函数题1-10 编程题 1-10
1 判断
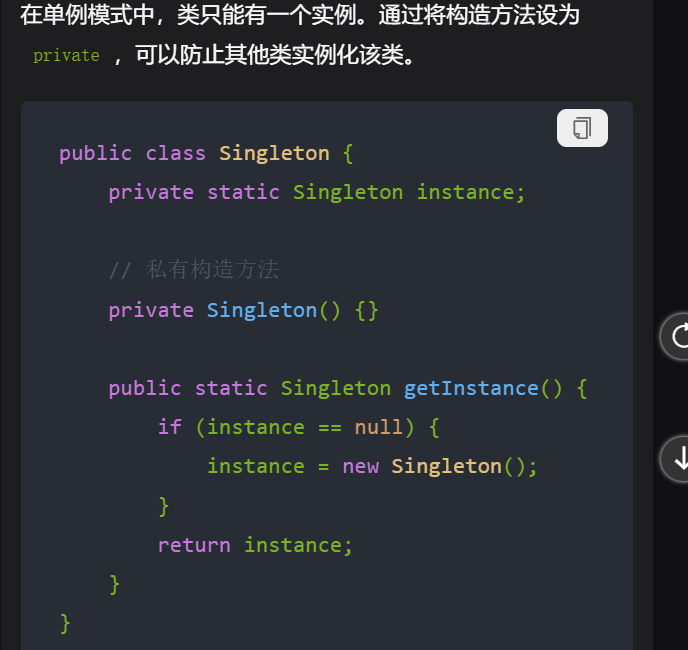
1,用static修饰的变量是类变量。
2,如果使用import语句引入了整个包中的类,那么可能会增加编译时间。但绝对不会影响程序运行的性能,因为当程序执行时,
只是将真正使用的类的字节码文件加载到内存。
3,
4,不允许使用final来修饰abstract方法。
abstract 方法:被声明为 abstract 的方法没有具体实现,子类必须提供实现。这是 abstract 的基本特性。
final 方法:被声明为 final 的方法无法被子类重写。这与 abstract 方法的意图相悖,因为 abstract 方法的目的是为了在子类中实现。
5,对于abstract类,不能创建该类的对象。

6,类:成员变量,方法,内部类。
7,类及其属性、方法可以同时使用多个修饰符。例如:
类:可以同时使用 public 和 abstract 修饰符,表示该类是公共的且是抽象类。
属性:可以同时使用 private 和 final,表示该属性是私有的且不能被修改。
方法:可以同时使用 public 和 static,表示该方法是公共的且属于类本身而不是实例。
8,一个类的静态方法不可以访问该类的非静态成员变量。
在静态方法中,不能直接调用非静态方法和非静态成员变量。静态方法属于类本身,而非静态方法和成员变量属于类的实例。
9,修饰符protected主要是允许其他包中的子类来访问父类的特定属性
10,类允许嵌套定义,方法不允许。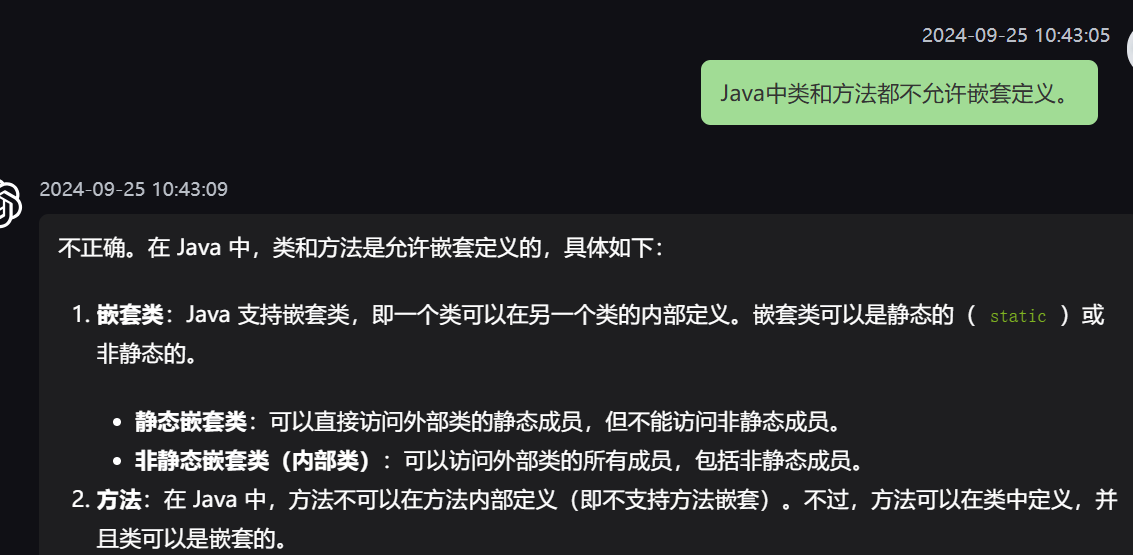
11,构造函数(方法)名应与类名相同,构造方法没有返回类型,包括 void
12,构造方法是可以被重载的。重载构造方法意味着在同一个类中可以定义多个构造方法,它们具有不同的参数列表(参数类型、数量或顺序不同)。
13,对象是具体的,类是抽象的。
14,在方法中使用不定长度参数时,声明的不定长参数必须在参数的最后一个。
public void exampleMethod(int fixedParam, String... varArgs) {
// 方法体
}
15,
局部变量是定义在方法或块内的变量,其作用范围仅限于该方法或块,方法结束后即被销毁。而成员变量是定义在类中的变量,属于对象或类,可以在类的所有方法中访问,生命周期与对象相同。
16,Java 会自动提供一个无参构造方法,但前提是类中没有定义任何构造方法。如果你定义了一个或多个构造方法(如你提供的代码),则 Java 不会自动生成无参构造方法。
17,枚举本身不支持添加或删除常量的功能,因为它们的实例在编译时就固定了。
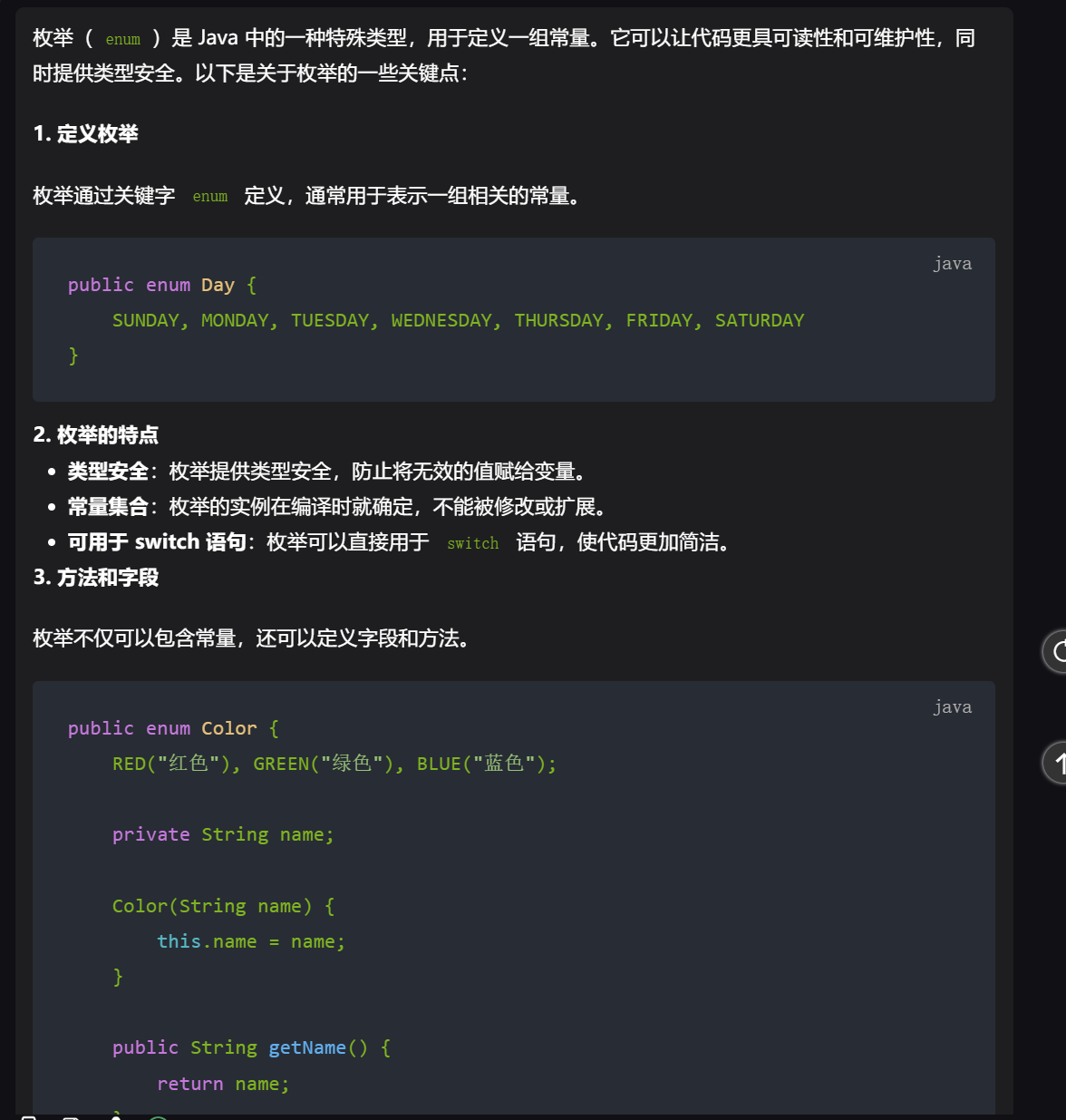
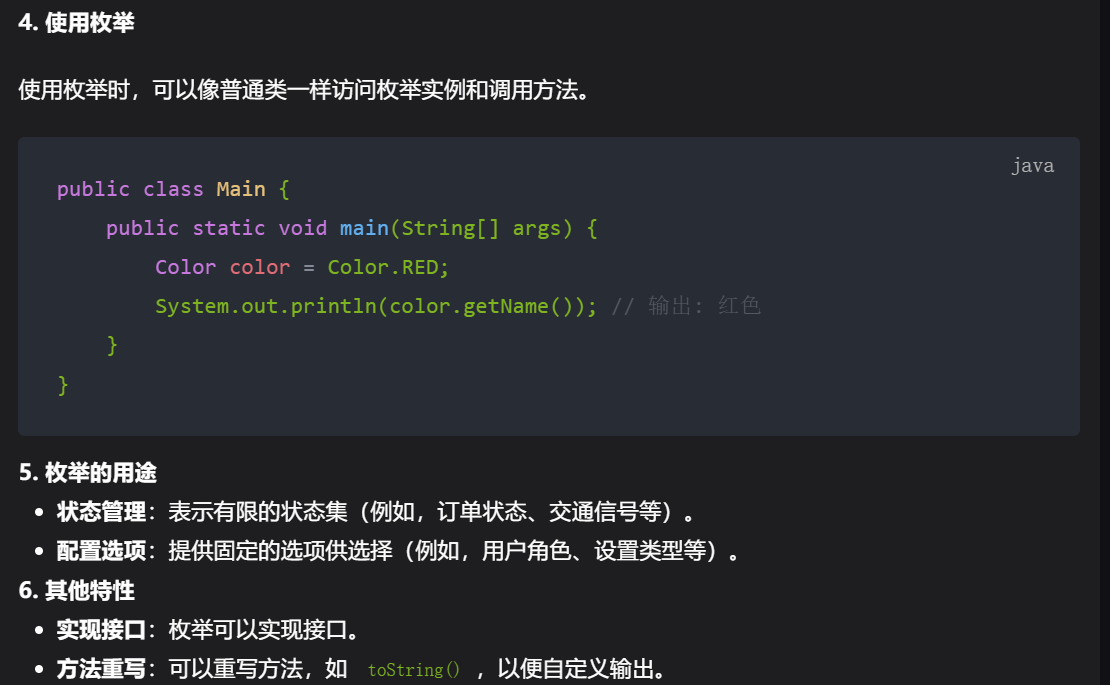
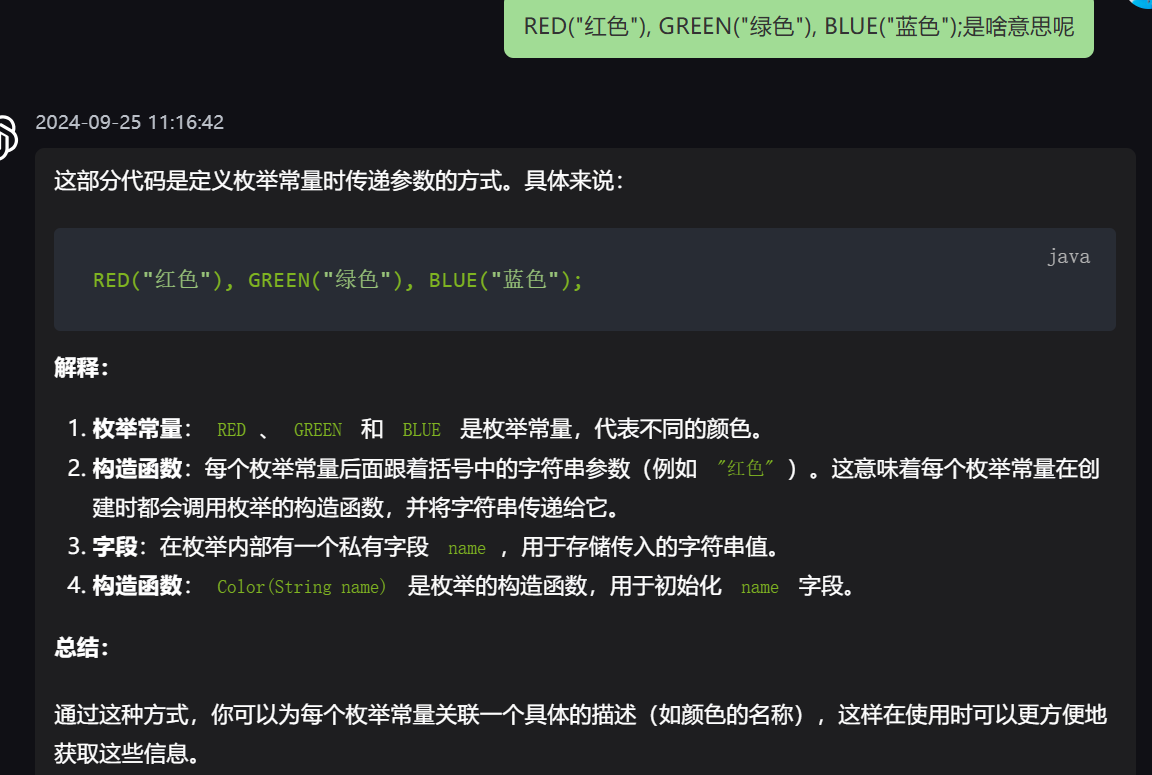
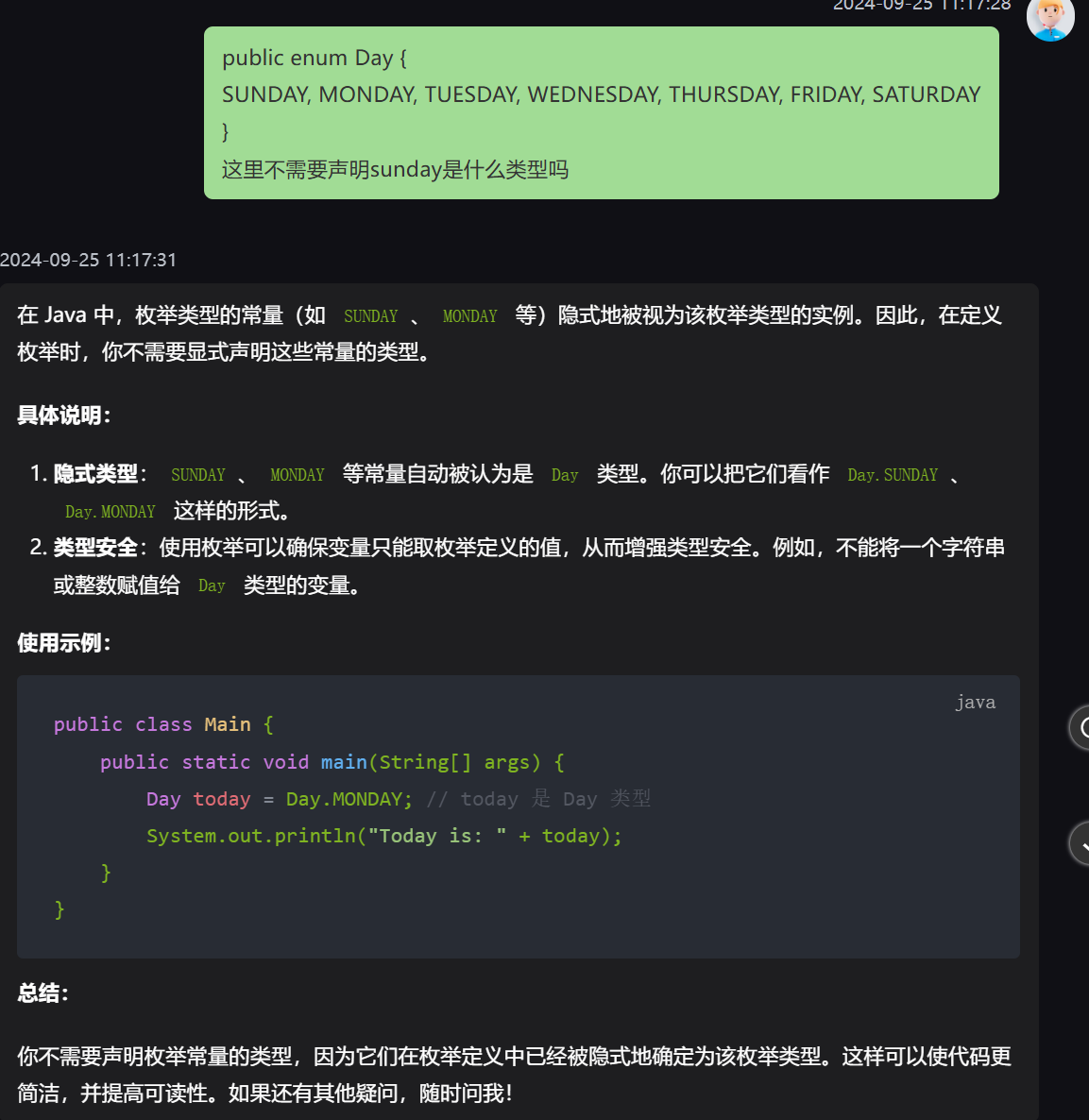
18,default 不能修饰类,但可以用在接口中的方法声明
default package包中的类即位于默认包中的类只能被同一默认包中的类访问,不能被其他任何包中的类访问
19,在JDK提供的系统类库中,使用java.lang包中的类时,可以直接使用,不必使用import来进行导入。
String、System 和 Math 都是来自 java.lang 包的类,因此不需要使用 import 语句。
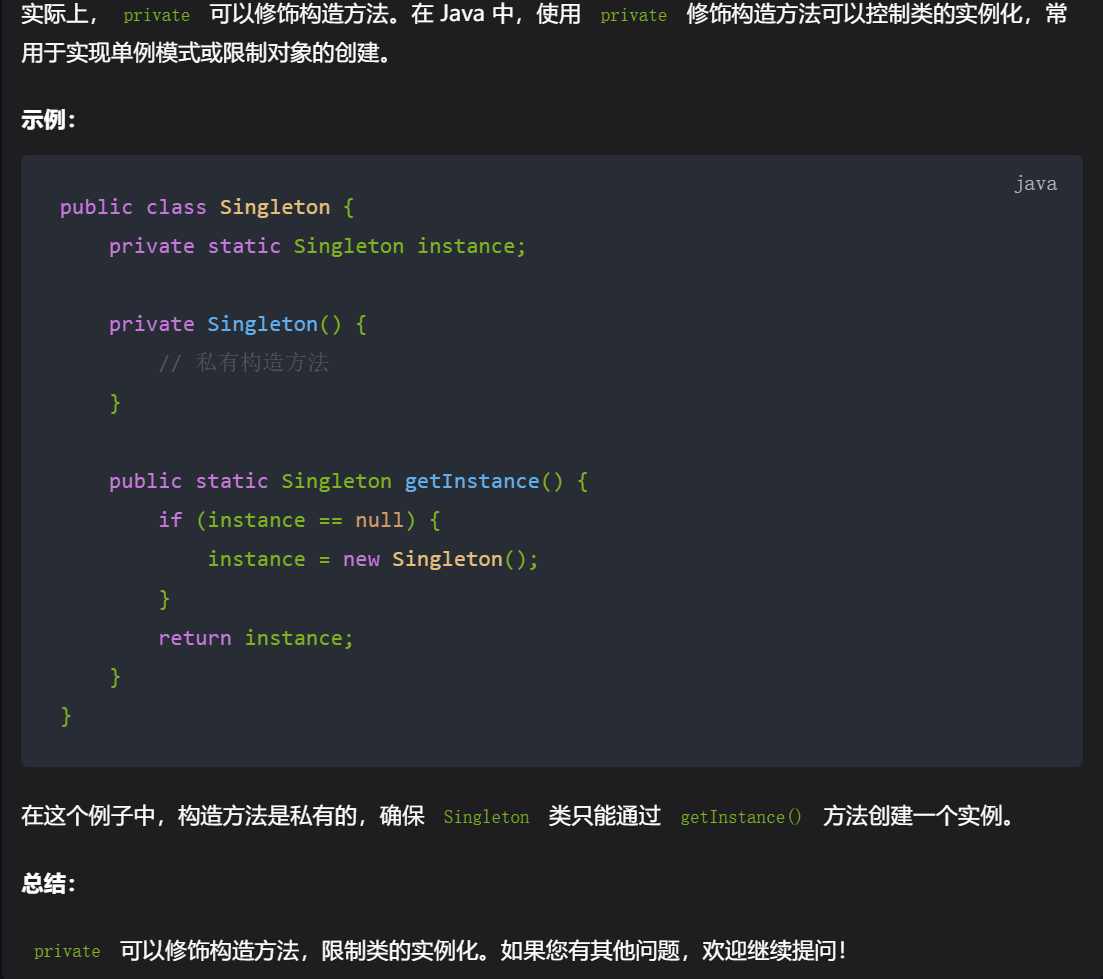
20,使用private修饰构造方法,然后定义一个公共方法来访问。
21,
用final关键字修饰的成员变量和局部变量是常量,常量的赋值次数只有一次。
2 单选
1,
class HasStatic {
private static int x = 100;
/*被标记为 private 的变量只能在定义它的类中访问,外部类或者子类无法直接访问这个变量.即使创建了多个 HasStatic 类的对象,所有对象都会指向同一个 x 变量。*/
2,
字符原理

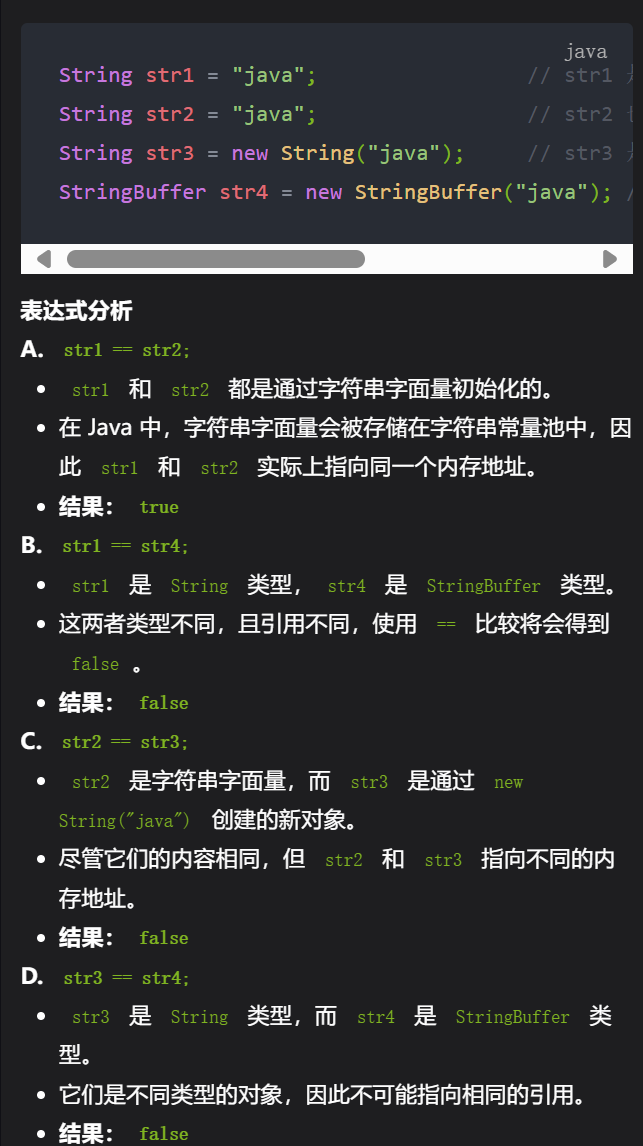
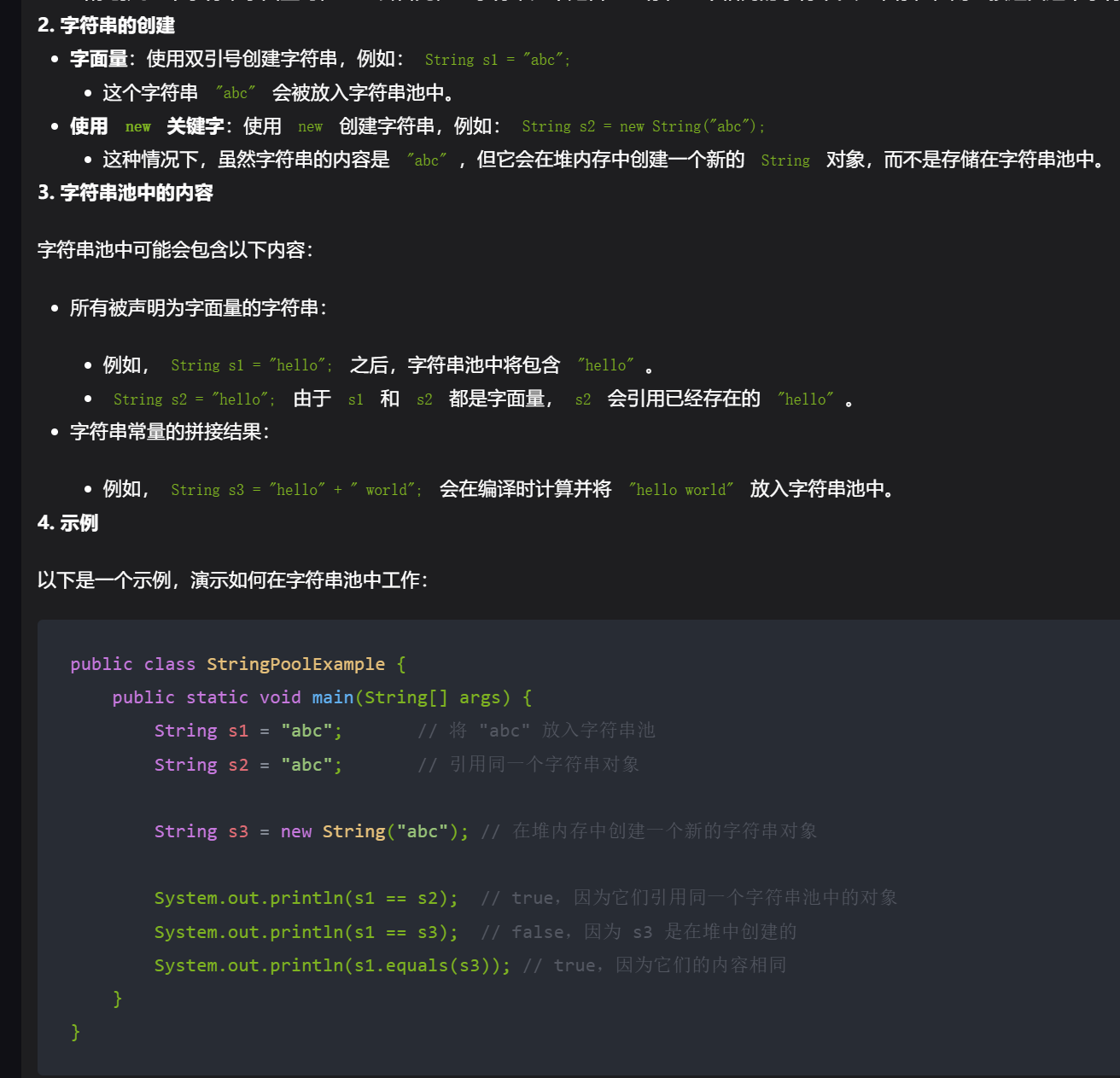
3,内存
Java的内存管理和垃圾回收是自动的,程序员不需要手动创建线程来释放内存。Java虚拟机(JVM)会自动处理内存的分配和回收。
垃圾回收器的主要职责就是自动释放不再使用的对象所占用的内存。它会定期扫描堆中的对象,回收那些不再被引用的对象的内存。
在Java中,程序员不能直接释放内存。Java的垃圾回收机制是自动的,程序员不能使用像C/C++中的free()函数来手动释放内存。
Java的垃圾回收是非确定性的,不能保证在指定的时间点进行内存回收。虽然可以建议JVM进行垃圾回收(通过System.gc()),但这只是一个请求,不能保证立即执行。
4,在一个源文件中,只能有一个公共类,且该类的名称必须与文件名相匹配
所以两个public class 是错的
5,重写vs重载
重写方法有访问权限要求,而重载没有


6,如果只写void,则方法的访问权限默认为包级私有(default),即该方法只能被同一包中的类访问
7,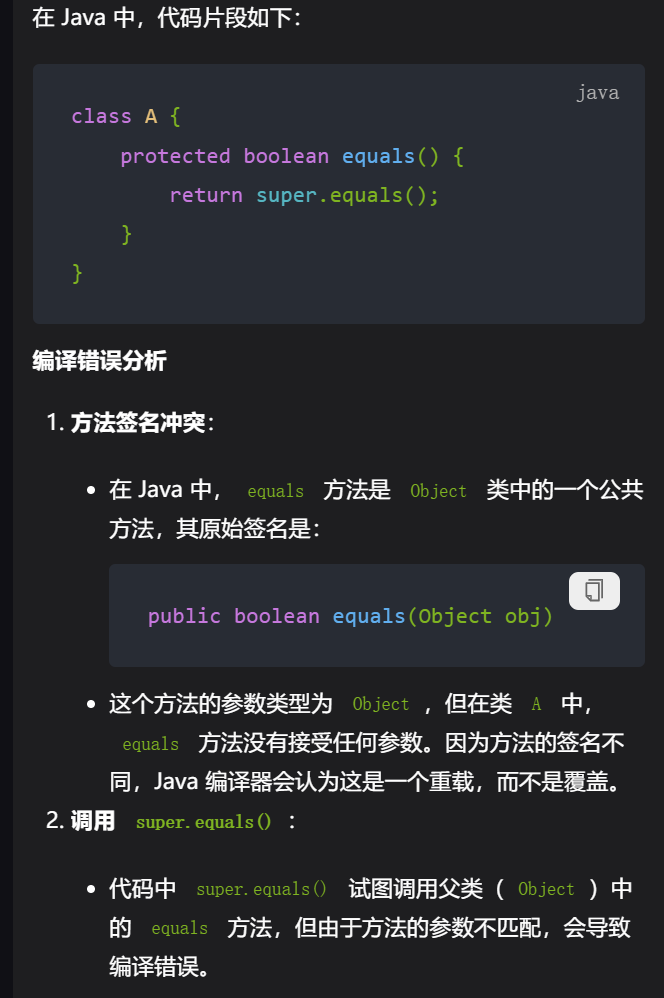
8,
9,只更改返回类型不能算作重载
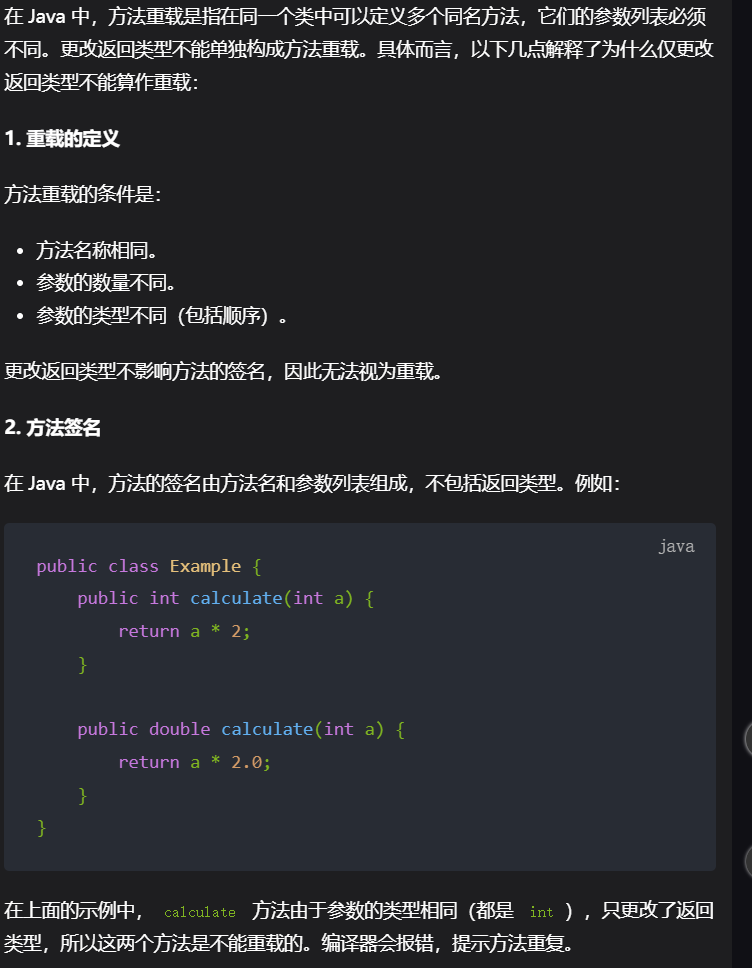
10,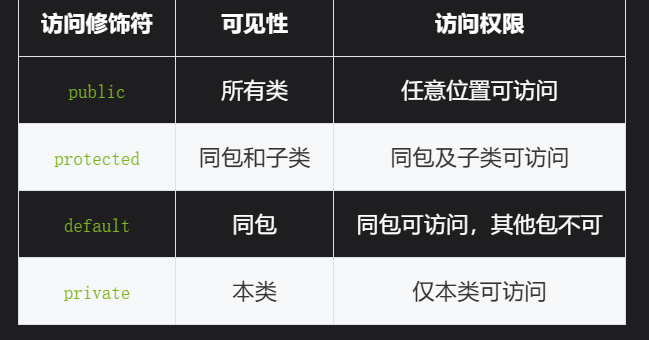
11,同一个抽象类中可以声明多个具有不同参数的抽象方法(即方法重载),非抽象方法必须有实现。
12,
public class Line {
public Point getPoint() {
return new Point() {
// 内部类代码
};
}
}
/*
new Point() { ... } 是一个匿名内部类的实例创建。这种方式定义了一个继承自 Point 类的匿名内部类。在 Java 中,匿名内部类是在创建类的同时定义的,没有显式的类名。
*/
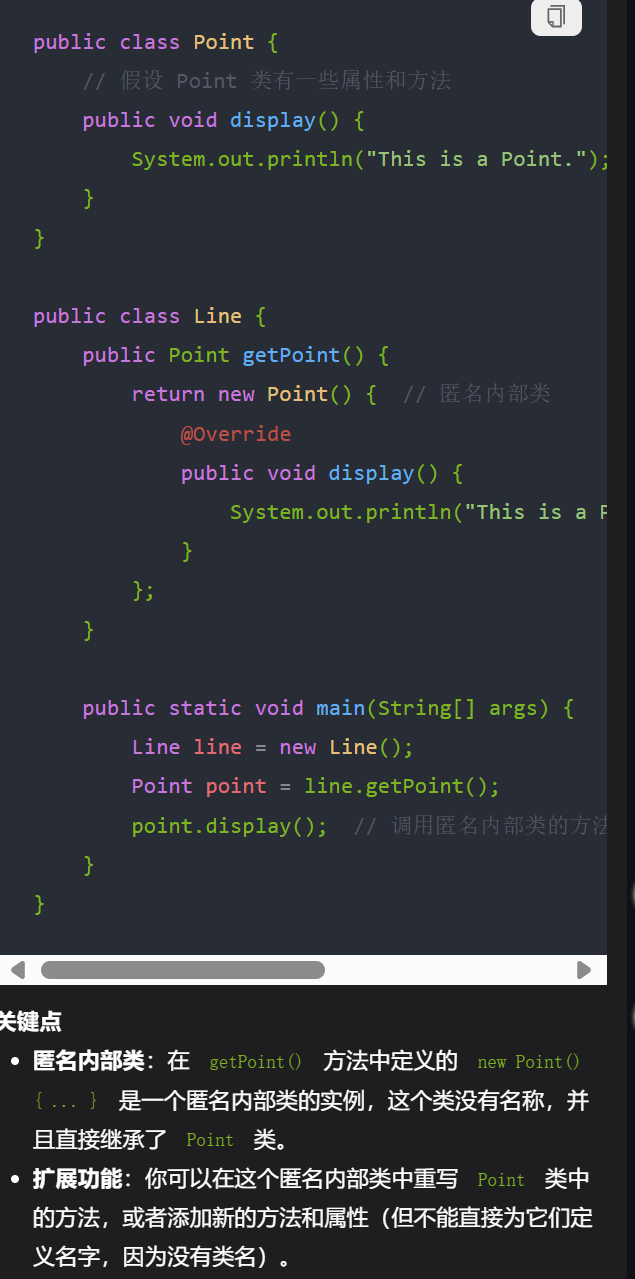
13,
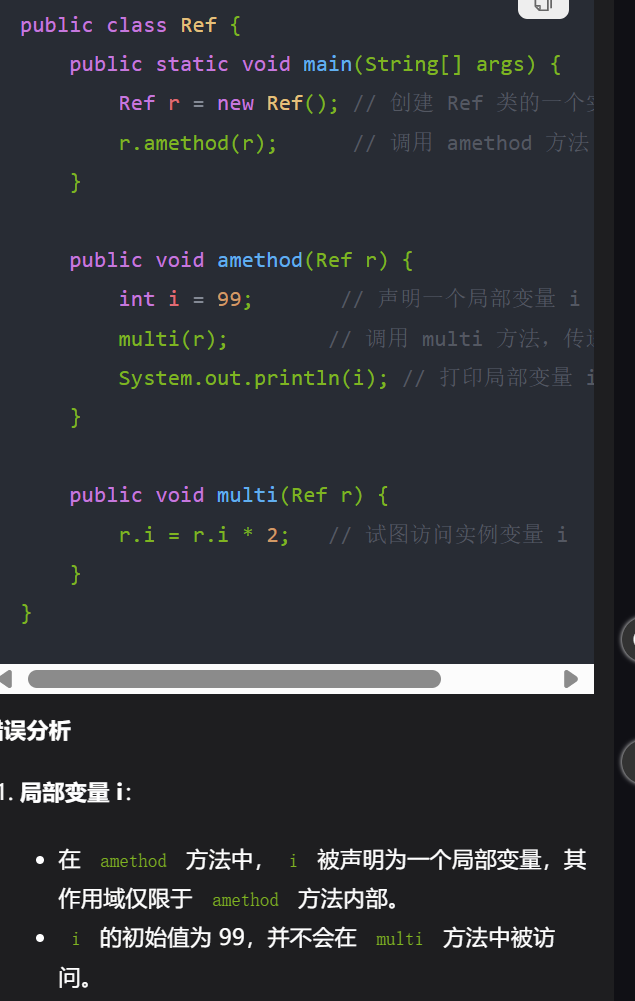
14,局部变量在使用之前必须被初始化(赋值,仅在所定义的代码块内(花括号对内)有效,局部变量可以与类中的成员变量同名,但在这种情况下,局部变量会隐藏成员变量。也就是说,如果局部变量和成员变量同名,局部变量将优先被访问。
成员变量如果未赋值,会有默认值(如 0、0.0、false 或 null),但局部变量如果未赋值则无法直接使用,编译器会提示错误。
15,

16,抽象类里可以有私有成员

17, 静态代码块的执行规则:
顺序:如果一个类中有多个静态代码块,它们会按照代码中出现的顺序依次执行。
一次性:每个静态块只在类被加载时执行一次,后续的对象实例化不会再次执行静态块。
18,构造方法不需要指定返回值类型,不能写 void。
19,
20,substring()返回指定字符串的一部分。
21,
22,字符串不可变性: 在 Java 中,String 是不可变的。这意味着对字符串对象的任何操作(如 substring 或 concat)不会改变原始字符串,而是返回一个新的字符串对象。
23,Math.random() 生成的是一个介于 0.0 和 1.0 之间的随机小数。
24,
对浮点数进行四舍五入

25,一个空类是合法的,Java的类分为两大部分:系统定义的类和用户自定义的类
26,
Java能够具有自动垃圾回收机制,在回收没有变量引用(指向)的对象时,会调用该类的( )方法进行处理。
finalize()
27,在 Java 中,局部变量(如 a)必须在使用前初始化。如果在声明后不初始化就尝试打印其值,编译器会报错,提示“可能尚未初始化”。
局部的int也不会自动初始化为0
28,
3 多选题
1,
final 修饰的方法可以被重载,但不能被重写(override),final 关键字可以修饰类、方法和变量,但不能修饰接口和抽象类。接口本身不能被 final 修饰,因为接口是为了被实现的。
2,
//包的引入方法
import cn.sdut.A;
import cn.sdut.B;
import cn.sdut.cs.C;
import cn.sdut.cs.D;
import cn.sdut.*;
import cn.sdut.cs.*;
3,.
成员变量定义位置无关紧要,其作用域是所有的成员方法
4,

默认访问权限的成员只能在同一包内访问,子类如果不在同一包内则无法访问。
5,
final 修饰的类不能被继承。,用 final 修饰的成员变量在初始化后不能再被赋值。用 final 修饰的方法不能被重写,但可以被重载。用 final 修饰的局部变量在初始化后不能再被赋值。
6,在 Java 中,this 关键字用于调用同一个类中的其他构造器。这种调用必须是在构造器的第一行进行的,并且可以用于重载构造器的调用。
4 填空
1,在 Java 中,this 关键字用于调用同一个类中的其他构造器。这种调用必须是在构造器的第一行进行的,并且可以用于重载构造器的调用。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test test = new Test(true);
}
}
class Test {
public Test(){
System.out.println("Constructor one invoked!");
}
public Test(int x){
this();
(2分)
System.out.println("Constructor two invoked!");
}
public Test(boolean b){
this(0);
}
}
System.out.println("Constructor three invoked!");
5 函数题
1)类的实现
##1
class Test{
public int sum(double...values)
//接受若干个,最后一个为valus
{
int result=0;
for(double i:values)
{
result+=i;
}
return result;
}
}
##2
class Point {
int x;
int y;
//1,声明
public Point(int x, int y) {
//2,有参构造器
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int dist(Point p) {
int tmp = (x - p.x) * (x - p.x) + (y - p.y) * (y - p.y);
return tmp;
//执行 Point 类中的 dist 方法。
//这种方式允许 p1 对象访问自己的属性并计算与 p2 之间的距离。
}
}
##3 函数返回值的格式化
double area=this.width*this.height;
return String.format("%.2f", area);
//返回字符串和数值混合
return "("+x+","+y+")";
##4Math数学库
Math.sqrt,Math.PI,Math.sqrt
int n = Math.max(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b));
(最大公约数要看绝对值)
##5返回一个类(多个属性需要返回)
class Matrix {
int n; // 属性
int[][] matrix = new int[n][n]; // 属性-矩阵
public Matrix(int row, int[][] matrix) { // 构造方法
this.n = row;
this.matrix = matrix;
}
public Matrix add(Matrix other) { // 矩阵相加
int[][] result = new int[n][n];
//不能直接先建立一个类,因为第二个属性还未知
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
result[i][j] = this.matrix[i][j] + other.matrix[i][j];
}
}
return new Matrix(n, result); //新建一个矩阵对象返回
}
##6方法重写
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.width + " by " + this.height;
}
##7 无参构造器,有参构造器
int balance;
static int accountNumber=0;
BankAccount(){
accountNumber++;
balance=0;
}
BankAccount(int balance){
accountNumber++;
this.balance=balance;
}
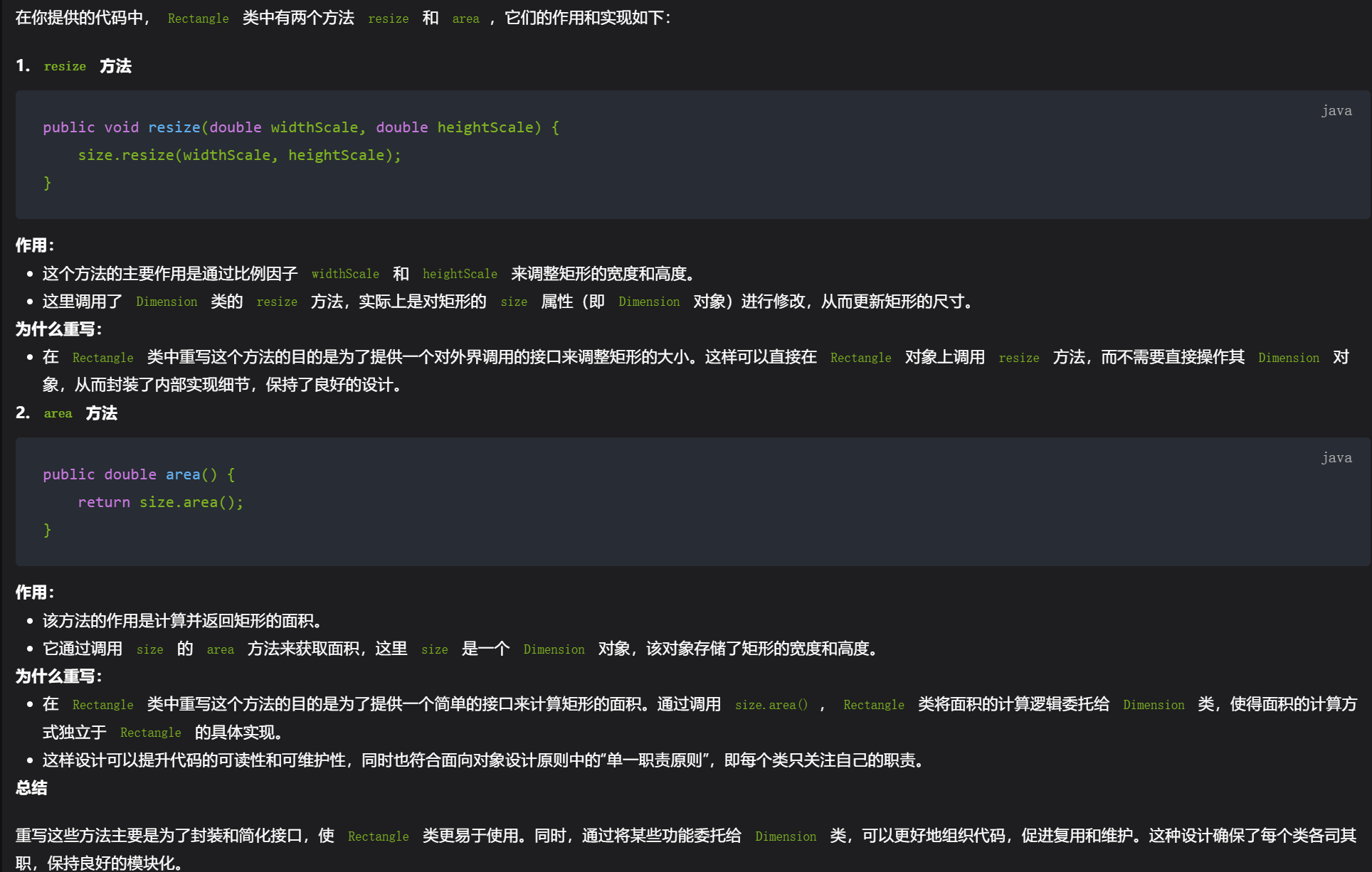
//第十题
/**
* 2D平面中带的点,有x和y坐标,如:(x,y)。
*/
class Point {
int x;
int y;
/**
* C创建一个坐标为(x,y)的点
* @param x x坐标
* @param y y坐标
*/
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/*
* 生成的字符串为:(x,y)
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "("+x+","+y+")";
}
/**
* 用dx和dy移动点。
* @param dx 在x轴上移动的距离
* @param dy 在y轴上移动的距离
*/
public void move(int dx, int dy) {
this.x += dx;
this.y += dy;
}
/**
* @param p 另外一个点
* @return 计算这个点和p点之间的距离。
*/
public double distance(Point p) {
return Math.sqrt((this.x - p.x) * (this.x - p.x) + (this.y - p.y) * (this.y - p.y));
}
}
/**
* 二维尺寸,有宽度和高度。
*/
class Dimension {
int width;
int height;
/**
* 创建具有指定宽度和高度的Dimension。
* @param width——Dimension的宽度
* @param height——Dimension的高度
*/
public Dimension(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
/*
* 生成的字符串为:"width by height"
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.width + " by " + this.height;
}
/**
* R按宽度和高度的比例调整尺寸。
* 虽然标度是双精度的,但结果应该是整数。
* @param widthScale 宽度比例尺
* @param heightScale 高度比例尺
*/
public void resize(double widthScale, double heightScale) {
this.width *= widthScale;
this.height *= heightScale;
}
/**
* @return 计算这个Dimension的面积.
*/
public int area() {
return width*height;
}
}
/**
* 表示一个矩形,在其左上角有一个点Point和一个维度Dimension.
*
*/
class Rectangle {
Point topleft;
Dimension size;
/**
* 创建一个矩形。
* @param topleft 左上角的坐标
* @param size 它的尺寸
*/
public Rectangle(Point topleft, Dimension size) {
this.topleft = topleft;
this.size = size;
}
/*
* 生成的字符串如下: "Rectangle at (x,y):width by height"
*/
public String toString() {
return "Rectangle at (" + topleft.x + "," + topleft.y + "):" + size.width + " by " + size.height;
}
/**
* 将矩形移动一段距离。
* @param dx 在x轴上移动的距离
* @param dy 在y轴上移动的距离
*/
public void move(int dx, int dy) {
topleft.move(dx, dy);
}
/**
* 调整矩形的宽度和高度
* @param widthScale 宽度比例尺
* @param heightScale 高度比例尺
*/
public void resize(double widthScale, double heightScale) {
size.resize(widthScale, heightScale);
}
/**
* @return 这个矩形的面积。
*/
public double area() {
return size.area();
}
/**
* 计算矩形左上角顶点与矩形r左上角点之间的距离。
* @param r 另一个矩形
* @return 这个矩形和r之间的距离。
*/
public double distance(Rectangle r) {
return this.topleft.distance(r.topleft);
}
}
2)接口
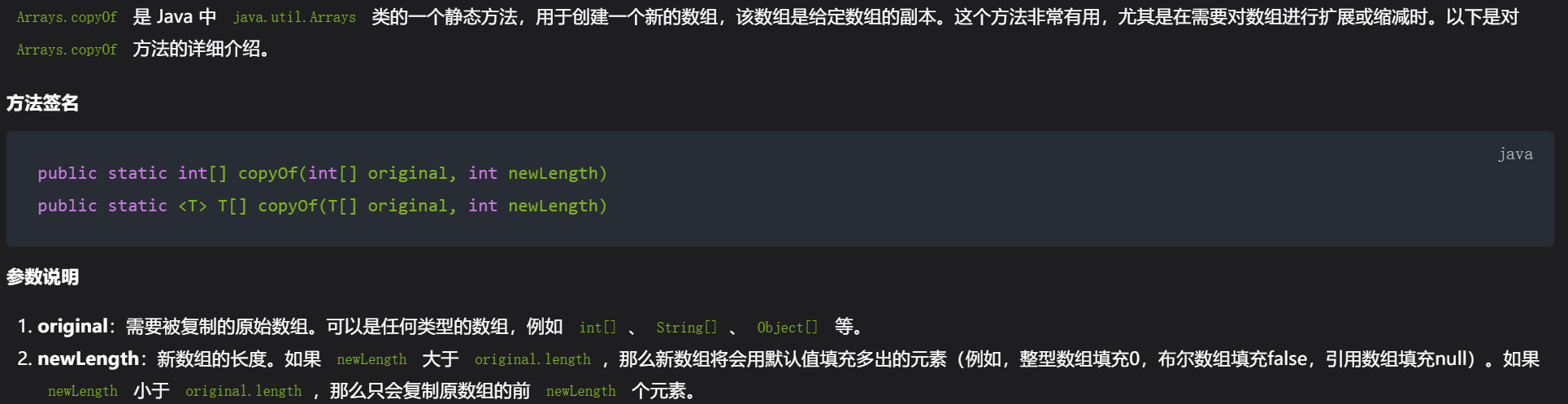
//数组复制
###1
interface IShape {
public abstract double getArea();
public abstract double getPerimeter();
}
//抽象的方法,必须在子类重写。
class RTriangle implements IShape{
private double a;
private double b;
RTriangle(double a, double b){
super();//还有一个super
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return this.a * this.b / 2.0;
}
@Override
public double getPerimeter() {
return this.a + this.b + Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b);
}
}
### 2 数组格式化输出
Arrays.toString(scores)
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scores = {85, 90, 78, 92};
// 使用 Arrays.toString 输出数组内容
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(scores));
// 输出: [85, 90, 78, 92]
}
}
### 2 深克隆
class Car implements Cloneable
{
private String name;
private CarDriver driver;
private int[] scores;
public Car() {
}
// @Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [name=" + name + ", driver=" + driver + ", scores=" + Arrays.toString(scores) + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public CarDriver getDriver() {
return driver;
}
public void setDriver(CarDriver driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public int[] getScores() {
return scores;
}
public void setScores(int[] scores) {
this.scores = scores;
}
@Override
protected Car clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Car car = new Car();
CarDriver D = new CarDriver();
if(driver==null)
D=null;
else
D.setName(driver.getName());
car.setDriver(D);
String Nm;
if(name==null)
Nm=null;
else
Nm=name;
car.setName(Nm);
if(scores==null)
car.setScores(null);
else
{
int c[] = Arrays.copyOf(scores, scores.length);
//数组复制函数
car.setScores(c);
}
return car;
}
}
6 编程题
1,
import java.util.Scanner;
class Point
{
int x, y;
public Point()
{
super();//调用了父类的无参数构造方法
}
public Point(int x, int y)
{
super();//调用了父类的无参数构造方法
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Point move(int x1, int y1)
{
x += x1;
y += y1;
return new Point(x, y);
//多个值需要通过类或数组返回
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "("+x+","+y+")";
/*MyClass obj = new MyClass(10);
System.out.println(obj.toString());默认的tostring返回地址*/
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(System.in);
while(cin.hasNext())
{
Point p = new Point(cin.nextInt(), cin.nextInt());
//可以直接这样输入赋值合并
int n = cin.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
p.move(cin.nextInt(), cin.nextInt());
}
System.out.println(p);
}
}
}
2,
/*创建和实例化不是一回事,创建数组后并没有实例化 Person 对象,
因此当尝试调用 setName 和 setAge 方法时会引发 NullPointerException*/
创建的同时实例化man[i] = new Man(a, b);
//错误
Person[] p = new Person[3];
p[0].setName ("zhangsan") ;
p[0].setAge (18);
//正确
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个大小为 3 的 Person 数组
Person[] p = new Person[3];
// 实例化每一个 Person 对象
p[0] = new Person("zhangsan", 18);
p[1] = new Person("lisi", 20);
p[2] = new Person("wangwu", 22);
// 遍历数组并打印每个人的名字和年龄
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) {
System.out.println(p[i].getName() + " " + p[i].getAge());
}
}
3,函数里返回一个保留两位小数的数
double A=radius*radius*Math.PI;
return (float)((Math.round(A * 100)) / 100.0);
4,根据空格分离字符串
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
while (s.hasNext()) {
String o = s.nextLine();
String [] c=o.split(" ");
//split(" ") 方法将输入字符串按空格分割,生成一个字符串数组 c。
int[] a = new int[c.length];
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = Integer.parseInt(c[i]);
/*Integer.parseInt(String s) 是 Java 的一个静态方法,
用于将字符串 s 转换为 int 类型。*/
}
if(a.length==1)
{
Rect r=new Rect(a[0],a[0]);
if(a[0]<0) System.out.println("0 0 0 0");
else System.out.println(r.getLength()+" "+r.getWidth()+" "+r.c()+" "+r.area());
}
else if(a.length==2){
Rect r=new Rect(a[0],a[1]);
if(a[0]<=0||a[1]<=0) System.out.println("0 0 0 0");
else System.out.println(r.getLength()+" "+r.getWidth()+" "+r.c()+" "+r.area());
}
else System.out.println("0 0 0 0");
}
}
}
5,最大公约数
public int gys(int a,int b){
//求最大公约数
int m=Math.max(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b));
int n=Math.min(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b));
//注意谁大谁小
int r;
while(n!=0){
r=m%n;
m=n;
n=r;
}
return m;
}
6,字符串转字符数组
//1
String str = sc.next();
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
//只读取到空格之前
//分数四则运算
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t -- != 0){
String str=sc.next();
char[] ch=str.toCharArray();
int g=0;//分割加减乘除号;
int f=0;//1代表加号,2代表减号,3代表乘,4代表除号
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++){
if(ch[i]=='+'){
g=i;
f=1;
break;
}
else if(ch[i]=='-'){
g=i;
f=2;
break;
}
else if(ch[i]=='*'){
g=i;
f=3;
break;
}
/*
'\\' 这是一个单独的反斜杠字符
'\'' 这是一个单独的单引号字符
转义字符第一个反斜杠用来转义第二个反斜杠
*/
else if(ch[i]=='\\'){
g=i;
f=4;
break;
}
}
String s1=str.substring(0, g);// 第一个分数
String s2=str.substring(g+1,str.length());
String p[]=s1.split("\\/");// 将第一个分数按 '/' 分割
String q[]=s2.split("\\/");
int a=Integer.parseInt(p[0]); // 第一个分数的分子
int b=Integer.parseInt(p[1]); // 第一个分数的分母
int c=Integer.parseInt(q[0]);
int d=Integer.parseInt(q[1]);
Fs fs1=new Fs(a,b);
Fs fs2=new Fs(c,d);
Fs result=new Fs();//构建Fs类的对象result,为空;对应下面的public Fs(){}
if(f==1){
result=fs1.add(fs2);
}
else if(f==2){
result=fs1.sub(fs2);
}
else if(f==3){
result=fs1.multiply(fs2);
}
else if(f==4){
result=fs1.divide(fs2);
}
if((result.fz%result.fm)==0){
System.out.println(result.fz/result.fm);
}
//根据是否是整数判断要不要输出分号,防止输出1/1;
else{
System.out.println(result.fz+"/"+result.fm);
}
}
sc.close();
}
}
class Fs{
int fz;
int fm;
public Fs(int fz,int fm){
this.fz=fz;
this.fm=fm;
}
public Fs(){}
public Fs add(Fs fs){
//加法运算
int newFz=fz*fs.fm+fm*fs.fz;
int newFm=fm*fs.fm;
int gys=gys(newFz,newFm);
return new Fs(newFz/gys,newFm/gys);
}
public Fs sub(Fs fs){
//减法运算
int newFz=fz*fs.fm-fm*fs.fz;
int newFm=fm*fs.fm;
int gys=gys(newFz,newFm);
return new Fs(newFz/gys,newFm/gys);
}
public Fs multiply(Fs fs){
//乘法运算
int newFz=fz*fs.fz;
int newFm=fm*fs.fm;
int gys=gys(newFz,newFm);
return new Fs(newFz/gys,newFm/gys);
}
public Fs divide(Fs fs){
//除法运算
int newFz=fz*fs.fm;
int newFm=fm*fs.fz;
int gys=gys(newFz,newFm);
return new Fs(newFz/gys,newFm/gys);
}
public int gys(int a,int b){
//求最大公约数
int m=Math.max(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b));
int n=Math.min(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b));
//注意谁大谁小
int r;
while(n!=0){
r=m%n;
m=n;
n=r;
}
return m;
}
}
//2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
//这道题只涉及加减
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while( in.hasNext() ){
String str = in.next();
char[]s = str.toCharArray();
//字符串转字符数组
int fk = 0;
int fh = 0;
int i;
for( i=0; i<str.length(); i++ ){
if( s[i]=='+' ){
fk = i;
fh = 1;
break;
}
else if( s[i]=='-' ){
fk = i;
fh = 2;
break;
}
}
String s1 = str.substring(0, fk);
String s2 = str.substring(fk+1, str.length());
String []p = s1.split("\\/"); //分离分子分母
String []q = s2.split("\\/");
/*
在正则表达式中,许多字符具有特殊的含义,
比如 .、*、+、?、^、$、{、[、( 等。
因此,如果要匹配这些字符本身,就需要使用反斜杠 \ 进行转义。
反斜杠 \ 也是一个特殊字符,用于转义。
为了在 Java 字符串中表示一个反斜杠,你需要使用两个反斜杠 \\
*/
int a = Integer.parseInt(p[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(p[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(q[0]);
int d = Integer.parseInt(q[1]);
//字符串转数字
Fs fs1 = new Fs(a, b);
Fs fs2 = new Fs(c, d);
Fs result = new Fs();
if( fh==1 )
result = fs1.add(fs2);
if( fh==2 )
result = fs1.sub(fs2);
if( (result.fz%result.fm) == 0 )
System.out.println(result.fz/result.fm);
else
System.out.println(result.fz+"/"+result.fm);
}
in.close();
}
}
class Fs {
int fz;
int fm;
public Fs( int fz, int fm ){
this.fz = fz;
this.fm = fm;
}
public Fs(){}
public Fs add( Fs fs ){
int newFz = fz*fs.fm + fm*fs.fz;
int newFm = fm*fs.fm;
int gys = gys(newFz,newFm);
return new Fs(newFz/gys, newFm/gys);
}
public Fs sub( Fs fs ){
int newFz = fz*fs.fm - fm*fs.fz;
int newFm = fm*fs.fm;
int gys = gys(newFz,newFm);
return new Fs(newFz/gys, newFm/gys);
}
public int gys( int a, int b ){
int m = Math.max(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b));
int n = Math.min(Math.abs(a), Math.abs(b));
int r;
while( n!=0 ){
r = m%n;
m = n;
n = r;
}
return m;
}
}
7,调用方法时,
//1),
public void showTime(Time time)
{
System.out.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n", time.h, time.m, time.s);
}
time.showTime(time);
//比较奇怪的是得写两遍time
//2),
public void showTime()
{
System.out.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n", this.h, this.m, this.s);
}
time.showTime();
//不传入就不需要两次
2)自己敲的
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (sc.hasNext()) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
int f1 = 0;
int f2 = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
if (c[i] == '-') {
f1 = i;
f2 = 2;
break;
}
if (c[i] == '+') {
f1 = i;
f2 = 1;
break;
}
}
String s1 = s.substring(0, i);
String s2 = s.substring(i + 1, s.length());
//注意这里用的是取子串需要对字符串进行操作,而不是字符数组c
String[] p = s1.split("/");
String[] q = s2.split("/");
int a = Integer.parseInt(p[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(p[1]);
int c1 = Integer.parseInt(q[0]);
int d = Integer.parseInt(q[1]);
fs fss = new fs(a, b);
fs fss2 = new fs(c1, d);
fs ans=new fs();
if(f2==1)
ans=fss.add(fss2);
if(f2==2)
ans=fss.mins(fss2);
if(ans.fz%ans.fm==0)
System.out.println(ans.fz/ans.fm);
else
System.out.println(ans.fz+"/"+ans.fm);
}
}
}
class fs {
int fz;
int fm;
public fs(int fz,int fm)
{
this.fz=fz;
this.fm=fm;
}
public fs(){};
public fs add(fs fs1)
{
int newfz=fz*fs1.fm+fm*fs1.fz;
int newfm = fm *fs1.fm;
int gcd=gcd(newfm,newfz);
//System.out.println(newfm+" "+newfz+" "+gcd);
return new fs(newfz/gcd,newfm/gcd);
}
public fs mins(fs fs1)
{
int newfz=fz*fs1.fm-fm*fs1.fz;
int newfm = fm *fs1.fm;
int gcd=gcd(newfz,newfm);
return new fs(newfz/gcd,newfm/gcd);
}
public int gcd(int a,int b)
{
a=Math.abs(a);
b=Math.abs(b);
int maxn=Math.max(a,b);
int minn=Math.min(a,b);
while(minn!=0)
{
int t=maxn%minn;
maxn=minn;
minn=t;
}
return maxn;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号