操作系统第四次实验:文件系统
姓名:张越
班级:计算1811
学号:201821121006
1.编写程序
在服务器上用Vim编写一个程序:实现Linux系统命令ls -lai的功能,给出源代码。
关于ls-lai
ls -l #以长格式显示目录下的内容列表。输出的信息从左到右依次包括文件名,文件类型、权限模式、硬连接数、所有者、组、文件大小和文件的最后修改时间等 ls -a #显示所有档案及目录(ls内定将档案名或目录名称为“.”的视为影藏,不会列出) ls -i #显示文件索引节点号(inode number),一个索引节点代表一个文件
.实验源代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<pwd.h>
#include<grp.h>
void error_printf(const char* );
void list_dir(const char* );
void list_message(const char* , const struct stat*);
void file_type(const struct stat* );
void file_power(const struct stat* );
void file_id(const struct stat* );
void file_mtime(const struct stat* );
void link_printf(const char* );
void error_printf(const char* funname)
{
perror(funname);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
/*
* EXIT_SUCCESS和EXIT_FAILURE是两个常量。
* EXIT_SUCCESS=0,EXIT_FAILURE=1。
* 0表示程序寿终正寝,1表示死于非命。
*/
}
void list_dir(const char* pathname)
{
DIR* ret_opendir = opendir(pathname); // 打开目录"pathname"
if(ret_opendir == NULL)
error_printf("opendir");
int ret_chdir = chdir(pathname); // 改变工作目录至"pathname",便于stat函数的使用
if(ret_chdir == -1)
error_printf("chdir");
struct dirent* ret_readdir = NULL; // 定义readdir函数返回的结构体变量
while(ret_readdir = readdir(ret_opendir)) // 判断是否读取到目录尾
{
char* filename = ret_readdir->d_name; // 获取文件名
struct stat file_message = {}; // 定义stat函数返回的结构体变量
int ret_stat = lstat(filename, &file_message); // 获取文件信息
if(ret_stat == -1) // stat读取文件错误则输出提示信息
printf("%s error!", filename);
else if(strcmp(filename,".") && strcmp(filename,"..")) // 不输出当前目录与上一级目录
list_message(filename, &file_message);
}
}
void list_message(const char* filename, const struct stat* file_message)
{
file_type(file_message); // 判断打印文件类型
printf("%d ",(int)file_message->st_ino);//添加索引号
file_power(file_message); // 判断并打印文件权限
printf("%d ", file_message->st_nlink); // 打印硬链接数
file_id(file_message); // 转换并打印用户id与组id
printf("%5ld ", file_message->st_size); // 打印文件大小
file_mtime(file_message); // 打印文件最后修改时间
printf("%s ", filename); // 打印文件名
if(S_ISLNK(file_message->st_mode)) // 如果是软链接文件,打印其指向的位置
link_printf(filename);
puts("");
}
void file_type(const struct stat* file_message)
{
mode_t mode = file_message->st_mode;
if (S_ISREG(mode)) printf("-"); // 普通文件
else if(S_ISDIR(mode)) printf("d"); // 目录文件
else if(S_ISCHR(mode)) printf("c"); // 字符设备文件
else if(S_ISBLK(mode)) printf("b"); // 块设备文件
else if(S_ISFIFO(mode)) printf("p"); // 管道文件
else if(S_ISLNK(mode)) printf("l"); // 链接文件
else printf("s"); // socket文件
}
void file_power(const struct stat* file_message)
{
mode_t mode = file_message->st_mode;
printf("%c", mode&S_IRUSR?'r':'-');
printf("%c", mode&S_IWUSR?'w':'-');
printf("%c", mode&S_IXUSR?'x':'-');
printf("%c", mode&S_IRGRP?'r':'-');
printf("%c", mode&S_IWGRP?'w':'-');
printf("%c", mode&S_IXGRP?'x':'-');
printf("%c", mode&S_IROTH?'r':'-');
printf("%c", mode&S_IWOTH?'w':'-');
printf("%c ", mode&S_IXOTH?'x':'-');
}
void file_id(const struct stat* file_message)
{
struct passwd* pwd;
pwd = getpwuid(file_message->st_uid);
printf("%s ",pwd->pw_name);
struct group* grp;
grp = getgrgid(file_message->st_gid);
printf("%s ",grp->gr_name);
}
void file_mtime(const struct stat* file_message)
{
struct tm* t = localtime(&file_message->st_mtime);
printf("%2d月 %2d %02d:%02d ", t->tm_mon+1, t->tm_mday, t->tm_hour, t->tm_min);
}
void link_printf(const char* filename)
{
char buf[1024] = "123";
if(0 == readlink(filename, buf, sizeof(buf)))
error_printf("readlink");
printf("-> %s ",buf);
}
int main()
{ char path[1024] = {};
strcpy(path,"./");
struct stat file_message = {};
int ret_stat = lstat(path, &file_message);
if(ret_stat == -1)
error_printf("stat");
if(S_ISDIR(file_message.st_mode)) // 判断是否为目录
list_dir(path);
else
list_message(path, &file_message);
return 0;
}
2. 分析运行结果
给出运行结果截图,对于每一列是如何获取的,结合源代码做解释

执行命令 ls -lai以后的运行结果

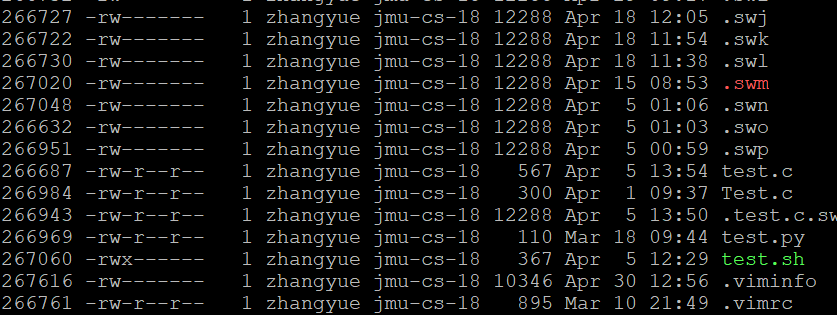
分析:
第一字段:为索引号;
printf("%d ",(int)file_message->st_ino);//用于添加索引号
第二字段:首字母代表文件的类型; “-”开头的是普通文件,代表无对应条件。"p"开头的是管道文件。"rwx"分别代表具有读写执行的权限等等。
void file_type(const struct stat* file_message)
57 {
58 //mode_t mode = (*get_message).st_mode;
59 mode_t mode = file_message->st_mode;
60
61 if (S_ISREG(mode)) printf("-"); // 普通文件
62 else if(S_ISDIR(mode)) printf("d"); // 目录文件
63 else if(S_ISCHR(mode)) printf("c"); // 字符设备文件
64 else if(S_ISBLK(mode)) printf("b"); // 块设备文件
65 else if(S_ISFIFO(mode)) printf("p"); // 管道文件
66 else if(S_ISLNK(mode)) printf("l"); // 链接文件
67 else printf("s"); // socket文件
68 }
第三字段:关于文件硬链接的连接数量
printf("%d ", file_message->st_nlink);
第四字段:文件拥有者
struct passwd* pwd;
pwd = getpwuid(file_message->st_uid);
printf("%s ",pwd->pw_name); //打印出文件拥有的人的名字
第五字段:拥有文件的用户所在的组
struct group* grp;
grp = getgrgid(file_message->st_gid);
printf("%s ",grp->gr_name);
第六字段:以字节为单位的文件大小
printf("%5ld ", file_message->st_size); // 打印文件大小
第七字段:最后修改文件的时间
struct tm* t = localtime(&file_message->st_mtime);
printf("%2d月 %2d %02d:%02d ", t->tm_mon+1, t->tm_mday, t->tm_hour, t->tm_min);
第八字段:文件名字
printf("%s ", filename);
3. 通过该实验产生新的疑问及解答
在linux系统中命令 ls-l 跟ls-lai的区别是什么?
答:第一个不会显示影藏文件,第二个会显示影藏文件,并别影藏文件以点开头的文件。
在运行结果中显示的Total的含义是什么?
答:total的意思是:列表中所有文件的磁盘空间占用总和,也就是资源占用总和,它的统计单位是kb。
实验参考链接 https://www.cnblogs.com/usingnamespace-caoliu/p/9351773.html
https://blog.csdn.net/apollon_krj/article/details/54710135





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号