linux预习3 文件操作
1.设备文件:/dev/console系统控制台;/dev/tty控制终端的别名(键盘和显示器);/dev/null空设备
2.系统调用:open,read,write,close,ioctl;把控制信息传递给设备驱动程序
write (int fildes, const void *buf, size_t nbytes)(文件,buf缓冲区内容,大小)
read(int fildes, viod *buf, size_t nbytes)(将与fildes相关联的文件读入n个)
open 通过path或者oflags(O_RDONLY; O_WRONLY; O_RDWR) /O_APPEND将写入的数据添加在末尾;
O_TRUNC文件长度设置为0;
O_CREAT 打开文件,如果不存在则创建文件;后接权限:
S_I(R, W, X)(USR,GRP,OTH)
复制文件eg:
#include <unidtd.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(){
char c;
int in, out;
in=open("file.in", O_RDONLY);
out=open("file.in",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR);
while(read(in,&c,1)==1)
write(out,&c,1);
exit(0);
}
3. fstat:通过文件描述符与打开调用的文件相关的文件的状态信息
stat:通过文件名,返回连接指向的文件信息
lstat:通过文件名,连接本身的信息
dup提供了一种复制文件描述符的方法,使我们能够通过两个或多个不同的描述符来访问同一个文件
dup2通过明确指定目标描述符来把一个文件描述符复制给另一个文件描述符;
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int fildes);
int dup2(int fildes, int fildes2);
4.标准I/O库
1. fopen 'r'只读,‘w’写并把文件截短为0;‘a’写,新内容追加在末尾;‘r+’以更新方式打开
2.fflush 清理缓冲区;
格式化输入输出:
printf:
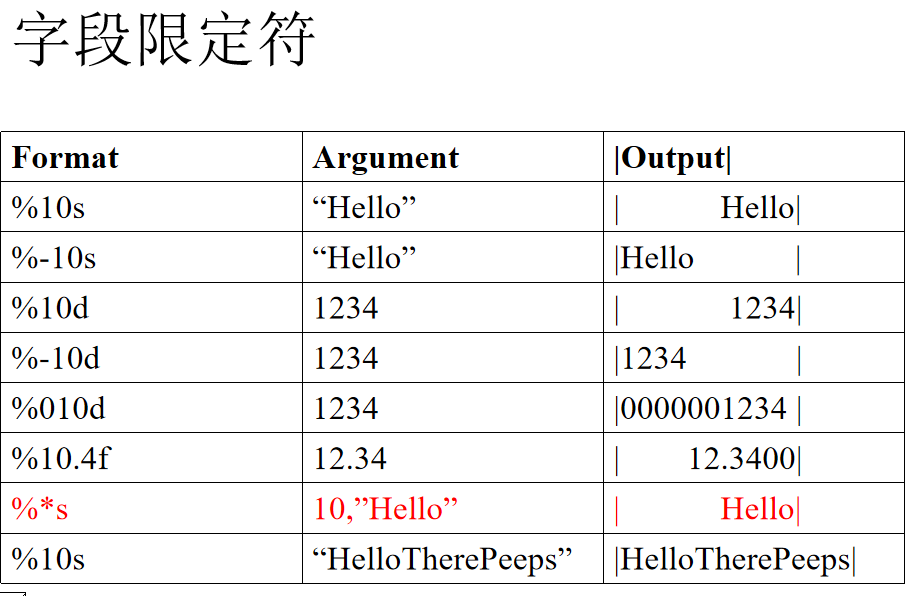
sscanf(从字符串中读取)eg: sscanf("2015.04.05", "%d.%d.%d", &a,&b,&c); //取需要的字符串
5.文件流错误:ferror函数测试文件流的错误标识,feof测试文件流的文件尾标识
6.目录扫描:eg
void printdir(char *dir, int depth)
{
DIR *dp; //目录流指针
struct dirent *entry;//目录项,包含d_ino(文件的inode节点号),d_name[]文件的名字
struct stat statbuf;//通过文件名,返回连接指向的文件信息
if((dp = opendir(dir)) == NULL) {//opendir 打开一个目录并建立目录流
fprintf(stderr,"cannot open directory: %s\n", dir);//用fprintf写入stderr
return;
}
chdir(dir);//系统调用,进入dir所指向的目录
while((entry = readdir(dp)) != NULL) {//readdir函数将目录项传给entry,判断目录是否为空
lstat(entry->d_name,&statbuf);//文件的名字,让statbuf连接
if(S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode)) {//判断statbuf是否是目录,st_mode文件权限和类型信息
/* Found a directory, but ignore . and .. */
if(strcmp(“.”,entry->d_name) == 0 ||
strcmp(“..”,entry->d_name) == 0)
continue;
printf(“%*s%s/\n”,depth,“ ”,entry->d_name);//derth 控制缩进的长短
/* Recurse at a new indent level */
printdir(entry->d_name,depth+4);//进入该目录
}
else printf(“%*s%s\n”,depth,“ ”,entry->d_name);
}
chdir(“..”);//回到上层目录
closedir(dp);}//少开点目录
int main()
{
printf("Directory scan of /home:\n");
printdir("/home",0);
printf("done.\n");
exit(0);
}
错误处理:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号