KeyEvent分发原理一——native层事件分发流程
事件的分发主要是两个类InputReader.cpp和InputDispatcher.cpp.
1.SystemService会启动两个线程:InputReaderThread和InputDispatcherThread,一个负责读取事件,一个负责分发事件
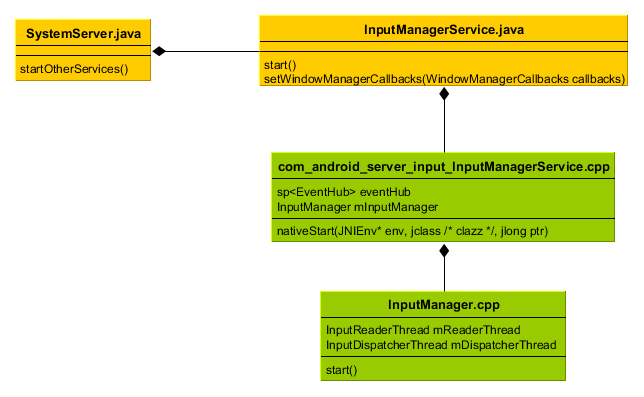
SystemServer.java
/**
* Starts a miscellaneous grab bag of stuff that has yet to be refactored and organized.
*/
private void startOtherServices(){
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputManagerCallback());
inputManager.start();
}
com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */, jlong ptr) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();
if (result) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Input manager could not be started.");
}
}
InputManager.cpp
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);
initialize();
}
void InputManager::initialize() {
mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader);
mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherThread(mDispatcher);
}
status_t InputManager::start() {
status_t result = mDispatcherThread->run("InputDispatcher", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputDispatcher thread due to error %d.", result);
return result;
}
result = mReaderThread->run("InputReader", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputReader thread due to error %d.", result);
mDispatcherThread->requestExit();
return result;
}
return OK;
}
在创建InputDispatcher和InputReader的时候,请注意mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);InputDispacher是传递给了InputReader的,所以InputReader在读取事件后可以操作InputDispatcher用来分发事件,这个很重要,有助于理解之后如何分发事件,下面是时序图:

2.InputReader读取事件
InputManager会启动两个线程,一个是InputReaderThread,一个是InputDispatcherThread, InputReaderThread持有InputReader, InputDispatcherThread持有InputDispatcher, 同时InputReader持有InputDispatcher,这是三者之间的关系。
InputReaderThread一旦启动就会执行threadLoop()方法,从而执行InputReader的loopOnce()
bool InputReaderThread::threadLoop() {
mReader->loopOnce();
return true;
}
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
Vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
oldGeneration = mGeneration;
timeoutMillis = -1;
uint32_t changes = mConfigurationChangesToRefresh;
if (changes) {
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh = 0;
timeoutMillis = 0;
refreshConfigurationLocked(changes);
} else if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(now, mNextTimeout);
}
} // release lock
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) {
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
if (mNextTimeout != LLONG_MAX) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
if (now >= mNextTimeout) {
#if DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS
ALOGD("Timeout expired, latency=%0.3fms", (now - mNextTimeout) * 0.000001f);
#endif
mNextTimeout = LLONG_MAX;
timeoutExpiredLocked(now);
}
}
if (oldGeneration != mGeneration) {
inputDevicesChanged = true;
getInputDevicesLocked(inputDevices);
}
} // release lock
// Send out a message that the describes the changed input devices.
if (inputDevicesChanged) {
mPolicy->notifyInputDevicesChanged(inputDevices);
}
// Flush queued events out to the listener.
// This must happen outside of the lock because the listener could potentially call
// back into the InputReader's methods, such as getScanCodeState, or become blocked
// on another thread similarly waiting to acquire the InputReader lock thereby
// resulting in a deadlock. This situation is actually quite plausible because the
// listener is actually the input dispatcher, which calls into the window manager,
// which occasionally calls into the input reader.
mQueuedListener->flush();
}
threadLoop是Thread(C++语言)中的循环机制,如果没有调用requestExit会不断执行threadLoop中的代码,所以InputReaderThread是一个一直存在不断读取事件的线程。
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE)
这行会将事件转变成可识别的Event, 如何工作的,不是本篇文章讨论的内容。mQueuedListener->flush();是将事件分发出去。那么mQueuedListener是什么呢?是InputListener一个实例
InputListener.h
/*
* An implementation of the listener interface that queues up and defers dispatch
* of decoded events until flushed.
*/
class QueuedInputListener : public InputListenerInterface {
protected:
virtual ~QueuedInputListener();
public:
QueuedInputListener(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& innerListener);
virtual void notifyConfigurationChanged(const NotifyConfigurationChangedArgs* args);
virtual void notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs* args);
virtual void notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args);
virtual void notifySwitch(const NotifySwitchArgs* args);
virtual void notifyDeviceReset(const NotifyDeviceResetArgs* args);
void flush();
private:
sp<InputListenerInterface> mInnerListener;
Vector<NotifyArgs*> mArgsQueue;
};
InputListener.cpp
void QueuedInputListener::flush() {
size_t count = mArgsQueue.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i];
args->notify(mInnerListener);
delete args;
}
mArgsQueue.clear();
}
从方法来看这个flush()会将mArgsQueue中的事件分发出去,那么事件又是什么时候加入到这个队列里面的呢?让我们再回到InputReader的loopOnce方法。在调用mQueuedListener->flush()之前会调用processEventsLocked,再调用processEventsForDeviceLocked,
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t deviceId,
const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
ssize_t deviceIndex = mDevices.indexOfKey(deviceId);
if (deviceIndex < 0) {
ALOGW("Discarding event for unknown deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
InputDevice* device = mDevices.valueAt(deviceIndex);
if (device->isIgnored()) {
//ALOGD("Discarding event for ignored deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
device->process(rawEvents, count);
}
再看这个方法device->process, 这里的device是什么呢,以keyevent为例,就是InputReader中的KeyboardInputMapper,这个类的定义在InputReader.h中,最终会执行processKey。
void KeyboardInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) { switch (rawEvent->type) { case EV_KEY: { int32_t scanCode = rawEvent->code; int32_t usageCode = mCurrentHidUsage; mCurrentHidUsage = 0; if (isKeyboardOrGamepadKey(scanCode)) { processKey(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->value != 0, scanCode, usageCode); } break; } case EV_MSC: { if (rawEvent->code == MSC_SCAN) { mCurrentHidUsage = rawEvent->value; } break; } case EV_SYN: { if (rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) { mCurrentHidUsage = 0; } } } }
void KeyboardInputMapper::processKey(nsecs_t when, bool down, int32_t scanCode, int32_t usageCode) { int32_t keyCode; int32_t keyMetaState; uint32_t policyFlags; if (getEventHub()->mapKey(getDeviceId(), scanCode, usageCode, mMetaState, &keyCode, &keyMetaState, &policyFlags)) { keyCode = AKEYCODE_UNKNOWN; keyMetaState = mMetaState; policyFlags = 0; } if (down) { // Rotate key codes according to orientation if needed. if (mParameters.orientationAware && mParameters.hasAssociatedDisplay) { keyCode = rotateKeyCode(keyCode, mOrientation); } // Add key down. ssize_t keyDownIndex = findKeyDown(scanCode); if (keyDownIndex >= 0) { // key repeat, be sure to use same keycode as before in case of rotation keyCode = mKeyDowns.itemAt(keyDownIndex).keyCode; } else { // key down if ((policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_VIRTUAL) && mContext->shouldDropVirtualKey(when, getDevice(), keyCode, scanCode)) { return; } if (policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_GESTURE) { mDevice->cancelTouch(when); } mKeyDowns.push(); KeyDown& keyDown = mKeyDowns.editTop(); keyDown.keyCode = keyCode; keyDown.scanCode = scanCode; } mDownTime = when; } else { // Remove key down. ssize_t keyDownIndex = findKeyDown(scanCode); if (keyDownIndex >= 0) { // key up, be sure to use same keycode as before in case of rotation keyCode = mKeyDowns.itemAt(keyDownIndex).keyCode; mKeyDowns.removeAt(size_t(keyDownIndex)); } else { // key was not actually down ALOGI("Dropping key up from device %s because the key was not down. " "keyCode=%d, scanCode=%d", getDeviceName().string(), keyCode, scanCode); return; } } int32_t oldMetaState = mMetaState; int32_t newMetaState = updateMetaState(keyCode, down, oldMetaState); bool metaStateChanged = oldMetaState != newMetaState; if (metaStateChanged) { mMetaState = newMetaState; updateLedState(false); // If global meta state changed send it along with the key. // If it has not changed then we'll use what keymap gave us, // since key replacement logic might temporarily reset a few // meta bits for given key. keyMetaState = newMetaState; } nsecs_t downTime = mDownTime; // Key down on external an keyboard should wake the device. // We don't do this for internal keyboards to prevent them from waking up in your pocket. // For internal keyboards, the key layout file should specify the policy flags for // each wake key individually. // TODO: Use the input device configuration to control this behavior more finely. if (down && getDevice()->isExternal()) { policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_WAKE; } if (mParameters.handlesKeyRepeat) { policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_DISABLE_KEY_REPEAT; } if (metaStateChanged) { getContext()->updateGlobalMetaState(); } if (down && !isMetaKey(keyCode)) { getContext()->fadePointer(); } NotifyKeyArgs args(when, getDeviceId(), mSource, policyFlags, down ? AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN : AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP, AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_FROM_SYSTEM, keyCode, scanCode, keyMetaState, downTime); getListener()->notifyKey(&args); }
方法中最后一行getListener()->notifyKey,就是将事件放到InputListener的队列里,再看看InputListener的notifyKey
InputListener.cpp
void QueuedInputListener::notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs* args) { mArgsQueue.push(new NotifyKeyArgs(*args)); }
到目前为止,事件已读取完毕,在InputReader中调用了InputListener.flush就会分发事件
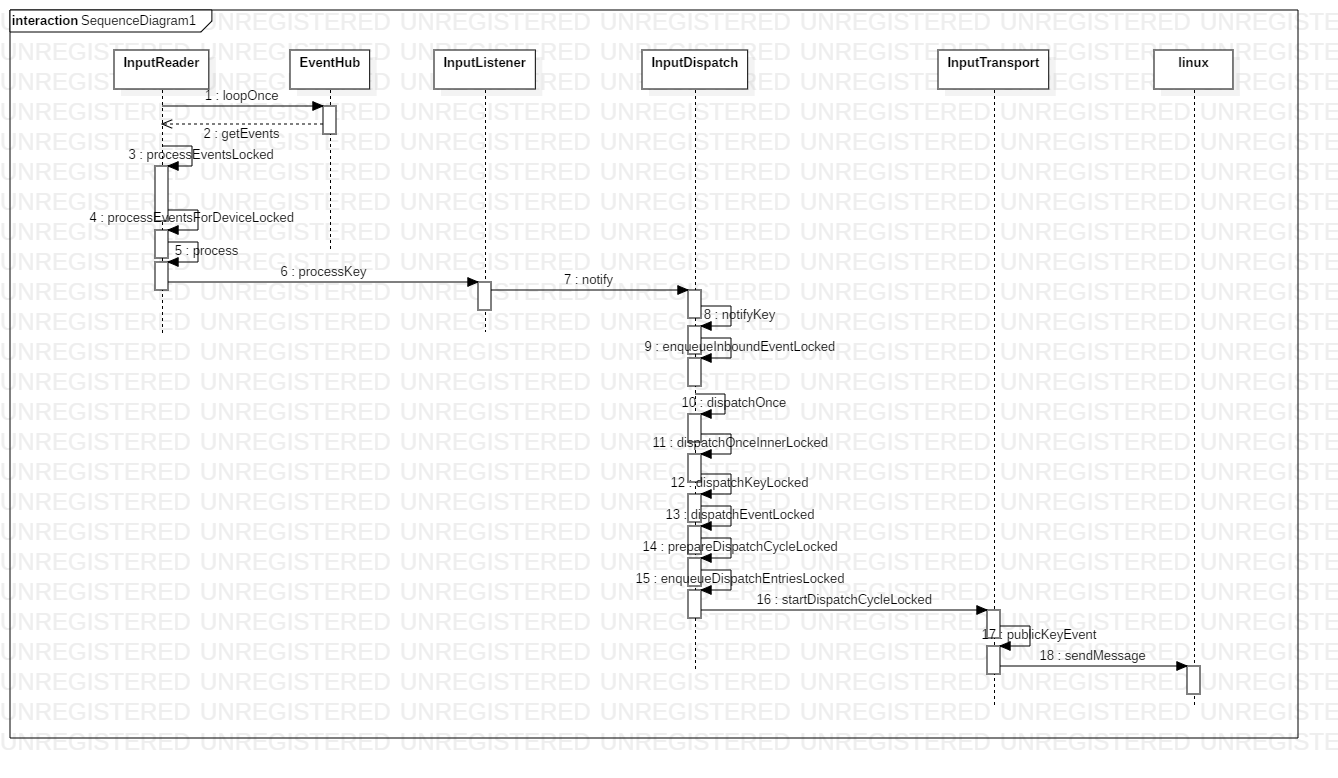
3.InputDispatch分发事件
我们再来看看flush这个方法
void QueuedInputListener::flush() { size_t count = mArgsQueue.size(); for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) { NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i]; args->notify(mInnerListener); delete args; } mArgsQueue.clear(); }
这里有两个疑问:一个是notify方法的函数体在哪里?二是mInnerListener是什么?要想找到答案我们得找到mQueuedListener初始化的地方,回到InputReader,在构造方法里面初始化了mQueuedListener
InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub, const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy, const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) : mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy), mGlobalMetaState(0), mGeneration(1), mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX), mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0) { mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener); { // acquire lock AutoMutex _l(mLock); refreshConfigurationLocked(0); updateGlobalMetaStateLocked(); } // release lock }
在初始化mQueuedListener时,传入了一个listener,并把这个listener赋值给了mInnerListener
QueuedInputListener::QueuedInputListener(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& innerListener) : mInnerListener(innerListener) { }
而这个listener又是什么呢?从第一页InputManager构造里面来看,这个listener就是InputDispatch.
InputManager::InputManager( const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub, const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy, const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) { mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy); mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher); initialize(); }
第二个问题解决了,notify的函数体就在InputListener中
void NotifyKeyArgs::notify(const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) const {
listener->notifyKey(this);
}
其实就是设用了InputDispatch中的notifyKey, 终于走到InputDispatch了,这里是真正处理事件分发的地方,看一下notifyKey都做了哪些事情
1 void InputDispatcher::notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs* args) { 2 #if DEBUG_INBOUND_EVENT_DETAILS 3 ALOGD("notifyKey - eventTime=%lld, deviceId=%d, source=0x%x, policyFlags=0x%x, action=0x%x, " 4 "flags=0x%x, keyCode=0x%x, scanCode=0x%x, metaState=0x%x, downTime=%lld", 5 args->eventTime, args->deviceId, args->source, args->policyFlags, 6 args->action, args->flags, args->keyCode, args->scanCode, 7 args->metaState, args->downTime); 8 #endif 9 if (!validateKeyEvent(args->action)) { 10 return; 11 } 12 13 uint32_t policyFlags = args->policyFlags; 14 int32_t flags = args->flags; 15 int32_t metaState = args->metaState; 16 if ((policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_VIRTUAL) || (flags & AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_VIRTUAL_HARD_KEY)) { 17 policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_VIRTUAL; 18 flags |= AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_VIRTUAL_HARD_KEY; 19 } 20 if (policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_FUNCTION) { 21 metaState |= AMETA_FUNCTION_ON; 22 } 23 24 policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED; 25 26 int32_t keyCode = args->keyCode; 27 if (metaState & AMETA_META_ON && args->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN) { 28 int32_t newKeyCode = AKEYCODE_UNKNOWN; 29 if (keyCode == AKEYCODE_DEL) { 30 newKeyCode = AKEYCODE_BACK; 31 } else if (keyCode == AKEYCODE_ENTER) { 32 newKeyCode = AKEYCODE_HOME; 33 } 34 if (newKeyCode != AKEYCODE_UNKNOWN) { 35 AutoMutex _l(mLock); 36 struct KeyReplacement replacement = {keyCode, args->deviceId}; 37 mReplacedKeys.add(replacement, newKeyCode); 38 keyCode = newKeyCode; 39 metaState &= ~AMETA_META_ON; 40 } 41 } else if (args->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP) { 42 // In order to maintain a consistent stream of up and down events, check to see if the key 43 // going up is one we've replaced in a down event and haven't yet replaced in an up event, 44 // even if the modifier was released between the down and the up events. 45 AutoMutex _l(mLock); 46 struct KeyReplacement replacement = {keyCode, args->deviceId}; 47 ssize_t index = mReplacedKeys.indexOfKey(replacement); 48 if (index >= 0) { 49 keyCode = mReplacedKeys.valueAt(index); 50 mReplacedKeys.removeItemsAt(index); 51 metaState &= ~AMETA_META_ON; 52 } 53 } 54 55 KeyEvent event; 56 event.initialize(args->deviceId, args->source, args->action, 57 flags, keyCode, args->scanCode, metaState, 0, 58 args->downTime, args->eventTime); 59 60 mPolicy->interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(&event, /*byref*/ policyFlags); 61 62 bool needWake; 63 { // acquire lock 64 mLock.lock(); 65 66 if (shouldSendKeyToInputFilterLocked(args)) { 67 mLock.unlock(); 68 69 policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_FILTERED; 70 if (!mPolicy->filterInputEvent(&event, policyFlags)) { 71 return; // event was consumed by the filter 72 } 73 74 mLock.lock(); 75 } 76 77 int32_t repeatCount = 0; 78 KeyEntry* newEntry = new KeyEntry(args->eventTime, 79 args->deviceId, args->source, policyFlags, 80 args->action, flags, keyCode, args->scanCode, 81 metaState, repeatCount, args->downTime); 82 83 needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(newEntry); 84 mLock.unlock(); 85 } // release lock 86 87 if (needWake) { 88 mLooper->wake(); 89 } 90 }
首先它会把事件包装成KeyEntry,再把keyentry放到队列里,再唤醒InputDispatchThread.同样的, InputDispatchThread也会执行theadLoop再执行dispatchOnce, 会不断的从队列里面拿事件分发出去。再看看InputDispatchThread中的ldispatch是怎么做的。
1 void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() { 2 nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX; 3 { // acquire lock 4 AutoMutex _l(mLock); 5 mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast(); 6 7 // Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands. 8 // The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards. 9 if (!haveCommandsLocked()) { 10 dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime); 11 } 12 13 // Run all pending commands if there are any. 14 // If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately. 15 if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) { 16 nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; 17 } 18 } // release lock 19 20 // Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down) 21 nsecs_t currentTime = now(); 22 int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime); 23 mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis); 24 }
从方法dispatchOnceInnerLocked走到dispatchKeyLocked,再走到dispatchEventLocked,再走到prepareDispatchCycleLocked,还有许多方法,但最终走到startDispatchCycleLocked
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ startDispatchCycle",
connection->getInputChannelName());
#endif
while (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL
&& !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.head;
dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime;
// Publish the event.
status_t status;
EventEntry* eventEntry = dispatchEntry->eventEntry;
switch (eventEntry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(eventEntry);
// Publish the key event.
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
keyEntry->deviceId, keyEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
keyEntry->keyCode, keyEntry->scanCode,
keyEntry->metaState, keyEntry->repeatCount, keyEntry->downTime,
keyEntry->eventTime);
break;
}
case EventEntry::TYPE_MOTION: {
MotionEntry* motionEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(eventEntry);
PointerCoords scaledCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
const PointerCoords* usingCoords = motionEntry->pointerCoords;
// Set the X and Y offset depending on the input source.
float xOffset, yOffset, scaleFactor;
if ((motionEntry->source & AINPUT_SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER)
&& !(dispatchEntry->targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_ZERO_COORDS)) {
scaleFactor = dispatchEntry->scaleFactor;
xOffset = dispatchEntry->xOffset * scaleFactor;
yOffset = dispatchEntry->yOffset * scaleFactor;
if (scaleFactor != 1.0f) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < motionEntry->pointerCount; i++) {
scaledCoords[i] = motionEntry->pointerCoords[i];
scaledCoords[i].scale(scaleFactor);
}
usingCoords = scaledCoords;
}
} else {
xOffset = 0.0f;
yOffset = 0.0f;
scaleFactor = 1.0f;
// We don't want the dispatch target to know.
if (dispatchEntry->targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_ZERO_COORDS) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < motionEntry->pointerCount; i++) {
scaledCoords[i].clear();
}
usingCoords = scaledCoords;
}
}
// Publish the motion event.
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
motionEntry->deviceId, motionEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, motionEntry->actionButton,
dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags, motionEntry->edgeFlags,
motionEntry->metaState, motionEntry->buttonState,
xOffset, yOffset, motionEntry->xPrecision, motionEntry->yPrecision,
motionEntry->downTime, motionEntry->eventTime,
motionEntry->pointerCount, motionEntry->pointerProperties,
usingCoords, dispatchEntry->inThumbMode, scaleFactor);
break;
}
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false);
return;
}
// Check the result.
if (status) {
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
if (connection->waitQueue.isEmpty()) {
ALOGE("channel '%s' ~ Could not publish event because the pipe is full. "
"This is unexpected because the wait queue is empty, so the pipe "
"should be empty and we shouldn't have any problems writing an "
"event to it, status=%d", connection->getInputChannelName(), status);
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
} else {
// Pipe is full and we are waiting for the app to finish process some events
// before sending more events to it.
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Could not publish event because the pipe is full, "
"waiting for the application to catch up",
connection->getInputChannelName());
#endif
connection->inputPublisherBlocked = true;
}
} else {
ALOGE("channel '%s' ~ Could not publish event due to an unexpected error, "
"status=%d", connection->getInputChannelName(), status);
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
}
return;
}
// Re-enqueue the event on the wait queue.
connection->outboundQueue.dequeue(dispatchEntry);
traceOutboundQueueLengthLocked(connection);
connection->waitQueue.enqueueAtTail(dispatchEntry);
traceWaitQueueLengthLocked(connection);
}
}
看TYPE_KEY分支,最后是通过publicKeyEvent方法将事件分发出去的。那么这里的inputPublisher是会呢,这个是InputTransport
status_t InputPublisher::publishKeyEvent(
uint32_t seq,
int32_t deviceId,
int32_t source,
int32_t action,
int32_t flags,
int32_t keyCode,
int32_t scanCode,
int32_t metaState,
int32_t repeatCount,
nsecs_t downTime,
nsecs_t eventTime) {
#if DEBUG_TRANSPORT_ACTIONS
ALOGD("channel '%s' publisher ~ publishKeyEvent: seq=%u, deviceId=%d, source=0x%x, "
"action=0x%x, flags=0x%x, keyCode=%d, scanCode=%d, metaState=0x%x, repeatCount=%d,"
"downTime=%lld, eventTime=%lld",
mChannel->getName().string(), seq,
deviceId, source, action, flags, keyCode, scanCode, metaState, repeatCount,
downTime, eventTime);
#endif
if (!seq) {
ALOGE("Attempted to publish a key event with sequence number 0.");
return BAD_VALUE;
}
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::TYPE_KEY;
msg.body.key.seq = seq;
msg.body.key.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.key.source = source;
msg.body.key.action = action;
msg.body.key.flags = flags;
msg.body.key.keyCode = keyCode;
msg.body.key.scanCode = scanCode;
msg.body.key.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.key.repeatCount = repeatCount;
msg.body.key.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.key.eventTime = eventTime;
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
size_t msgLength = msg->size();
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
nWrite = ::send(mFd, msg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
最终是通过调用了linux的多进程通信的方式将事件发送给主线程中的view, 这个机制不在本章讨论范围内,大概的实现就是要建立两个channel, 用来通信,我们这里的inputdispatch相当于一个channel用来分发事件,还有一个通来接收,在android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp中。
4.Java层接受事件消息
我们先从Java层建立接收的receiver开始,在ViewRootImpl的setView方法中会看建立 InputChannel和WindowInputEventReceiver
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
......
// Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window
// manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving
// any other events from the system.
requestLayout();
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
......
if (mInputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());
}
......
InputStage nativePostImeStage = new NativePostImeInputStage(viewPostImeStage,
"aq:native-post-ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage earlyPostImeStage = new EarlyPostImeInputStage(nativePostImeStage);
InputStage imeStage = new ImeInputStage(earlyPostImeStage,
"aq:ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage viewPreImeStage = new ViewPreImeInputStage(imeStage);
InputStage nativePreImeStage = new NativePreImeInputStage(viewPreImeStage,
"aq:native-pre-ime:" + counterSuffix);
}
}
}
WindowInputEventReceiver是继承自InputEventReceiver,我们直接看InputEventReceiver在nativie层的实现,android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp,这里有个addFd的机制,这个会不断的回调handleEvent,这人机制在以下文章有说明
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012860933
在向上走到java层最后调用的方法是android_view_InputEventReceiver中consumeEvents
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents(JNIEnv* env,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, bool* outConsumedBatch) {
......
for (;;) {
uint32_t seq;
InputEvent* inputEvent;
status_t status = mInputConsumer.consume(&mInputEventFactory,
consumeBatches, frameTime, &seq, &inputEvent);
......
if (inputEventObj) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dispatching input event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),
gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
ALOGE("Exception dispatching input event.");
skipCallbacks = true;
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputEventObj);
} else {
ALOGW("channel '%s' ~ Failed to obtain event object.",
getInputChannelName().c_str());
skipCallbacks = true;
}
}
......
}
}
其中mInputConsumer.consume还是在InputTransport.cpp中
status_t InputConsumer::consume(InputEventFactoryInterface* factory,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, uint32_t* outSeq, InputEvent** outEvent) {
#if DEBUG_TRANSPORT_ACTIONS
ALOGD("channel '%s' consumer ~ consume: consumeBatches=%s, frameTime=%lld",
mChannel->getName().string(), consumeBatches ? "true" : "false", frameTime);
#endif
*outSeq = 0;
*outEvent = NULL;
// Fetch the next input message.
// Loop until an event can be returned or no additional events are received.
while (!*outEvent) {
if (mMsgDeferred) {
// mMsg contains a valid input message from the previous call to consume
// that has not yet been processed.
mMsgDeferred = false;
} else {
// Receive a fresh message.
status_t result = mChannel->receiveMessage(&mMsg);
if (result) {
// Consume the next batched event unless batches are being held for later.
if (consumeBatches || result != WOULD_BLOCK) {
result = consumeBatch(factory, frameTime, outSeq, outEvent);
if (*outEvent) {
#if DEBUG_TRANSPORT_ACTIONS
ALOGD("channel '%s' consumer ~ consumed batch event, seq=%u",
mChannel->getName().string(), *outSeq);
#endif
break;
}
}
return result;
}
}
......
}
会从InputChannelmChannel->receiveMessage(&mMsg);获取从linux传过来的事件消息,然后再调用env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj)(android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp);回调给InputEventReceiver
InputEventReceiver.java
// Called from native code.
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event) {
mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);
onInputEvent(event);
}

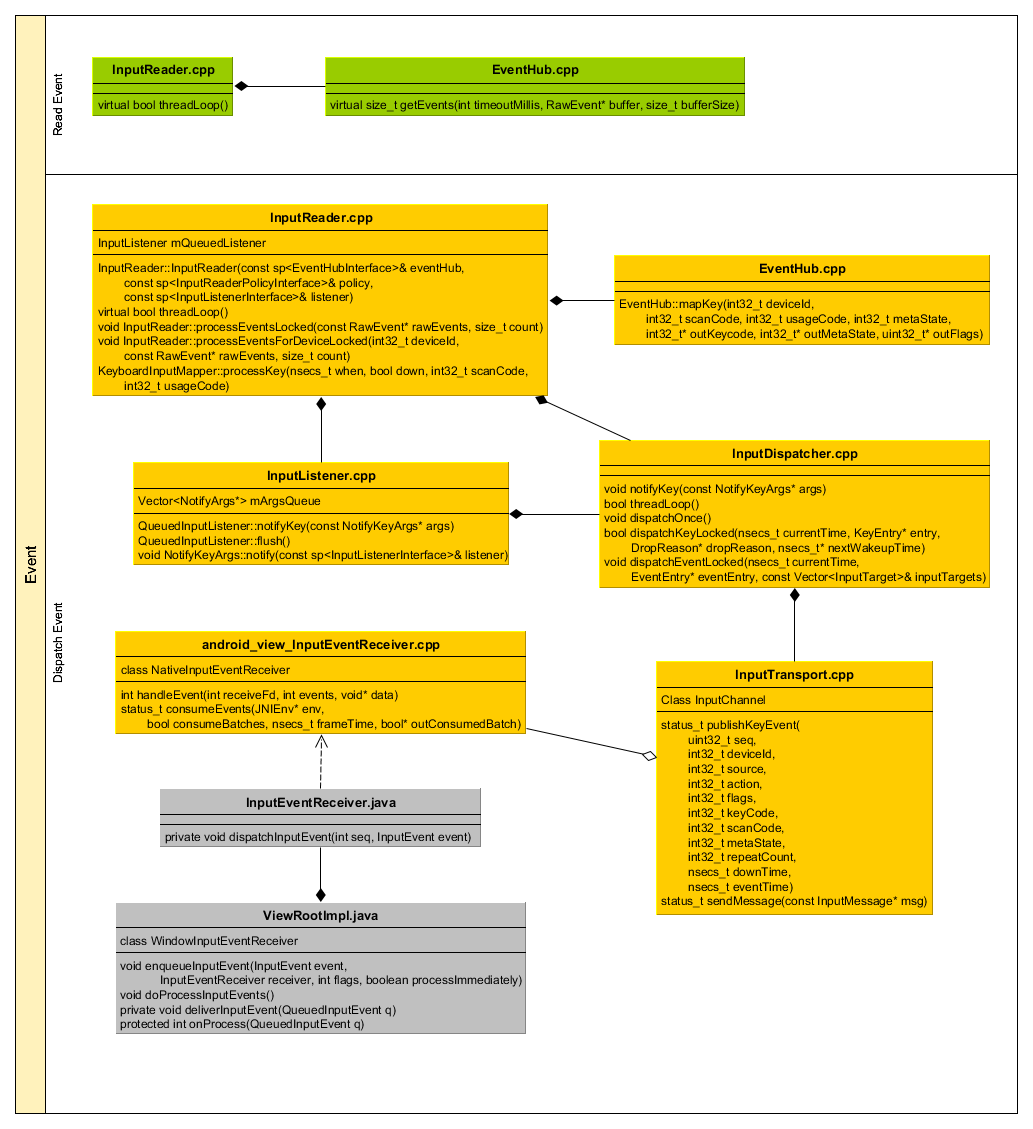
至此,java层就收到事件消息,以下是涉及的所有类



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号