Java I/O小结及文件操作实例
Java I/O
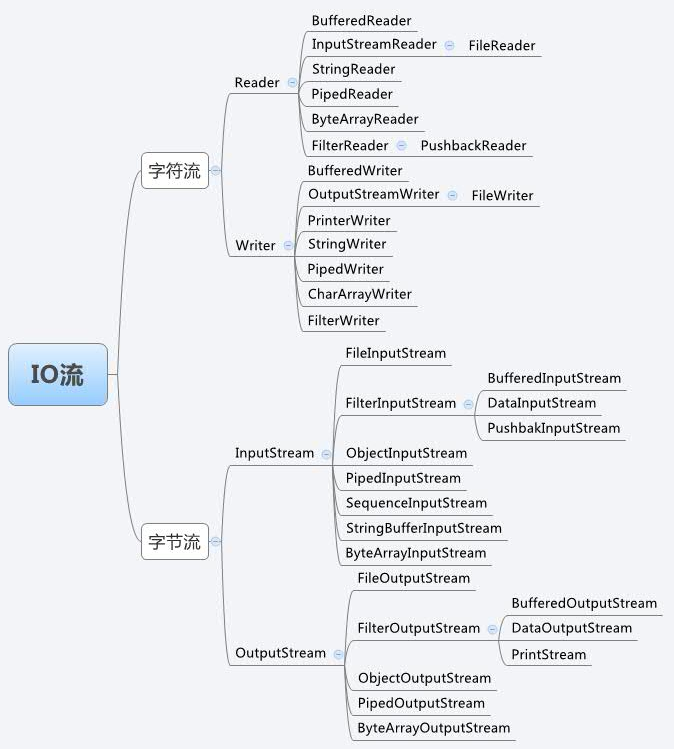
Java中有哪几种流?
按流向区分:输入流InputStream和输出流OutputStream
按处理数据单位区分:字符流和字节流,字节流继承自InputStream和OutputStream,字符流继承自InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
按功能类型区分:节点流(可以从一个特定的节点读写数据,如FileReader)和处理流(对一个已存在的流进行封装,对流进行读写,如BufferedReader)。FileReader不能一行行读,BufferedReader可以一行行地读
字符流与字节流的转换
InputStreamReader(InputStream in);
OutPutStreamWriter(OutPutSteam out);
字符流和字节流的区别
字节流在操作的时候本身是不会用到缓冲区(内存)的,是与文件本身直接操作的,而字符流在操作的时候是使用到缓冲区的
字节流在操作文件时,即使不关闭资源(close方法),文件也能输出,但是如果字符流不使用close()方法的话,则不会输出任何内容,说明字符流用的是缓冲区,并且可以使用flush()方法强制进行刷新缓冲区,这时才能在不close的情况下输出内容。一般情况我们会先调用flush()方法,再调用close()方法关闭流。
缓冲区:一段特殊的内存,用来临时存放读取的数据,因为如果频繁操作文件,性能会变低,为了提升性能,把数据先读入缓冲区中,后面的操作就变快了。
字节流和字符流的使用:
字节流是最基本的,我们平常处理文件例如图片、音频、视频,都是用字节流来完成文件的上传和下载,但是有时候需要处理文本文件,例如txt,就绪要用到字符流,需要用到InputStreamReader,OutputStreamWrite进行流之间的转化,实际上是通过byte[]和String来关联。总而言之,字符流只能处理文本文件,字节流能够处理所有文件。
序列化和反序列化
序列化就是处理对象流的一种机制,将对象转化成对象流,然后对流进行读写操作,也可以把流在网络上进行传输,序列化对象的类必须实现Serializable接口。
反序列化就是将对象流转化成对象。
实例
import cn.hutool.core.date.DateUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.io.IoUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.lang.UUID;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* <P><B>Description: </B> TODO 添加描述 </P>
* Revision Trail: (Date/Author/Description)
* 2021/05/07 Larry Wang CREATE
*
* @author Larry Wang
* @version 1.0
*/
public class FileTest {
//文件实际磁盘路径
private final String attachmentPath = "D:/attachment/";
/*
* 上传文件
*/
public String uploadFile(MultipartFile file, String type) {
String fileId = UUID.randomUUID().toString(true);
BufferedInputStream in = null;
//MultipartFile 转 File
File desFile = null;
try {
desFile = multipartFileToFile(file);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String fileName = desFile.getName();
//生成相对路径
String relativePath = DateUtil.format(new Date(), "yyyyMMdd/") + fileName;
//文件实际存放路径
String filePath = attachmentPath + relativePath;
in = FileUtil.getInputStream(desFile);
BufferedOutputStream out = FileUtil.getOutputStream(filePath);
IoUtil.copy(in, out, IoUtil.DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
IoUtil.close(out);
IoUtil.close(in);
//删除本地临时文件
deleteTempFile(desFile);
return relativePath;
}
/*
下载文件
*/
public void downloadFile(HttpServletResponse response) {
String relativePath = "文件url";
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(relativePath)) {
String path = attachmentPath + relativePath;
try {
// path是指欲下载的文件的路径。
File file = new File(path);
// 取得文件名。
String filename = file.getName();
// 取得文件的后缀名。
String ext = filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf(".") + 1).toUpperCase();
// 以流的形式下载文件。
InputStream fis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(path));
byte[] buffer = new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(buffer);
fis.close();
// 清空response
response.reset();
// 设置response的Header
response.addHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=" + new String(filename.getBytes()));
response.addHeader("Content-Length", "" + file.length());
OutputStream toClient = new BufferedOutputStream(response.getOutputStream());
response.setContentType("application/octet-stream");
response.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");
response.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
response.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Methods", "GET, POST, DELETE, PUT");
response.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "*");
toClient.write(buffer);
toClient.flush();
toClient.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/*
* 预览文件
*/
public void viewFile(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String relativePath = "文件url";
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(relativePath)) {
String filePath = attachmentPath + relativePath;
File fileLoad = new File(filePath);
try {
showFile(request, response, fileLoad);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//multipartFile转File
public static File multipartFileToFile(MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
File toFile = null;
InputStream ins = null;
ins = file.getInputStream();
toFile = new File(file.getOriginalFilename());
inputStreamToFile(ins, toFile);
ins.close();
return toFile;
}
//获取流文件
private static void inputStreamToFile(InputStream ins, File file) {
try {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
int bytesRead = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[8192];
while ((bytesRead = ins.read(buffer, 0, 8192)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
os.close();
ins.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 删除本地临时文件
* @param file
*/
public static void deleteTempFile(File file) {
if (file != null) {
File del = new File(file.toURI());
del.delete();
}
}
//预览文件
public static void showFile(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, File fileLoad)
throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
String filename = fileLoad.getName();
String suffix = filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf(".") + 1);
String contentType;
//根据文件后缀设置contentType
if ("avi".equalsIgnoreCase(suffix)) {
contentType = "video/avi";
} else if ("wmv".equalsIgnoreCase(suffix)) {
contentType = "video/x-ms-wmv";
} else if ("mp4".equalsIgnoreCase(suffix)) {
contentType = "video/mp4";
} else if ("pdf".equalsIgnoreCase(suffix)) {
contentType = "application/pdf";
} else if ("html".equalsIgnoreCase(suffix)) {
contentType = "text/html";
} else {
contentType = "image/jpeg";
}
response.setContentType(contentType);
response.setContentLengthLong(fileLoad.length());
String range = request.getHeader("Range");
int start = 0;
long end;
if (StrUtil.isBlank(range)) {
response.setHeader("Accept-Ranges", "bytes");
} else {
response.setStatus(206);
if (range.endsWith("-")) {
start = Integer.parseInt(range.substring(6, range.length() - 1));
end = fileLoad.length() - 1;
} else {
String[] split = range.substring(6).split("-");
start = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
end = Integer.parseInt(split[1]);
}
range = "bytes " + start + "-" + end + "/" + fileLoad.length();
response.setHeader("Content-Range", range);
response.setContentLengthLong(end - start + 1);
}
fis = new FileInputStream(fileLoad);
if (start != 0) {
fis.skip(start);
}
os = response.getOutputStream();
int count;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1 * 1024];
while ((count = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, count);
}
os.flush();
} finally {
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
}
}
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号