'ab'.isidentifier() True >>> '_ab'.isidentifier() True # 是否都是小写 >>> '12afdsafl'.islower() True >>> '12afdsaADfl'.islower() False >>> # 是否只有数字 >>> '12afdsaADfl'.isnumeric() False >>> '12'.isnumeric() True # 是否可以被打印 >>> '1234'.isprintable() True >>> '123asdf4'.isprintable() True # 是否空格 >>> '123asdf4'.isspace() False >>> '123asdf4 '.isspace() False >>> ' '.isspace() True >>> # 是否第一个字符都是大写 >>> s = 'hello world!' >>> s.istitle() False >>> s = 'Hello World!' # 开头和空格后第一个字符是否大写 >>> s.istitle() True >>> s = 'Hello world!' >>> s.istitle() False # 是否都是大写 >>> 'hello'.isupper() False >>> 'Hello'.isupper() False >>> 'HELLO'.isupper() True # 增加长度 >>> s.ljust(50) 'Hello world! ' >>> s.ljust(50,'-') 'Hello world!--------------------------------------' >>> # 脱掉空格 'hello world ' >>> s = '\n hello world ' >>> s '\n hello world ' >>> s.strip() 'hello world' >>> s.lstrip() 'hello world ' >>> s.rstrip() '\n hello world' # 解密加密,密码表 >>> str_in = 'asdffs' >>> str_out = '#$%Fdfdfs' >>> str_out = '#$%Fdf' >>> str.maketrans(str_in, str_out) {97: 35, 115: 102, 100: 37, 102: 100} >>> table = str.maketrans(str_in, str_out) # 生成密码表 >>> table {97: 35, 115: 102, 100: 37, 102: 100} >>> s = 'hello world!' >>> s.translate(table) # 通过密码表进行加密 'hello worl%!' >>> s1 = s.translate(table) >>> s.translate(s1) # 通过密码表进行解密 'hello world!' # 替换 >>> s = 'hello world' >>> s.replace('o','H') 'hellH wHrld' >>> s.replace('o','H', 1) # 规定替换几次 'hellH world' # 分割 >>> s.split() ['hello', 'world'] >>> s.rsplit('o') ['hell', ' w', 'rld'] >>> s.rsplit('o',1) # 从右边开始分割,只分割一次 ['hello w', 'rld'] >>> s = 'a\nb\nc\nsfs' >>> s.splitlines() # 根据换行符分割 ['a', 'b', 'c', 'sfs'] # 常用 isdigit replace find count strip center split format


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号