【中英】【吴恩达课后测验】Course 5 - 序列模型 - 第三周测验 - 序列模型与注意力机制
【中英】【吴恩达课后测验】Course 5 - 序列模型 - 第三周测验 - 序列模型与注意力机制
-
想一想使用如下的编码-解码模型来进行机器翻译:
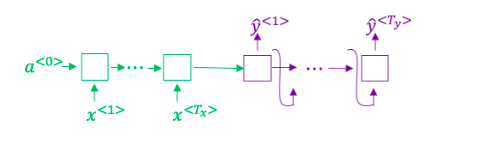
这个模型是“条件语言模型”,编码器部分(绿色显示)的意义是建模中输入句子x的概率 -
在集束搜索中,如果增加集束宽度\(b\),以下哪一项是正确的?
-
在机器翻译中,如果我们在不使用句子归一化的情况下使用集束搜索,那么算法会输出过短的译文。
-
假设你正在构建一个能够让语音片段\(x\)转为译文\(y\)的基于RNN模型的语音识别系统,你的程序使用了集束搜索来试着找寻最大的\(P(y|x)\)的值\(y\)。在开发集样本中,给定一个输入音频,你的程序会输出译文\(\hat{y} =\) "I'm building an A Eye system in Silly con Valley.",人工翻译为\(y^* =\) "I'm building an AI system in Silicon Valley."
在你的模型中,
\(P(\hat{y} \mid x) = 1.09*10^{-7}\)
\(P(y^* \mid x) = 7.21*10^{-8}\)
那么,你会增加集束宽度\(B\)来帮助修正这个样本吗?
博主注:皮这一下好开心~(~ ̄▽ ̄)~
-
接着使用第4题那里的样本,假设你花了几周的时间来研究你的算法,现在你发现,对于绝大多数让算法出错的例子而言,\(P(y^* \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)\),这表明你应该将注意力集中在改进搜索算法上,对吗?
-
回想一下机器翻译的模型:
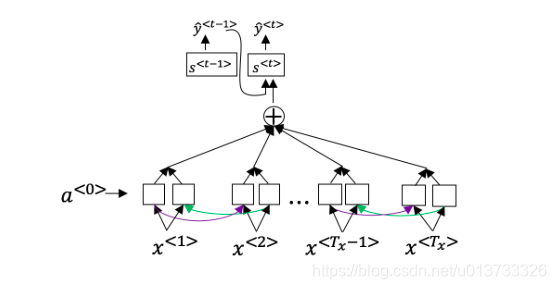
除此之外,还有个公式 \(a^{<t,t'>} = \frac{\text{exp}(e^{<t,t'>})}{\sum^{T_x}_{t'=1}\text{exp}(e^{<t,t'>})}\)下面关于 \(\alpha^{<t,t’>}\) 的选项那个(些)是正确的?
-
网络通过学习的值\(e^{<t,t'>}\)来学习在哪里关注“关注点”,这个值是用一个小的神经网络的计算出来的:
这个神经网络的输入中,我们不能将 \(s^{<t>}\)替换为\(s^{<t-1>}\)。这是因为\(s^{<t>}\)依赖于\(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\),而\(\alpha^{<t,t'>}\)又依赖于\(e^{<t,t'>}\);所以在我们需要评估这个网络时,我们还没有计算出\(s^{t}\)。
-
与题1中的编码-解码模型(没有使用注意力机制)相比,我们希望有注意力机制的模型在下面的情况下有着最大的优势:
9.在CTC模型下,不使用"空白"字符(_)分割的相同字符串将会被折叠。那么在CTC模型下,以下字符串将会被折叠成什么样子?__c_oo_o_kk___b_ooooo__oo__kkk
- 在触发词检测中, \(x^{<t>}\) 是:
Sequence models & Attention mechanism
- Consider using this encoder-decoder model for machine translation.

- [x] No, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the RNN rather than to the search algorithm.
- [ ] No, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the search algorithm rather than to the RNN.
- [ ] Yes, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the RNN rather than to the search algorithm.
- [ ] Yes, because $P(y^∗ \mid x) \leq P(\hat{y} \mid x)$ indicates the error should be attributed to the search algorithm rather than to the RNN.
- Continuing the example from Q4, suppose you work on your algorithm for a few more weeks, and now find that for the vast majority of examples on which your algorithm makes a mistake, \(P(y^∗ \mid x) > P(\hat{y} \mid x)\). This suggest you should focus your attention on improving the search algorithm.
- Consider the attention model for machine translation.

Further, here is the formula for \(\alpha^{<t,t′>}\).
Which of the following statements about \(\alpha^{<t,t′>}\) are true? Check all that apply.
-
The network learns where to “pay attention” by learning the values e<t,t′>, which are computed using a small neural network:
We can't replace \(s^{<t-1>}\) with \(s^{<t>}\) as an input to this neural network. This is because \(s^{<t>}\) depends on \(\alpha^{<t,t′>}\) which in turn depends on \(e^{<t,t′>}\); so at the time we need to evalute this network, we haven’t computed \(s^{<t>}\) yet.
- Compared to the encoder-decoder model shown in Question 1 of this quiz (which does not use an attention mechanism), we expect the attention model to have the greatest advantage when:
- Under the CTC model, identical repeated characters not separated by the "blank" character (_) are collapsed. Under the CTC model, what does the following string collapse to? __c_oo_o_kk___b_ooooo__oo__kkk
- In trigger word detection, \(x^{<t>}\) is:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号