普通生成函数
普通生成函数
定义
对于一个序列 \(a_0, a_1, a_2, a_3, ..., a_n\)
用一个函数表示它 \(G(x) = a_0 + a_1 \times x + a_2 \times x ^ 2 + ... + a_n \times x ^ n\)
称 \(G(x)\) 是序列的普通生成函数
普通生成函数用来解决多重集组合问题
问题
有 \(n\) 种物品,每种物品有 \(a_i\) 个,问取 \(m\) 个的组合数
构造普通生成函数 :
对于第 \(i\) 种物品,其生成函数为 \(\qquad G_i(x) = 1 + x + x ^ 2 + ... + x ^ {a_i}\)
求\(\qquad\prod_{i=1}^{n}G_i\)
得到了\(\qquad\sum_{j=0}^{m}b_jx^j \qquad (b_j为系数)\)
系数表示的是组合数,指数是选择的个数
如果问题为
有 \(n\) 种物品,每种物品有 \(a_i\) 个,每种物品至少取 \(c_i\) 个,问取 \(m\) 个的组合数
发现构成的生成函数为 \(\qquad G_i(x) = x ^ {c_i} + ... + x ^ {a_i}\)
同理,也可以得到答案
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
void solve() {
vector<int> cnt(m + 1);
cnt[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
auto old = cnt;
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j ++) {
cnt[j] = 0;
}
for (int j = a; j <= b; j ++) {
for (int k = 0; k + j <= m; k ++) {
cnt[k + j] += old[k];
}
}
}
cout << cnt[m] << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
while (cin >> n >> m) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
如果问题为
有一定数量的 \(1\)、\(2\)、\(5\) 三种面值的硬币,求组合可以达到的金额
可以用指数来表示可以选择的个数,然后将生成函数相乘,所有系数非 \(0\) 的是可以选到的值
形如
\(\qquad G_1(x) = 1 + x + x ^ 2 + ... + x ^ {a}\)
\(\qquad G_2(x) = 1 + x ^ 2+ x ^ 4 + ... + x ^ {b \times 2}\)
\(\qquad G_5(x) = 1 + x ^ 5 + x^{10} + ... + x ^ {c \times 5}\)
求得 \(G_1 \times G_2 \times G_5\)
如果系数非 \(0\) 则代表可以取到 (预处理时\(x^0\)的系数为\(1\))
小凯爱数学
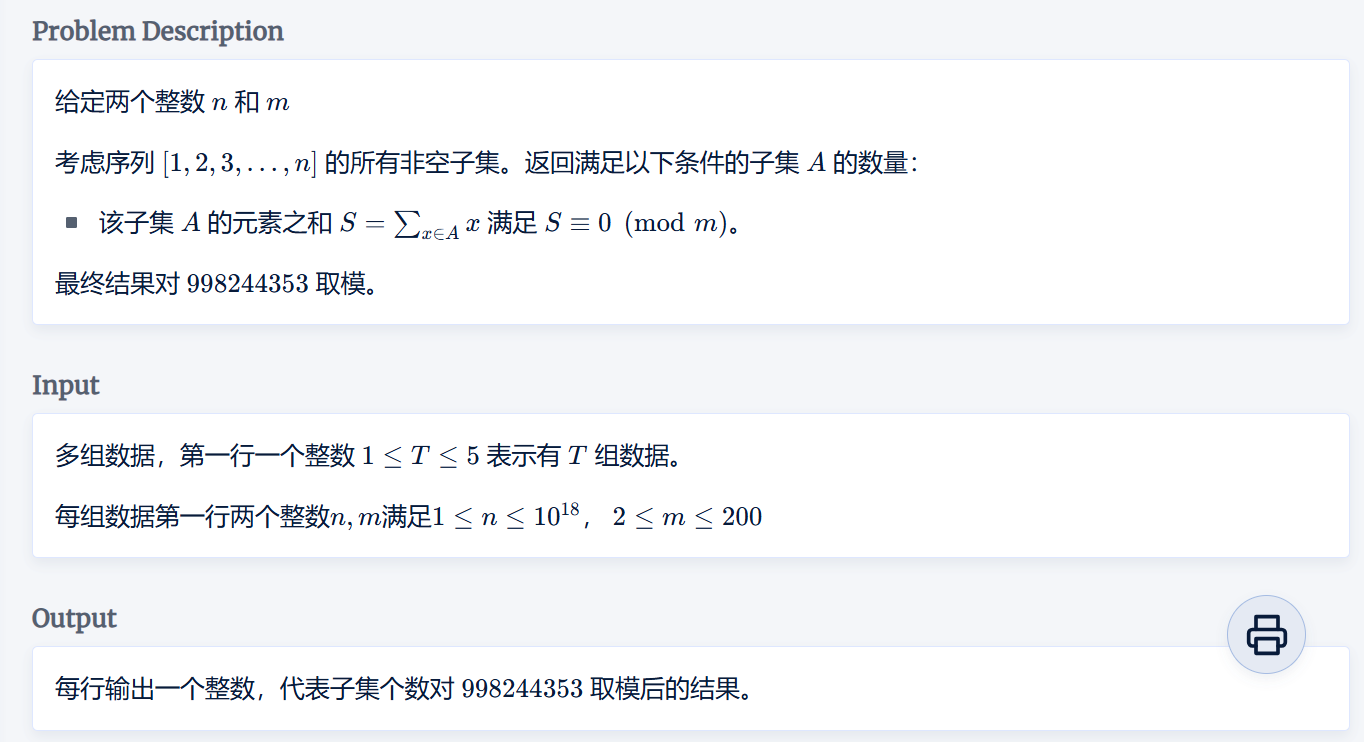
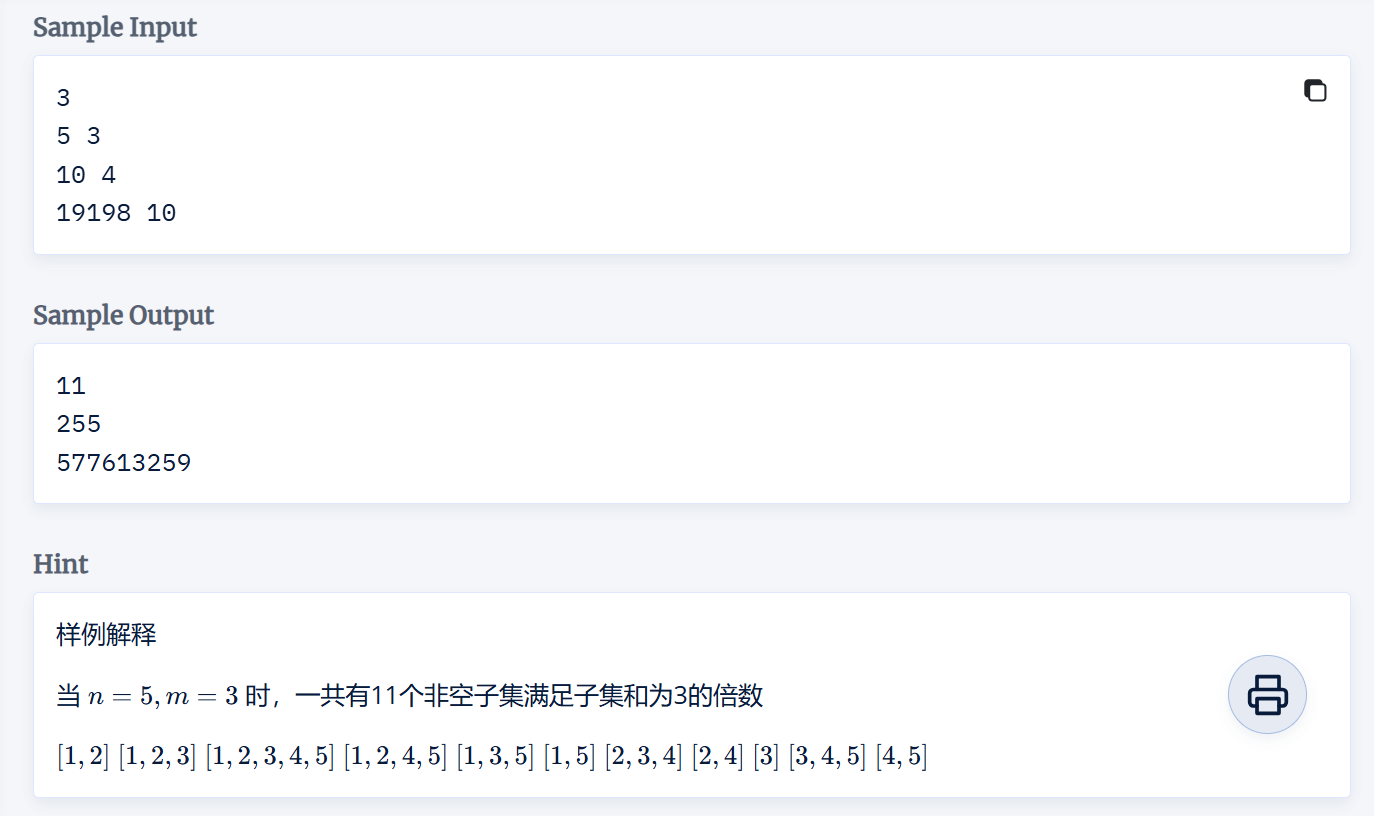
想求和为 \(S≡0(modm)\) 的组合数
\(m\) 相对较小,先求得余数为 \(0 \sim {m-1}\) 的数的个数
如果一个一个看的话,类似于 \(01\)背包问题,如果余数为 \(r\)
则生成函数为 \((1 + x^r)\)
最后得到的生成函数是 \(\prod_{i=0}^{m - 1}(1 + x^i)^{cnt_i}\)
这道题可以看作上方第三道例题的一种情况,因为 \(n\) 非常大,做一些优化来保证空间和时间
可以用类似快速幂的技巧,求得 \((1 + x^i)^{cnt_i}\) 的值
最终得到答案
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 998244353;
void times_g(vector<ll> &a, vector<ll> &b, int m) {
vector<ll> res(m, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
if (a[i] == 0) continue;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++) {
if (b[j] == 0) continue;
res[(i + j) % m] =(res[(i + j) % m] + a[i] * b[j]) % mod;
}
}
a = res;
}
void qmi_g(vector<ll> &q, vector<ll> &p, ll b, int m) {
vector<ll> res(m, 0);
res[0] = 1;
auto a = p;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) times_g(res, a, m);
times_g(a, a, m);
b >>= 1;
}
times_g(q, res, m);
}
void solve() {
ll n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<ll> cnt(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
cnt[i] = n / m;
if (i && n % m >= i) cnt[i] ++;
}
vector<ll> res(m, 0), a(m, 0);
res[0] = a[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
if (~(i - 1)) a[i - 1] --;
a[i] ++;
qmi_g(res, a, cnt[i], m);
}
cout << (res[0] - 1 + mod) % mod << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号