质因数分解
算法重要的理论基础
1.一个数的最小因数一定是质因数,通俗易懂,如果是合数那还能再质因数分解为更小的质因数。
2.i <= x / i;利用两个数相乘等于一个数,这两个因数一定有一个大一个小,再不济就是两个相等的情况,如果超过了就表示没有因数了。
//质因数分解模板
//y总代码
#include
#define int long long
using namespace std;
inline void divide(int x)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
if (x % i == 0)
{
int s = 0;
while (x % i == 0) x /= i, s ++ ;
cout << i << ' ' << s << endl;
}
if (x > 1) cout << x << ' ' << 1 << endl;
cout << endl;
}
signed main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
divide(x);
}
return 0;
}
这里给出相关例题,n个1——1e9数据相乘得到的数的乘积有多少个约数呢?
算法基础理论
1.任意一个数都能够质因数分解,且分解的素因数序列有且只有一个。
有了这个理论基础,以及之前学习的如何分解质因数。就只需要将所有数的质因数都利用map或者unordered_map记录起来,后面只要算有多少种组合方式就行了,可以确定的是保证每种组合个不相等
//y总代码
以下是代码
#include
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 110, mod = 1e9 + 7;
signed main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map primes;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
primes[i] ++ ;
}
if (x > 1) primes[x] ++ ;
}
int res = 1;
for (auto p : primes) res = res * (p.second + 1) % mod;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
https://www.acwing.com/video/296/
还有一道题目很有营养以我的水平,就是在上一道例题的基础上求的是所有的约数的和。
借用一位我觉得不错的佬的图
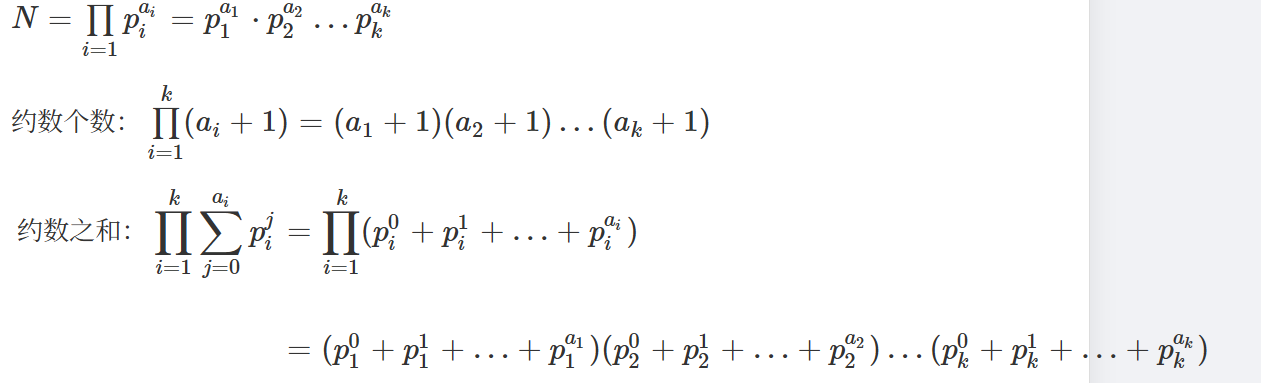
第一个我认为的精髓就是利用分配律把这些括号消除就得到了所有组合的和很秒。也就是各种组合方案得到的数求和。
第二个我认为的精髓就在于y总代码如何计算(p0 + p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + ... + pn)如果换我之前写法是会定义两个int类型变量
一个用来记录P的n次方,另外记录sum总和,但是y总使用了一个变量写法,有点精辟。
//y总代码
//
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map primes;
while (n -- )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
while (x % i == 0)
{
x /= i;
primes[i] ++ ;
}
if (x > 1) primes[x] ++ ;
}
LL res = 1;
for (auto p : primes)
{
LL a = p.first, b = p.second;
LL t = 1;
while (b -- ) t = (t * a + 1) % mod;
res = res * t % mod;
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号