CSS
1、什么是CSS
层叠样式表,美化网页
CSS的三种导入方式
1、内部样式
2、外部样式(链接式,导入式)
3、行内样式
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>导出方式</title> 6 <!-- 内部样式--> 7 <style> 8 h1{ 9 color: aqua; 10 } 11 </style> 12 <!-- 外部样式--> 13 <link rel="stylesheet" herf="css/style.css"> 14 </head> 15 <body> 16 -- 优先级:就近原则 17 -- 行内样式 18 <h1 style="color: aqua">导出方式</h1> 19 </body> 20 </html>
选择器
作用:选择页面上的某一个或者某一类元素
1、基本选择器
- 标签选择器:
标签选择器,会选择到页面上所有这个标签的元素
- 类选择器:类选择器的格式.Class的名称
- 好处:可以多个标签归类,是同一个Class,可以复用
- id选择器:#id名称{ }; ID必须保证全局唯一
不遵循就近原则,ID选择器>类选择器>标签选择器
2、层次选择器
- 后代选择器
- 子选择器
- 相邻兄弟选择器
- 通用选择器
1 /*后代选择器*/ 2 body p{ 3 background:red; 4 } 5 /*子选择器*/ 6 body >p{ 7 background: aqua; 8 } 9 /*相邻兄弟选择器 只有一个 向下选择*/ 10 .active +p{ 11 background: aquamarine; 12 } 13 /* 通用选择器,当前选中的元素的向下的所有兄弟元素*/ 14 .active ~p{ 15 background: burlywood; 16 }
3、结构伪类选择器
伪类:条件
1 <style> 2 /*选中p:定位到父元素,选择当前多的第一个元素 3 选择当前p元素的父级元素,选中父级元素的第一个, 4 并且是当前元素才生效,按顺序来*/ 5 p:nth-child(1){ 6 background: burlywood; 7 } 8 /*选中父元素下的p元素的第二个,按类型来*/ 9 p:nth-of-type(2){ 10 background: aquamarine; 11 } 12 /*选中ul 的第一个元素*/ 13 ul li:first-child{ 14 background: aliceblue; 15 } 16 ul li:last-child{ 17 background: beige; 18 } 19 20 </style>
4、属性选择器
标签[ ]
=:绝对等于
*=:包含
$=:以这个结尾
美化网页元素
span标签:重点要突出的字用span标签套起来
1 /*text-align: center; 居中*/ 2 /*text-indent: 2em; 段落首行缩进两个字母*/ 3 height: 300px; 4 /*line-height: 300px; 行高*/ 5 /*text-decoration: underline; 上划线*/ 6 /*text-decoration: line-through; 中划线*/ 7 /*text-decoration: overline; 下划线*/
文本样式
1 /*text-align: center; 居中*/ 2 /*text-indent: 2em; 段落首行缩进两个字母*/ 3 height: 300px; 4 /*line-height: 300px; 行高*/ 5 /*text-decoration: underline; 上划线*/ 6 /*text-decoration: line-through; 中划线*/ 7 /*text-decoration: overline; 下划线*/
/*a{text-decoration: none;} 超链接去下划线*/
文本阴影、超链接伪类
1、a:active是超级链接的初始状态
2、a:hover是把鼠标放上去时的状况
3、a:link 是鼠标点击时
4、a:visited是访问过后的情况。
列表
1 #nav{ 2 width: 400px; 3 background: aquamarine; 4 } 5 .active{ 6 font-size: 18px; 7 font-weight: bold; 8 text-indent: 1em; 9 line-height: 35px; 10 background: red; 11 } 12 h2{ 13 color: brown; 14 background: aqua; 15 } 16 ul li{ 17 height: 35px; 18 text-decoration: none; 19 background: aquamarine; 20 list-style: none; 21 22 } 23 a{ 24 text-decoration: none; 25 26 } 27 a:hover{ 28 color: crimson; 29 } 30 </style>

盒子模型
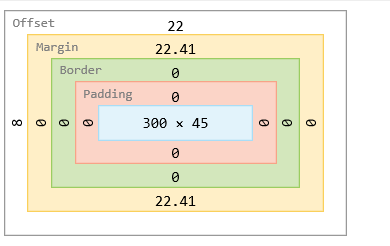
margin:外边框
padding:内边框
border:边框
边框:
1、粗细
2、样式
3、颜色
border:样式 粗细 颜色
盒子的计算方式:这个元素到底多大?
margin+border+padding+内容宽度
圆角边框
broder-radius
前端网站:Element 飞冰
浮动
display:block 块元素 inline 行内元素 inline-block 是块元素,但是可以内联,在一行! none 消失
这个也是实现行内元素排列的方式,但是我们很多情况都是用float
-
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <title>Title</title> 6 <!-- block,块元素 7 inline 行内元素 8 inline-block 是块元素,但是可以内联,在一行! 9 none: 消失--> 10 <style> 11 div{ 12 width: 100px; 13 height:100px; 14 border: 1px solid red; 15 display: inline; 16 } 17 span{ 18 width: 100px; 19 height:100px; 20 border: 1px solid red; 21 display: block; 22 } 23 </style> 24 </head> 25 <body> 26 <div>div块元素</div> 27 <span>span行内元素</span> 28 </body> 29 </html>
float
左右浮动
clear:right clear:left both, none 不允许有浮动元素
父级元素塌陷问题
解决方案
- 增加父级元素的高度
- 增加一个空的div标签,清除浮动
3.overflow
4.父类添加一个伪类:
1 #father:after{ 2 content:''; 3 display:block; 4 clear:both; 5 }
对比:
- display
方向不可以控制
- float
定位
相对定位
position:relative;相对于原来的位置,进行指定的偏移,相对定位的话,它仍然在标准文档流中,原来的位置会被保留
-
1 div{ 2 position: relative/*相对定位*/ 3 top: -20px;/*相对当前的位置 向上移动,负值相反方向*/ 4 left: 20px;/*相对当前的位置 向右移动*/ 5 bottom: -20px;/*相对当前的位置 向下移动*/ 6 right: 20px;/*相对当前的位置 向左移动*/ 7 }
绝对定位
定位:基于xxx定位,上下左右~
- 没有父级元素定位的前提下,相对于浏览器定位
- 假设父级元素存在定位我们通常会相对与父元素
- 在父级元素范围内移动
-
1 div{ 2 position: absolute;/*绝对定位*/ 3 top: -20px;/*相对当前的位置 向上移动,负值相反方向*/ 4 left: 20px;/*相对当前的位置 向右移动*/ 5 }
固定定位fixed
position:fixed
z-index
font-size:12px
line-height:25px
opacity:0.5 透明度


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号