JUC并发编程(java.util.concurrent)
线程和进程
进程:一个程序
一个进程往往可以包含多个线程,至少包含一个
线程:
对于java而言:Thread,Runnable,Callable
java不可以开启线程
并发(多个线程操作同一个资源)
CPU一核
并行(多人一起行走)
CPU多核,多个线程可以同是执行,线程池
//获取CPU的核数 System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
并发编程的本质:充分利用CPU的资源
线程的六个状态

//新生 NEW //运行 RUNNABLE //阻塞 BLOCKED //等待,死死地等 WAITING //超时等待 TIMED WAITING //终止 TERMINATEO
//新生 NEW //运行 RUNNABLE //阻塞 BLOCKED //等待,死死地等 WAITING //超时等待 TIMED WAITING //终止 TERMINATE
wite/sleep的区别
1、来自不同的类
wait——>Object
sleep——>Thread
2、关于锁的释放
waut会释放锁,sleep不会释放锁
3、使用的范围不同
wait:必须同步在代码块中
sleep:可以在任何地方用
4、是否捕获异常
wait不需要捕获异常
sleep必须捕获异常(可能超时等待)
lock锁
- 传统:synchronized
//线程是一个单独的资源类,没有任何附属的操作 public class saleTicket { public static void main(String[] args){ //并发、多线程操作同一个资源类,把资源类丢进线程里 Ticket ticket=new Ticket(); Ticket ticket2=new Ticket(); //@FunctionalInterface 函数式接口 //lambda表达式 (参数)->{代码} new Thread(()->{ for(int i=1;i<50;i++){ ticket.sale();} },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ ticket.sale();} },"B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for(int i=0;i<50;i++){ ticket.sale();} },"C").start(); } } class Ticket{ //属性、方法 private int number=50; //synchronized 本质:队列,排队、、锁 public synchronized void sale(){ if(number>0){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "卖出了"+(number--)+"票,剩余:"+number+"张"); } } }
- Lock接口
公平锁:十分公平,先来后到
非公平锁:不公平,可以插队(默认)
//lock三部曲 //1、new ReentrantLock(); //2、lock.lock();//加锁 //3、finally=>lock.unlock();//解锁 class Ticket2{ int number=30; Lock lock= new ReentrantLock(); public void sale(){ lock.lock();//加锁 try{ if(number>0){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "卖出了"+(number--)+"票,剩余:"+number+"张"); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock();//解锁 } } }
Synchronized和look的区别
-
-
- Synchronized是内置的关键字,look是一个java类
- Synchronized无法判断获取锁的状态,lock可以判断是否获取了锁
- Synchronized会自动释放锁,lock必须手动释放锁,否则死锁
- Synchronized线程一(获得锁,阻塞),线程二(等待)lock就不一定等待下去(Lock.tryLock()尝试获取锁)
- Synchronized是可重入锁,不可以中断,非公平。Lock可重入锁,可以判断,非公平(可以自己设置)
- Synchornized审核锁少量的代码同步问题,Lock适合锁大量的同步代码
-
生产者和消费者问题
Synchornized版
public class PC { public static void main(String[] args) { Data data = new Data(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrement(); } },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increment(); } },"B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrement(); } },"C").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increment(); } },"D").start(); } } class Data { private int number = 0; public synchronized void increment() { if (number > 0) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } number++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number); this.notifyAll(); } public synchronized void decrement() { if (number <= 0) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } number--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number); this.notifyAll(); } }
当线程大于两个时便可能存在虚假唤醒的情况:因为使用的是if,执行完if内的内容唤醒后便会继续执行后续代码而不会再次判断等待条件, 换句话说,等待应该总是出现在循环中的
public class PC { public static void main(String[] args) { Data data = new Data(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrement(); } },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increment(); } },"B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrement(); } },"C").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increment(); } },"D").start(); } } class Data { private int number = 0; public synchronized void increment() { while (number > 0) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } number++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number); this.notifyAll(); } public synchronized void decrement() { while (number <= 0) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } number--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number); this.notifyAll(); } }
存在ABCD四个线程;IF判断改为while判断,解决虚假唤醒问题
Lock版
public class PC { public static void main(String[] args) { Data data = new Data(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrement(); } },"A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increment(); } },"B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrement(); } },"C").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increment(); } },"D").start(); } } class Data { private int number = 0; public synchronized void increment() { while (number > 0) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } number++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number); this.notifyAll(); } public synchronized void decrement() { while (number <= 0) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } number--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + number); this.notifyAll(); } }
condition实现精准通知唤醒
public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { Data01 data01 = new Data01(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { data01.A(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "A").start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { data01.B(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "B").start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { data01.C(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }, "C").start(); } } // 判断等待,业务,通知 //A执行完调用B,B执行完调用C,C执行完调用A class Data01 { private int num = 1;// 1A 2B 3C private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition(); private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition(); private Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition(); public void A() throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try { // 业务代码,判断=>执行=>通知! while (num!=1){ condition1.await(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>AAAAA"); num = 2; // 唤醒指定的线程,B condition2.signal(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void B() throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try { while (num!=2){ condition2.await(); } num = 3; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>BBBBB"); // 唤醒指定的线程,C condition3.signal(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void C() throws InterruptedException { lock.lock(); try { while (num!=3){ condition3.await(); } num = 1; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>CCCCC"); // 唤醒指定的线程,A condition1.signal(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
8锁现象
synchronized 锁的对象是方法的调用者,方法调用同一个锁,谁先拿到谁先用
普通方法先于调用锁的方法
两个对象,两个方法,按时间排序
static静态方法类一加载就有了,锁的是class类模板
一个类只有一个Class对象
一个普通的同步方法,一个静态同步方法,
小结
- new this 具体的一个手机
- static Class 唯一的一个模板
例3、
1 package com.haust.lock8; 2 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 3 /** 4 * 5、增加两个静态的同步方法,只有一个对象,先打印 发短信?打电话? 5 * 6、两个对象!增加两个静态的同步方法, 先打印 发短信?打电话? 6 */ 7 public class Test3 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // 两个对象的Class类模板只有一个,static,锁的是Class 10 Phone3 phone1 = new Phone3(); 11 Phone3 phone2 = new Phone3(); 12 //锁的存在 13 new Thread(()->{ 14 phone1.sendSms(); 15 },"A").start(); 16 // 捕获 17 try { 18 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 19 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 new Thread(()->{ 23 phone2.call(); 24 },"B").start(); 25 } 26 } 27 // Phone3唯一的一个 Class 对象 28 class Phone3{ 29 // synchronized 锁的对象是方法的调用者! 30 // static 静态方法 31 // 类一加载就有了!锁的是Class 32 public static synchronized void sendSms(){ 33 try { 34 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); 35 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 System.out.println("发短信"); 39 } 40 public static synchronized void call(){ 41 System.out.println("打电话"); 42 } 43 } 44 // 先执行发短信,后执行打电话
例4、
1 package com.haust.lock8; 2 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 3 /** 4 * 5、增加两个静态的同步方法,只有一个对象,先打印 发短信?打电话? 5 * 6、两个对象!增加两个静态的同步方法, 先打印 发短信?打电话? 6 */ 7 public class Test3 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // 两个对象的Class类模板只有一个,static,锁的是Class 10 Phone3 phone1 = new Phone3(); 11 Phone3 phone2 = new Phone3(); 12 //锁的存在 13 new Thread(()->{ 14 phone1.sendSms(); 15 },"A").start(); 16 // 捕获 17 try { 18 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 19 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 new Thread(()->{ 23 phone2.call(); 24 },"B").start(); 25 } 26 } 27 // Phone3唯一的一个 Class 对象 28 class Phone3{ 29 // synchronized 锁的对象是方法的调用者! 30 // static 静态方法 31 // 类一加载就有了!锁的是Class 32 public static synchronized void sendSms(){ 33 try { 34 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); 35 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 System.out.println("发短信"); 39 } 40 public static synchronized void call(){ 41 System.out.println("打电话"); 42 } 43 } 44 // 先执行发短信,后执行打电话
集合类不安全
List不安全
并发下ArrayList不安全
解决方案:
1 List<String> list=new Vector<>(); 2 List<String> list=Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); 3 List<String> list=new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
CopyOnWrite 写入时复制,简称COW 计算机程序设计领域的一种优化政策
多个线程使用的时候,list,读取的时候,固定的,写入(覆盖)
在写入的时候避免覆盖,造成数据问题
读写分离
synchronized效率低
set不安全
ConcurrentModificationException //并发修改异常解决方案:
1 List<String> list=Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
2 List<String> list=new CopyOnWriteSet<>();
HashSet底层是什么?
1 public HashSet(){ 2 map=new HashMap<>(); 3 } 4 5 //set本质就是map key 是无法重复的 6 public boolean add(E e){ 7 return map.put(e.PRESENT)=null;//PRESENT是一个不变的值 8 }
Map不安全
解决方法:
1 Map<String,String> map =new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
Callable
1、可以有返回值
2、可以抛出异常
3、方法不同:call()
1 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 2 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 3 import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; 4 5 public class callableTest { 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { 7 new Thread().start(); 8 MyThread thread =new MyThread(); 9 FutureTask futureTask=new FutureTask(thread);//适配类 10 new Thread(futureTask,"a").start(); 11 new Thread(futureTask,"b").start();//结果被缓存,提高效率 12 Integer i=(Integer) futureTask.get();//get方法可能会产生阻塞 13 //放在最后或者使用异步通信来处理 14 System.out.println(i); 15 16 } 17 } 18 class MyThread implements Callable<Integer>{ 19 public Integer call(){ 20 System.out.println("call()");//打印一个 21 //耗时操作 22 return 1; 23 } 24 } 25
常用辅助类
CountDownLatch 减法计数器
定义一个计数器
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(5);
等待计数器归零向下执行
countDownLatch.await();
计数器减一
countDownLatch.countDown();
例1:
1 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; 2 3 4 public class CountDownLatchDemo { 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 6 CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6); 7 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 8 new Thread(()-> { 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Go out"); 10 // 计数器-1 11 countDownLatch.countDown(); 12 },String.valueOf(i)).start(); 13 } 14 // 等到计数器归零 才继续往下执行 15 countDownLatch.await(); 16 System.out.println("Close door"); 17 } 18 }
2.CyclicBarrier 加法计数器
1 import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier; 4 5 6 public class CyclicBarrierDemo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(7,() -> System.out.println("召唤神龙!!!!!!!")); 9 for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) { 10 final int temp = i; 11 new Thread(() -> { 12 System.out.println("收集到了第"+ temp + "颗龙珠!"); 13 try { 14 cyclicBarrier.await(); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } catch (BrokenBarrierException e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 }).start(); 21 } 22 } 23 }
3.Semaphore信号
定义信号量
val semaphore: Semaphore = Semaphore(3)
信号量获取
semaphore.acquire()
信号量释放
1 semaphore.release() 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; 4 5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 6 7 public class SemaphoreDemo { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // 作用:多个共享资源的互斥使用 高并发下限流 10 Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); 11 for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) { 12 new Thread(()-> { 13 try { 14 // 获取信号量,如果信号量满了线程等待 15 semaphore.acquire(); 16 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "抢到了车位"); 17 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "离开了车位"); 19 // 释放当前信号量 唤醒等待的线程 20 semaphore.release(); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 },String.valueOf(i)).start(); 25 } 26 } 27 }
原理:
semaphore.acquire();获得,假设已经满了则等待,等待其他线程释放。
semaphore.release();释放,会将当前的信号量释放+1,然后唤醒等待的线程。
作用:多个资源互斥的使用,并发限流,控制最大的线程数!
读写锁ReadWriteLook
读锁(共享锁)多个线程可以同时占有
写锁(独占锁)一次只能被一个线程占有
1 import java.lang.reflect.Array; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 7 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; 8 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 9 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; 10 11 public class test2 { 12 public static void main(String[] args){ 13 MyCacheLock mychche =new MyCacheLock(); 14 for (int i = 1; i <5 ; i++) { 15 final int temp=i; 16 new Thread(()->{ 17 mychche.put(temp+"",temp+""); 18 },String.valueOf(i)).start(); 19 } 20 for (int i = 1; i <5 ; i++) { 21 final int temp=i; 22 new Thread(()->{ 23 mychche.get(temp+"",temp+""); 24 },String.valueOf(i)).start(); 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 /*class MyCache{ 29 private volatile Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>(); 30 //存 写 31 public void put(String key,Object value){ 32 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入"+key); 33 map.put(key,value); 34 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入ok"+key); 35 36 } 37 public void get(String key,Object value){ 38 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取"+key); 39 Object o=map.get(key); 40 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取ok"+key); 41 42 } 43 }*/ 44 class MyCacheLock { 45 private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock= new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 46 private volatile Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>(); 47 //存 写 48 public void put(String key,Object value){ 49 readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();//加锁 50 try { 51 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入"+key); 52 map.put(key,value); 53 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写入ok"+key); 54 55 }catch (Exception e){ 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 }finally { 58 readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); 59 } 60 } 61 public void get(String key,Object value){ 62 ReadWriteLock readWriteLock=new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 63 readWriteLock.readLock().lock(); 64 try{ 65 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取"+key); 66 Object o=map.get(key); 67 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取ok"+key); 68 69 }catch (Exception e){ 70 e.printStackTrace(); 71 } 72 finally { 73 readWriteLock.readLock().unlock(); 74 } 75 76 } 77 }
阻塞队列(BlockingQueue)
四组API
| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 有返回值 | 阻塞等待 | 超时等待 |
| 添加 | add() | offer() | put() | offer(e,time,unit ) |
| 移除 | remove() | poll() | take() | poll(time,unit) |
| 检测队首元素 | element() | peek() | - | - |
1、抛出异常
1 public static void test1(){ 2 //对列的大小 3 ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3); 4 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a")); 5 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b")); 6 System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c")); 7 //System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d")); 8 //IllegalStateException抛出异常 9 System.out.println("============"); 10 System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 11 System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 12 System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 13 //System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove()); 14 //NoSuchElementException抛出异常
2、有返回值
1 public static void test2(){ 2 ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3); 3 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a")); 4 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b")); 5 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c")); 6 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d"));//返回false 7 System.out.println("==========="); 8 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll()); 9 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll()); 10 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll()); 11 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());//返回NULL 12 }
3、阻塞等待
1 public static void test3() throws InterruptedException { 2 ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue=new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3); 3 4 blockingQueue.put("a"); 5 blockingQueue.put("b"); 6 blockingQueue.put("c"); 7 blockingQueue.put("d");//一直等待 8 System.out.println("==========="); 9 System.out.println(blockingQueue.take()); 10 System.out.println(blockingQueue.take()); 11 System.out.println(blockingQueue.take()); 12 System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());//一直等待 13 14 }
4、超时等待
1 public static void test4() throws InterruptedException { 2 ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3); 3 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 4 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 5 6 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 7 System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d", 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 8 System.out.println("=========="); 9 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 10 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 11 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 12 System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); 13 14 15 }
SynchronousQueue同步队列
没有容量
进去一个元素,必须等待取出来之后才能往里面放一个元素
put();take();
和其他的BlockingQueue不一样,SynchronousQueue不存储元素
put进去一个元素,必须从里面先take取出来,否则不能put进去值
1 SynchronousQueue<Object> blockingDeque=new SynchronousQueue<Object>();//同步队列 2 3 new Thread(()->{ 4 try { 5 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put 1"); 6 blockingDeque.put("1"); 7 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put 1"); 8 blockingDeque.put("2"); 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put 1"); 10 blockingDeque.put("3"); 11 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put 2"); 15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"put 3"); 16 17 },"t1").start(); 18 new Thread(()->{ 19 try { 20 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+blockingDeque.take()); 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+blockingDeque.take()); 23 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+blockingDeque.take()); 24 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 },"t2").start(); 29 }
线程池(三大方法,七大参数,四种拒绝策略)
池化技术:优化资源的使用
程序运行的本质是占用系统的资源
池化技术:事先准备好一些资源,有人要用,就来这里拿,用完之后还回来
线程池的好处:
- 降低资源的消耗
- 提高响应的速度
- 方便管理
- 线程的复用,可以控制最大并发放、管理线程
三个方法
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 ExecutorService threadpool= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//单个线程 3 Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//可伸缩的,遇强则强,遇弱则弱 4 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//创建一个固定的线程池的大小 5 6 try { 7 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 8 threadpool.execute(() -> { 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok"); 10 }); 11 } 12 }catch (Exception e){ 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 finally { 16 //线程结束,程序结束,关闭线程池 17 threadpool.shutdown(); 18 } 19 20 } 21 }
七大参数:
1 public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,//核心线程数 2 int maximumPoolSize,//最大线程数 3 long keepAliveTime,//线程未被使用时存活时间 4 TimeUnit unit,//时间单位 5 BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,//阻塞队列 未获取到线程的等待队列 6 ThreadFactory threadFactory,//线程工厂 一般不用动 7 RejectedExecutionHandler handler//拒绝策略) { 8 if (corePoolSize < 0 || 9 maximumPoolSize <= 0 || 10 maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || 11 keepAliveTime < 0) 12 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 13 if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) 14 throw new NullPointerException(); 15 this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ? 16 null : 17 AccessController.getContext(); 18 this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; 19 this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; 20 this.workQueue = workQueue; 21 this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); 22 this.threadFactory = threadFactory; 23 this.handler = handler; 24 }
4. 【强制】线程池不允许使用 Executors 去创建,而是通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 的方式,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。说明:Executors 返回的线程池对象的弊端如下: 1)FixedThreadPool 和 SingleThreadPool:允许的请求队列长度为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会堆积大量的请求,从而导致 OOM。 2)CachedThreadPool 和 ScheduledThreadPool:允许的创建线程数量为 Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建大量的线程,从而导致 OOM。
手动创建一个线程池
1 ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, 2 3L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, 3 new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), 4 Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), 5 new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());//等待队列满后的拒绝策略
四种拒绝策略
1 /** 2 * new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() 满员后直接抛出异常 3 * new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() 满员后 新来的哪个线程发起的 就丢回去让哪个线程执行 4 * new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() 满员后直接丢掉新来的 不抛出异常 5 * new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() 满员后尝试与更早的线程竞争 竞争失败也不抛出异常 6 **/
最大线程应该如何设置?
- CPU密集型:最大线程数,CPU几核的就是几,可以保持CPU效率最高。
- IO密集型:判断程序中十分耗IO的线程数量,大于这个数,一般是这个数的两倍。
四大函数式接口
新时代程序员必须掌握:lambda表达式、链式编程、函数式接口、stream流式计算。
函数式接口:只有一个方法的接口。
Function函数型接口
有一个输入参数,有一个输出(返回值)。
1 import java.util.function.Function; 2 public class FunctionTest { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Function<String, String> function = new Function<String, String>() { 5 /** 6 * Applies this function to the given argument. 7 * 8 * @param s the function argument 9 * @return the function result 10 */ 11 @Override 12 public String apply(String s) { 13 return s+":hhhh"; 14 } 15 }; 16 System.out.println(function.apply("123")); 17 Function<String, String> function2 = (a) ->{ return a + ":hhhh";}; 18 System.out.println(function2.apply("456")); 19 } 20 }
predicate断定型接口
有一个输入参数,返回值只能是boolean值。
1 import java.util.function.Predicate; 2 public class PredicateTest { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 断定型接口 有一个入参,返回值只能是布尔值 5 Predicate<String> predicate = new Predicate<String>() { 6 /** 7 * Evaluates this predicate on the given argument. 8 * 9 * @param s the input argument 10 * @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate, 11 * otherwise {@code false} 12 */ 13 @Override 14 public boolean test(String s) { 15 return s != null && s.equals("HELLO"); 16 } 17 }; 18 System.out.println(predicate.test("WORLD")); 19 Predicate<String> predicate2 = a -> a != null && a.equals("HELLO"); 20 System.out.println(predicate2.test("HELLO")); 21 } 22 }
consumer消费型接口
有一个输入参数,没有返回值。
1 import java.util.function.Consumer; 2 public class ConsumerTest { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 消费型接口 只有输入没有返回 5 Consumer<String> consumer = new Consumer<String>() { 6 @Override 7 public void accept(String s) { 8 System.out.println(s); 9 } 10 }; 11 consumer.accept("Hello"); 12 Consumer<String> consumer2 = System.out::print; 13 consumer2.accept("World"); 14 } 15 }
supplier供给型接口
没有输入参数,有一个输出(返回值)。
1 import java.util.function.Supplier; 2 public class SupplierTest { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 // 供给型接口 只返回 不输入 5 Supplier<Integer> supplier = new Supplier<Integer>() { 6 @Override 7 public Integer get() { 8 System.out.println("get"); 9 return 1025; 10 } 11 }; 12 System.out.println(supplier.get()); 13 Supplier<Integer> supplier2 = () -> { 14 System.out.println("get"); 15 return 1024; 16 }; 17 System.out.println(supplier2.get()); 18 } 19 }
Stream流式计算
1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 import java.util.List; 3 import java.util.Locale; 4 5 /* 6 * 筛选: 7 * 1、ID必须是偶数 8 * 2、年龄小于25 9 * 3、用户名转为大写字母 10 * 4、用户名字母倒着排序 11 * 5、只输出一个用户*/ 12 public class Test5 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 User u1=new User(1,"a",21); 15 User u2=new User(2,"b",25); 16 User u3=new User(3,"c",28); 17 User u4=new User(4,"d",24); 18 User u5=new User(5,"e",26); 19 List<User> list= Arrays.asList(u1,u2,u3,u4,u5); 20 //链式编程 21 list.stream().filter((u)->{return u.getID()%2==0;}) 22 .filter((u)->{return u.getAge()<26;}) 23 .map((u)->{return u.getName().toUpperCase();}) 24 .sorted((t1,t2)->{return t2.compareTo(t1);}) 25 .limit(1) 26 .forEach(System.out::println); 27 } 28 }
ForkJoin
大数据量
双端队列
特点:工作窃取
1 public class Demo02 extends RecursiveTask<Long> { 2 private long start; 3 private long end; 4 //临界值 5 private long temp=10000L; 6 public Demo02(Long start,Long end){ 7 this.start=start; 8 this.end=end; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 protected Long compute() { 13 long sum; 14 if((end-start)>0){ 15 for (Long i = 0L; i>start; i++) { 16 sum=+i; 17 System.out.println(sum); 18 } 19 } 20 else{ 21 Long middle=(start+end)/2;//中间值 22 Demo02 task1=new Demo02(start,middle); 23 task1.fork();//拆分任务,把任务压入线程队列 24 Demo02 task2=new Demo02(middle+1, end); 25 task2.fork(); 26 task1.join();// 27 task2.join(); 28 return task1.join()+task2.join(); 29 } 30 return null; 31 } 32 }
异步回调
异步调用: Ajax
1 import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture; 2 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 3 4 public class test02{ 5 public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { 6 int psw = 12312; 7 int password = 12312; 8 String name = "zhangsan"; 9 //没有返回值的runAsync()异步回调 10 /* CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture=CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{ 11 if(password==psw){ 12 if(name=="zhangsan"){ 13 System.out.println("登录成功!"); 14 } 15 } 16 17 }); 18 completableFuture.get();*/ 19 CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture=CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{ 20 if(password==psw){ 21 if(name=="zhang"){ 22 System.out.println("登录成功!"); 23 } 24 } 25 return 1024;}); 26 System.out.println(completableFuture.whenComplete((t,u)->{ 27 System.out.println("t="+t);//正确的返回结果 28 System.out.println("u="+u);//错误信息 29 }).exceptionally((e)->{ 30 e.printStackTrace();//打印堆栈信息 31 System.out.println(e.getMessage());//获取详情信息 32 return 233; 33 })); 34 } 35 36 }
JMM
java内存模型,不存在的东西,是一个约定
关于JMM的一些同步的约定
1、线程解锁前,必须把共享变量立刻刷出主存
2、线程加锁前,必须读取主存中的最新值到工作内存中!
3、加锁和解锁是同一把锁
线程 工作内存和主存
八大原子操作
主内存与工作内存之间的具体交互协议,Java内存模型定义了八种操作来完成:
- Lock(锁定)
作用于主内存的变量,把一个变量标记为一条线程独占状态 - Unlock(解锁)
作用于主内存的变量,把一个处于锁定状态的变量释放出来,释放后的变量才可以被其他线程锁
- Read(读取)
作用于主内存的变量,把一个变量从主内存传输到线程的工作内存中 - Write(写入)
作用于主内存的变量,把Store操作从工作内存中得到的变量的值放入主内存的变量中
- Load(加载)
作用于工作内存的变量,把Read操作从主内存中得到的变量值放入工作内存的变量副本中 - Store(存储)
作用于工作内存的变量,把工作内存中的一个变量的值传递到主内存中
- Use(使用)
作用于工作内存的变量,把工作内存中一个变量的值传递给执行引擎,每当虚拟机遇到一个需要使用变量的值的字节码指令时将会执行这个操作 - Assign(赋值)
作用于工作内存的变量,把一个从执行引擎接收到的值赋给工作内存的变量,每当虚拟机遇到一个给变量赋值的字节码指令时执行这个操作 - Store(存储)
作用于工作内存的变量,把工作内存中的一个变量的值传递到主内存中
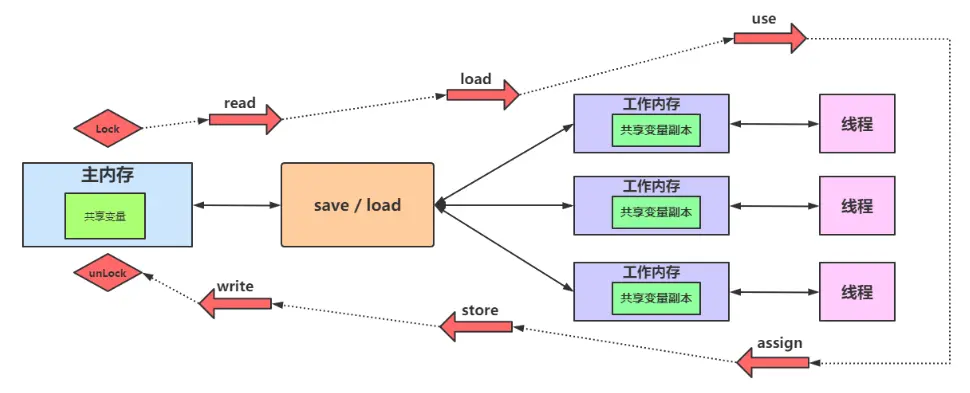
同步原则
- 不允许一个线程无原因地(没有发生过assign操作)把数据从工作内存同步回主内存中
- 一个新的变量只能在主内存中诞生,不允许在工作内存中直接使用一个未被初始化(load或assign)的变量。即对一个变量实施use和store之前,必须先执行assign和load操作
- 如果对一个变量执行lock操作,将会清空工作内存中此变量的值,在执行引擎使用这个变量之前需要重新执行load或assign操作初始化变量的值
- 如果一个变量事先没有被lock操作锁定,则不允许对它执行unlock操作;也不允许去unlock一个被其他线程锁定的变量
- 对一个变量执行unlock操作之前,必须先把此变量同步到主内存中(执行store和write操作)
Volatile
java虚拟机提供的轻量级的同步机制
1、保证可见性
2、不保证原子性
原子性:不能被分割
线程A在执行任务时不能被分割也不能被打扰,要么同时成功,要么同时失败
如果不加 lock和Sychronized,如何保证原子性?
使用原子类解决原子性问题
3、禁止指令重排
指令重排:你写的程序,剪辑并不是按照你写的那样去执行的
源代码-->编译器优化的重排--->指令并行也可能重排--->内存系统也可能重排--->执行
单例模式
构造器私有
CAS:
比较当前工作内存中的值和主内存中的值,如果这个值是期望的则更新,如果不是则一致循环。
缺点:
- 循环会耗时
- 一次只能保证一个共享变量的原子性
-
ABA问题(狸猫换太子)
Unsafe类
java无法操作内存,
java可以调用c++ Native
C++可以操作内存
java的后门,可以通过Unsafe类操作
1 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 2 3 public class CASDemo { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 AtomicInteger atomicInteger=new AtomicInteger(2022) ; 7 //期望、更新 8 //如果期望值达到了,那么更新,否则不更新 9 //CAS 是CPU的并发原语 10 atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2022,2023); 11 System.out.println(atomicInteger.get()); 12 } 13 }
原子引用
带版本号的原子
解决ABA问题
1 package Single; 2 3 import jdk.dynalink.beans.StaticClass; 4 5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 6 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 7 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicStampedReference; 8 9 public class CASDemo { 10 //如果泛型是包装类,注意对象的引用问题, 11 //正常业务中,这里面比较的是一个对象 12 static AtomicStampedReference<Integer> atomicStampedReference=new AtomicStampedReference<>(2,1); 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 new Thread(()->{ 16 int temp=atomicStampedReference.getStamp();//获得版本号 17 System.out.println("a1=>"+temp); 18 try{ 19 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(2, 3, 24 atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1)); 25 System.out.println("a2=>"+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); 26 System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(3, 2, 27 atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1)); 28 System.out.println("a3=>"+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); 29 },"a").start(); 30 new Thread(()->{ 31 int temp=atomicStampedReference.getStamp(); 32 System.out.println("b1=>"+temp); 33 try{ 34 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 35 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 System.out.println(atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(2, 4, 39 atomicStampedReference.getStamp(), atomicStampedReference.getStamp() + 1)); 40 System.out.println("b2=>"+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()); 41 },"b").start(); 42 } 43 }
各类锁的理解
1、公平锁、非公平锁
公平锁:不能插队,先来后到
非公平锁:可以插队(默认)
2、可重入锁
拿到了外面的锁就相当于拿到了里面的锁
3、自旋锁
不断的循环、遍历、迭代(CAS实现)
4、死锁
测试死锁,排查问题
1、日志
2、查看堆栈信息
解决死锁:
1、使用JPS -1定位进程号
2、使用Jstack进程号,找到死锁问题
1 package Single; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 5 public class DeadLock { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 String lockA="lockA"; 8 String lockB="lockB"; 9 new Thread(new MyThread(lockA,lockB),"t1").start(); 10 new Thread(new MyThread(lockB,lockA),"t2").start(); 11 12 } 13 } 14 class MyThread implements Runnable{ 15 private String lockA; 16 private String lockB; 17 public MyThread(String lockA, String lockB){ 18 this.lockA=lockA; 19 this.lockB=lockB; 20 } 21 22 @Override 23 public void run() { 24 synchronized (lockA){ 25 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"lock:"+lockA+"get=>"+lockB); 26 try { 27 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 synchronized (lockB){ 33 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"lock:"+lockB+"get=>"+lockA); 34 try { 35 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); 36 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 } 39 } 40 41 } 42 }
姓名:许颖
学号:210162704048
标题:JUC学习https://i.cnblogs.com/posts/edit;postId=16903629





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号