实现Vehicle类的不同版本理解封装
实现Vehicle类的不同版本理解封装
版本一
没有数据隐藏的类

创建一个Vehicle 类实现上面的 UML 类图。
- 含有两个
public属性:
| 属性 | 解释 |
|---|---|
load |
车辆当前载货量 |
maxLoad |
车辆最大载货量 |
-
含有一个公有的构造函数用于初始化最大载货量属性
maxLoamaxLoad。 -
含有两个公有的函数:
| 权限 | 数据类型 | 方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
public |
double |
getLoad() |
用于得到当前的载货量 |
public |
double |
getMaxLoad() |
用于取得最大载货量 |
(注意:所有的数据都是假定以千克(kilograms)作为单位的。
在这个版本的Vehicle类中,你将把所有成员的属性设置为 public,这样在下面测试程序 TestVehicle1 中可以直接访问这些成员。
Vehicle实现类:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
class Vehicle {
public:
double load;
double maxLoad;
Vehicle(double max_load) : maxLoad(max_load), load(0.0) {}
double getLoad() const { return load; }
double getMaxLoad() const { return maxLoad; }
};
int main() {
Vehicle vehicle(10000.0);
cout << "Add box #1 (500kg)" << endl;
vehicle.load += 500.0;
cout << "Add box #2 (250)" << endl;
vehicle.load += 250.0;
cout << "Add box #3 (5000)" << endl;
vehicle.load += 5000.0;
cout << "Add box #4 (4000)" << endl;
vehicle.load += 4000.0;
cout << "Add box #5 (300)" << endl;
vehicle.load += 300.0;
cout << "Vehicle load is " << fixed << setprecision(1) << vehicle.getLoad() << " kg" << endl;
return 0;
}
总结与反思
从程序的运行结果来看,你发现了什么问题?思考如何才能避免?
一遍过的 暂时没有需要注意的. 结果输出需要使用浮点格式 fixed << setprecision(1)
版本二:
基本数据隐藏
为了解决第一个版本中的问题,你应该隐藏类中的数据成员(load 和maxLoad) 并且提供一个方法addBox, 来检查车辆是否会发生超载。

创建一个 Vehicle 类实现上面的UML类图。
-
把
load和maxLoad属性修改为 private(私有的)。 -
添加
addBox方法。public boolean addBox(double weight); //参数为所加箱子重量这个方法必须检查加上一个箱子后是否会超过车辆的最大载货量。如果超过了, 应该拒绝装载这个箱子并返回
false;否则把箱子加到车上并返回true。 注意:所有的数据都是假定以千克(kilograms)作为单位的。
Vehicle实现类:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
class Vehicle {
private:
double load;
double maxLoad;
public:
Vehicle(double max_load) : maxLoad(max_load), load(0.0) {}
double getLoad() const {
return load;
}
double getMaxLoad() const {
return maxLoad;
}
bool addBox(double weight) {
if (load + weight > maxLoad) {
return false;
} else {
load += weight;
return true;
}
}
};
int main() {
Vehicle vehicle(10000.0);
cout << "Add box #1 (500kg)" << vehicle.addBox(500.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (250kg)" << vehicle.addBox(250.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (5000kg)" << vehicle.addBox(5000.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (4000kg)" << vehicle.addBox(4000.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (300kg)" << vehicle.addBox(300.0) << endl;
cout << "Vehicle load is " << fixed << setprecision(1) << vehicle.getLoad() << " kg" << endl;
return 0;
}
版本三
现在假设你将要作一些关于车辆发动机和轮胎等磨损的计算,这些计算使 用牛顿表示的重量。
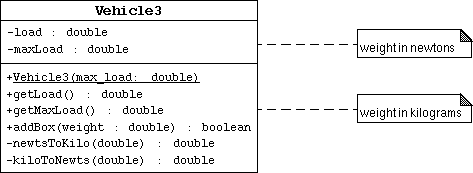
创建一个Vehicle 类实现上面的 UML 类图。
修改构造方法,getLoad(), getMaxLoad(), 和 addBox() 方法,使它们使用一个从千克
到牛顿的相互转换。你可以定义下面的私有方法:
private double kiloToNewts(double weight) { ...... };
private double newtsToKilo(double weight) { ...... };
注意 vehicle 对象的内部数据是以牛顿为单位的,而外部数据(在方法中传递的参数)还是以千克为单位 。
Vehicle类的实现代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Vehicle {
private:
double load;
double maxLoad;
double kiloToNewts(double weight) const {
return weight * 9.81;
}
double newtsToKilo(double weight) const {
return weight / 9.81;
}
public:
Vehicle(double max_load) : maxLoad(max_load), load(0.0) {}
double getLoad() const {
return load;
}
double getMaxLoad() const {
return maxLoad;
}
bool addBox(double weight) {
double weightInNewts = kiloToNewts(weight);
if (load + weightInNewts > maxLoad) {
return false;
} else {
load += weightInNewts;
return true;
}
}
double newtsToKilo(double weight) {
return weight / 9.81;
}
double kiloToNewts(double weight) {
return weight * 9.81;
}
};
int main() {
Vehicle vehicle(10000.0);
cout << "Add box #1 (500kg)" << vehicle.addBox(500.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (250kg)" << vehicle.addBox(250.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (5000kg)" << vehicle.addBox(5000.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (4000kg)" << vehicle.addBox(4000.0) << endl;
cout << "Add box #1 (300kg)" << vehicle.addBox(300.0) << endl;
cout << "Vehicle load is " << fixed << setprecision(1) << vehicle.getLoad() << " kg" << endl;
return 0;
}
程序运行结果:
Add box #1 (500kg)1
Add box #1 (250kg)1
Add box #1 (5000kg)0
Add box #1 (4000kg)0
Add box #1 (300kg)0
Vehicle load is 7357.5 kg
对 Vehicle 类的第二个和第三个版本采用相同的测试代码,输出的结果有没有发生变化?从代码可维护性的角度谈谈封装的好处。
浅谈封装的好处:
-
信息隐藏
封装可以隐藏内部的具体细节, 消费者只需要调用生产者内部接口,消费者不参与服务内部的实现过程。
-
简化接口
封装后可以简化接口类的设计。即使的方法实现多么复杂,外部的接口依旧可以保持简单的接口调用。
-
易拓展性
通过对接口的的抽象定义,可以实现对后期服务的拓展和维护。抽丝剥茧将程序的结构高度保持高内聚、低耦合的特性,方便协同开发。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号