SpringMVC复习
SpringMVC
概述
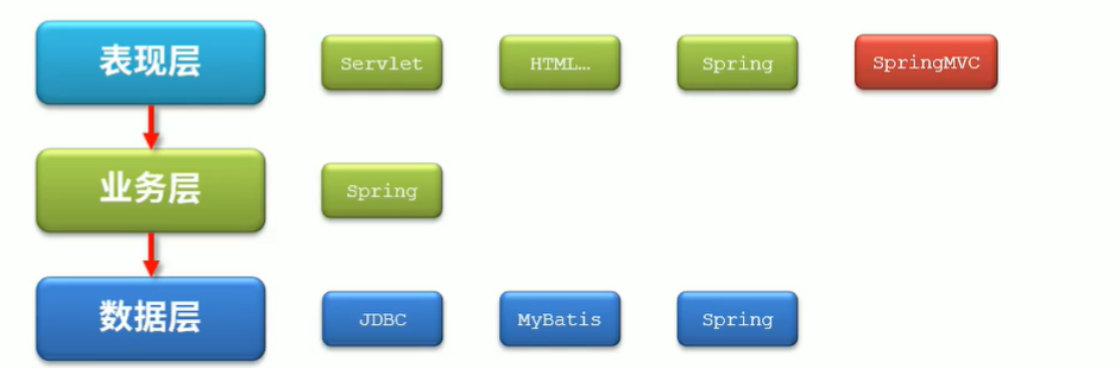
三层架构
- 表现层:负责数据展示
- 业务层:负责业务处理
- 数据层:负责数据操作
MVC
(Model View Controller),一种用于设计创建Web应用程序表现层的模式
-
Model(模型):数据模型,用于封装数据
-
View(视图):页面视图,用于展示数据
JSP
HTML
-
Controller(控制器):处理用户交互的调度器,用于根据用户需求处理程序逻辑
- Servlet
- SpringMVC
简介
- SpringMVC是一种基于Java实现的MVC模型的轻量级Web框架
优点
- 使用简单
- 性能突出(相比于现有框架技术)
- 灵活性强
SpringMVC技术架构图
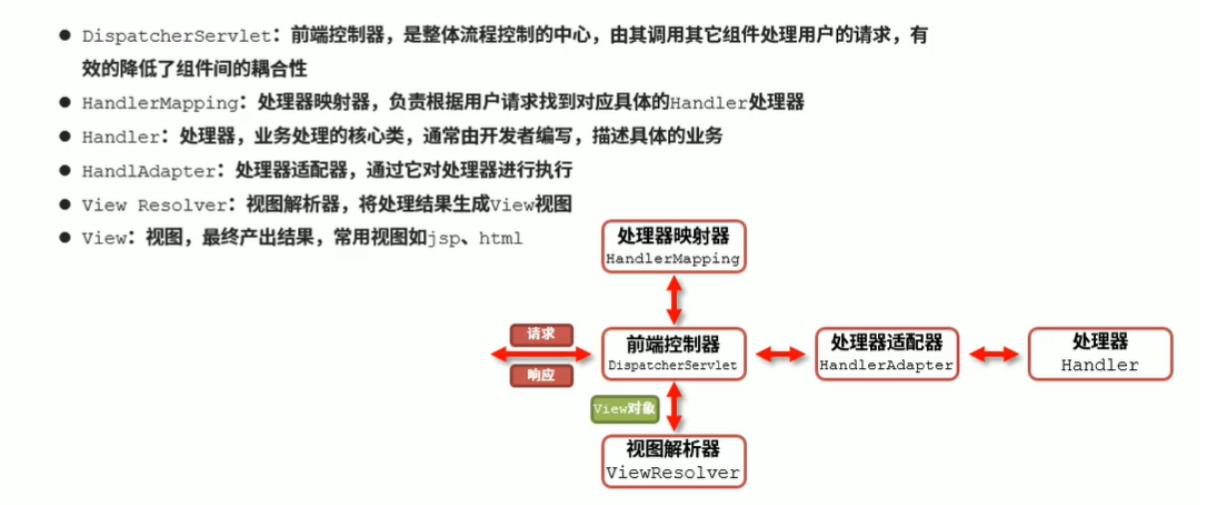
请求
参数名与处理器方法形参名保持一致
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam1?name=itheima&age=14
@RequestMapping("/requestParam1")
public String requestParam1(String name,int age){
System.out.println(name+","+age);
return "page.jsp";
}
请求参数类型
- 普通类型参数
- POJO类型参数
- 数组类型参数
- 集合类型参数
普通类型参数
//方法传递普通类型参数,数量任意,类型必须匹配
//http://localhost/requestParam1?name=itheima
//http://localhost/requestParam1?name=itheima&age=14
@RequestMapping("/requestParam1")
public String requestParam1(String name,int age){
System.out.println(name+","+age);
return "page.jsp";
}
如果请求链接上传的是username能不能映射name呢?http://localhost/requestParam1?userName=itheima
可以
@RequestParam 的使用
类型: 形参注解
位置:处理器类中的方法形参前方
作用:绑定请求参数与对应处理方法形参间的关系
@RequestMapping("/requestParam2")
public String requestParam2(@RequestParam(
name = "userName",
required = true,
defaultValue = "itheima") String name){
System.out.println("name="+name);
return "page.jsp";
}
POJO类型参数传参
当POJO中使用简单类型属性时, 参数名称与POJO类属性名保持一致
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam3?name=itheima&age=14
Controller
@RequestMapping("/requestParam3")
public String requestParam3(User user){
System.out.println("name="+user.getName());
return "page.jsp";
}
结果
User
POJO类
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
参数冲突
当POJO类型属性与其他形参出现同名问题时,将被同时赋值
建议使用@RequestParam注解进行区分
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam4?name=itheima&age=14
@RequestMapping("/requestParam4")
public String requestParam4(User user,String age){
System.out.println("user.age="+user.getAge()+",age="+age);
return "page.jsp";
}
结果
user=User{name='Jock', age=39, address=null, nick=null, addresses=null, addressMap=null},age=39
复杂POJO类型参数
当POJO中出现对象属性时,参数名称与对象层次结构名称保持一致
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam5?address.province=beijing
@RequestMapping("/requestParam5")
public String requestParam5(User user){
System.out.println("user.address="+user.getAddress().getProvince());
return "page.jsp";
}
结果
beijing
当POJO中出现List,保存对象数据,参数名称与对象层次结构名称保持一致,使用数组格式描述集合中对象的位置
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam7?addresses[0].province=bj&addresses[1].province=tj
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private List<Address> addresses;
}
public class Address {
private String province;
private String city;
private String address;
}
@RequestMapping("/requestParam7")
public String requestParam7(User user){
System.out.println("user.addresses="+user.getAddress());
return "page.jsp";
}
当POJO中出现Map,保存对象数据,参数名称与对象层次结构名称保持一致,使用映射格式描述集合中对象的位置
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam8?addressMap[’home’].province=bj&addressMap[’job’].province=tj
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Map<String,Address> addressMap;
}
public class Address {
private String province;
private String city;
private String address;
}
@RequestMapping("/requestParam8")
public String requestParam8(User user){
System.out.println("user.addressMap="+user.getAddressMap());
return "page.jsp";
}
数组与集合类型参数传参
数组类型参数
请求参数名与处理器方法形参名保持一致,且请求参数数量> 1个
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam9?nick=Jockme&nick=zahc
@RequestMapping("/requestParam9")
public String requestParam9(String[] nick){
System.out.println(nick[0]+","+nick[1]);
return "page.jsp";
}
集合类型参数
保存简单类型数据,请求参数名与处理器方法形参名保持一致,且请求参数数量> 1个
访问URL: http://localhost/requestParam10?nick=Jockme&nick=zahc
@RequestMapping("/requestParam10")
public String requestParam10(@RequestParam("nick") List<String> nick){
System.out.println(nick);
return "page.jsp";
}
注意: SpringMVC默认将List作为对象处理,赋值前先创建对象,然后将nick作为对象的属性进行处理。由于
List是接口,无法创建对象,报无法找到构造方法异常;修复类型为可创建对象的ArrayList类型后,对象可
以创建,但没有nick属性,因此数据为空。此时需要告知SpringMVC的处理器nick是一组数据,而不是一个单
一数据。通过@RequestParam注解,将数量大于1个names参数打包成参数数组后, SpringMVC才能识别该数
据格式,并判定形参类型是否为数组或集合,并按数组或集合对象的形式操作数据。
请求映射 @RequestMapping
方法注解
名称: @RequestMapping
类型: 方法注解
位置:处理器类中的方法定义上方
作用:绑定请求地址与对应处理方法间的关系
范例:
访问路径: /requestURL1
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/requestURL2")
public String requestURL2() {
return "page.jsp";
}
}
类注解
名称: @RequestMapping
类型: 类注解
位置:处理器类定义上方
作用:为当前处理器中所有方法设定公共的访问路径前缀
范例:
访问路径: /user/requestURL1
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/requestURL2")
public String requestURL2() {
return "page.jsp";
}
}
RequestMapping属性

响应
页面跳转
- 转发(默认)
@RequestMapping("/showPage1")
public String showPage1() {
System.out.println("user mvc controller is running ...");
return "forward:page.jsp";
}
- 重定向
@RequestMapping("/showPage2")
public String showPage2() {
System.out.println("user mvc controller is running ...");
return "redirect:page.jsp";
}
注意:页面访问地址中所携带的 /
页面访问快捷设定 (InternalResourceViewResolver)
展示页面的保存位置通常固定,且结构相似,可以设定通用的访问路径,简化页面配置格式
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
/bean>
public String showPage3() {
return "page";
}
如果未设定了返回值,使用void类型,则默认使用访问路径作页面地址的前缀后缀
//最简页面配置方式,使用访问路径作为页面名称,省略返回值
@RequestMapping("/showPage5")
public void showPage5() {
System.out.println("user mvc controller is running ...");
}
注意:设置了快捷访问后不支持前面加 return "forward:page" 这种
带数据页面跳转
- 方式一:使用HttpServletRequest类型形参进行数据传递
@RequestMapping("/showPageAndData1")
public String showPageAndData1(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute("name","itheima");
return "page";
}
- 方式二:使用Model类型形参进行数据传递
@RequestMapping("/showPageAndData2")
public String showPageAndData2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name","itheima");
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("SpringMVC入门实战");
book.setPrice(66.6d);
model.addAttribute("book",book);
return "page";
}
- 方式三:使用ModelAndView类型形参进行数据传递,将该对象作为返回值传递给调用者
//使用ModelAndView形参传递参数,该对象还封装了页面信息
@RequestMapping("/showPageAndData3")
public ModelAndView showPageAndData3(ModelAndView modelAndView) {
//ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(); 替换形参中的参数
Book book = new Book();
book.setName("SpringMVC入门案例");
book.setPrice(66.66d);
//添加数据的方式,key对value
modelAndView.addObject("book",book);
//添加数据的方式,key对value
modelAndView.addObject("name","Jockme");
//设置页面的方式,该方法最后一次执行的结果生效
modelAndView.setViewName("page");
//返回值设定成ModelAndView对象
return modelAndView;
}
返回Json数据
-
方式一:基于response返回数据的简化格式,返回JSON数据
//使用jackson进行json数据格式转化 @RequestMapping("/showData3") @ResponseBody public String showData3() throws JsonProcessingException { Book book = new Book(); book.setName("SpringMVC入门案例"); book.setPrice(66.66d); ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper(); return om.writeValueAsString(book); }
@ResponseBody注解的控制器方法进行结果转换,由于返回值为引用类型,自动调用jackson提供的类型转换器进行格式转换
-
使用SpringMVC提供的消息类型转换器将对象与集合数据自动转换为JSON数据
//使用SpringMVC注解驱动,对标注@ResponseBody注解的控制器方法进行结果转换,由于返回值为引用类型,自动调用jackson提供的类型转换器进行格式转换 @RequestMapping("/showData4") @ResponseBody public Book showData4() { Book book = new Book(); book.setName("SpringMVC入门案例"); book.setPrice(66.66d); return book; }需要手工添加信息类型转换器
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"> <property name="messageConverters"> <list> <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"/> </list> </property> </bean -
方式三:使用SpringMVC注解驱动简化配置
<!--开启springmvc注解驱动,对@ResponseBody的注解进行格式增强,追加其类型转换的功能,具体实现由MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter进行-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
Servlet相关接口-Servlet相关接口替换方案
HttpServletRequest / HttpServletResponse / HttpSession
-
SpringMVC提供访问原始Servlet接口API的功能,通过形参声明即可
@RequestMapping("/servletApi") public String servletApi(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session){ System.out.println(request); System.out.println(response); System.out.println(session); request.setAttribute("name","itheima"); System.out.println(request.getAttribute("name")); return "page.jsp"; } -
Head数据获取
名称: @RequestHeader
类型: 形参注解
位置:处理器类中的方法形参前方
作用:绑定请求头数据与对应处理方法形参间的关系
范例:@RequestMapping("/headApi") public String headApi(@RequestHeader("Accept-Language") String head){ System.out.println(head); return "page.jsp"; } -
Cookie数据获取
名称: @CookieValue
类型: 形参注解
位置:处理器类中的方法形参前方
作用:绑定请求Cookie数据与对应处理方法形参间的关系
范例:@RequestMapping("/cookieApi") public String cookieApi(@CookieValue("JSESSIONID") String jsessionid){ System.out.println(jsessionid); return "page.jsp"; } -
Session数据获取
名称: @SessionAttribute
类型: 形参注解
位置:处理器类中的方法形参前方
作用:绑定请求Session数据与对应处理方法形参间的关系
范例:@RequestMapping("/sessionApi") public String sessionApi(@SessionAttribute("name") String name){ System.out.println(name); return "page.jsp"; } -
Session数据设置(了解)
名称: @SessionAttributes
类型: 类注解
位置:处理器类上方
作用:声明放入session范围的变量名称,适用于Model类型数据传参
范例:@Controller @SessionAttributes(names={"name"}) public class ServletController { @RequestMapping("/setSessionData2") public String setSessionDate2(Model model) { model.addAttribute("name", "Jock2"); return "page.jsp"; } } -
注解式参数数据封装底层原理
数据的来源不同,对应的处理策略要进行区分
Head
Cookie
Session
SpringMVC使用策略模式进行处理分发
顶层接口: HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
实现类: ……
异步调用
发送异步请求(回顾)
<a href="javascript:void(0);" id="testAjax">访问controller</a>
<script type="text/javascript" src="/js/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function(){
$("#testAjax").click(function(){ //为id="testAjax"的组件绑定点击事件
$.ajax({ //发送异步调用
type:"POST", //请求方式: POST请求
url:"ajaxController", //请求参数(也就是请求内容)
data:'ajax message', //请求参数(也就是请求内容)
dataType:"text", //响应正文类型
contentType:"application/text", //请求正文的MIME类型
});
});
});
</script>
@RequestBody
名称: @RequestBody
类型: 形参注解
位置:处理器类中的方法形参前方
作用:将异步提交数据组织成标准请求参数格式,并赋值给形参
范例:
@RequestMapping("/ajaxController")
public String ajaxController(@RequestBody String message){
System.out.println(message);
return "page.jsp";
}
- 注解添加到Pojo参数前方时,封装的异步提交数据按照Pojo的属性格式进行关系映射
- 注解添加到集合参数前方时,封装的异步提交数据按照集合的存储结构进行关系映射
@RequestMapping("/ajaxPojoToController")
//如果处理参数是POJO,且页面发送的请求数据格式与POJO中的属性对应,@RequestBody注解可以自动映射对应请求数据到POJO中
//注意:POJO中的属性如果请求数据中没有,属性值为null,POJO中没有的属性如果请求数据中有,不进行映射
public String ajaxPojoToController(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("controller pojo :"+user);
return "page.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("/ajaxListToController")
//如果处理参数是List集合且封装了POJO,且页面发送的数据是JSON格式的对象数组,数据将自动映射到集合参数中
public String ajaxListToController(@RequestBody List<User> userList){
System.out.println("controller list :"+userList);
return "page.jsp";
}
异步请求接受响应数据
- 方法返回值为Pojo时,自动封装数据成json对象数据
@RequestMapping("/ajaxReturnJson")
@ResponseBody
public User ajaxReturnJson(){
System.out.println("controller return json pojo...");
User user = new User();
user.setName("Jockme");
user.setAge(40);
return user;
}
- 方法返回值为List时,自动封装数据成json对象数组数据
@RequestMapping("/ajaxReturnJsonList")
@ResponseBody
//基于jackon技术,使用@ResponseBody注解可以将返回的保存POJO对象的集合转成json数组格式数据
public List ajaxReturnJsonList(){
System.out.println("controller return json list...");
User user1 = new User();
user1.setName("Tom");
user1.setAge(3);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setName("Jerry");
user2.setAge(5);
ArrayList al = new ArrayList();
al.add(user1);
al.add(user2);
return al;
}
异步请求-跨域访问
- 当通过域名A下的操作访问域名B下的资源时,称为跨域访问
- 跨域访问时,会出现无法访问的现象

跨域环境搭建
- 为当前主机添加备用域名
- 修改windows安装目录中的host文件
- 格式: ip 域名
- 动态刷新DNS
- 命令: ipconfig /displaydns
- 命令: ipconfig /flushdns
跨域访问支持
名称: @CrossOrigin
类型: 方法注解 、 类注解
位置:处理器类中的方法上方 或 类上方
作用:设置当前处理器方法/处理器类中所有方法支持跨域访问
范例:
@RequestMapping("/cross")
@ResponseBody
//使用@CrossOrigin开启跨域访问
//标注在处理器方法上方表示该方法支持跨域访问
//标注在处理器类上方表示该处理器类中的所有处理器方法均支持跨域访问
@CrossOrigin
public User cross(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("controller cross..."+request.getRequestURL());
User user = new User();
user.setName("Jockme");
user.setAge(39);
return user;
}
拦截器
拦截器概念
- 请求处理过程解析
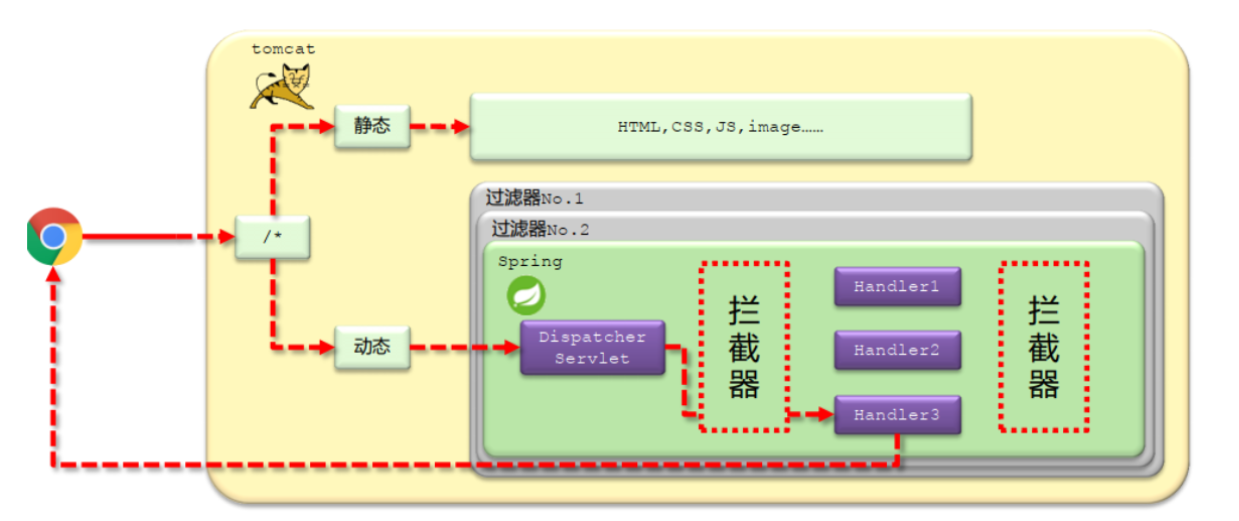
拦截器:是一种动态拦截方法调用的机制
作用:
- 在指定的方法调用前后执行预先设定好的代码
- 阻止原始方法的执行
核心原理:AOP思想
拦截器链:多个拦截器按照一定的顺序,对原始被调用功能进行增强
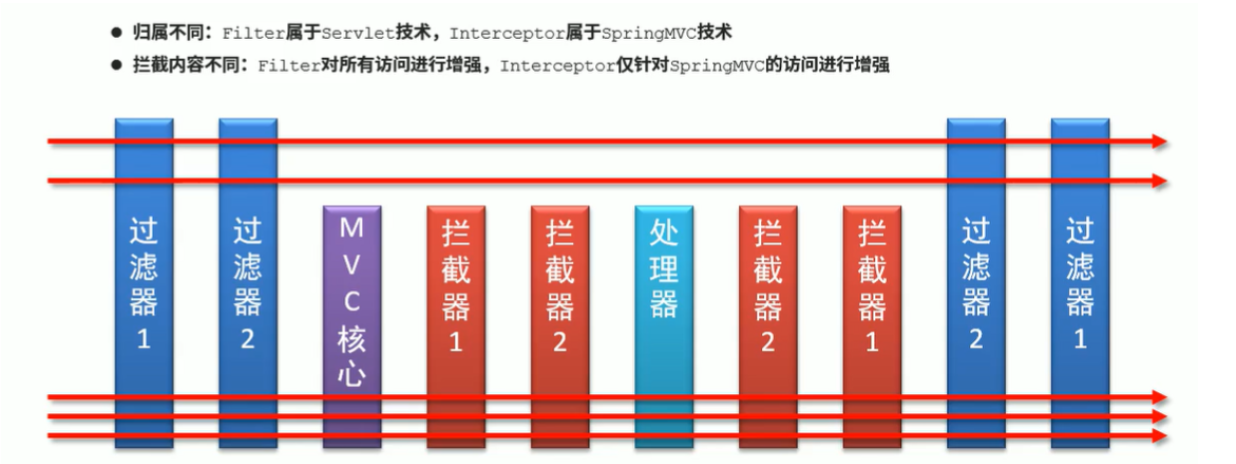
三个方法的运行顺序为 preHandle -> postHandle -> afterCompletion
如果preHandle返回值为false,三个方法仅运行preHandle
参数
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, //对请求响应做操作
Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView, //对结果修正
Exception ex //异常处理
拦截器配置
<!--开启拦截器使用-->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--开启具体的拦截器的使用,可以配置多个-->
<mvc:interceptor>
<!--设置拦截器的拦截路径,支持*通配-->
<!--/** 表示拦截所有映射-->
<!--/* 表示拦截所有/开头的映射-->
<!--/user/* 表示拦截所有/user/开头的映射-->
<!--/user/add* 表示拦截所有/user/开头,且具体映射名称以add开头的映射-->
<!--/user/*All 表示拦截所有/user/开头,且具体映射名称以All结尾的映射-->
<mvc:mapping path="/*"/>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<mvc:mapping path="/handleRun*"/>
<!--设置拦截排除的路径,配置/**或/*,达到快速配置的目的-->
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/b*"/>
<!--指定具体的拦截器类-->
<bean class="MyInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
<!--配置多个拦截器,配置顺序即为最终运行顺序-->
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/*"/>
<bean class="MyInterceptor2"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/*"/>
<bean class="MyInterceptor3"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
异常处理
HandlerExceptionResolver接口(异常处理器)
@Component
public class ExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler,
Exception ex) {
System.out.println("异常处理器正在执行中");
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//定义异常现象出现后,反馈给用户查看的信息
modelAndView.addObject("msg","出错啦! ");
//定义异常现象出现后,反馈给用户查看的页面
modelAndView.setViewName("error.jsp");
return modelAndView;
}
}
根据异常的种类不同,进行分门别类的管理,返回不同的信息
public class ExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler,
Exception ex) {
System.out.println("my exception is running ...."+ex);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
if( ex instanceof NullPointerException){
modelAndView.addObject("msg","空指针异常");
}else if ( ex instanceof ArithmeticException){
modelAndView.addObject("msg","算数运算异常");
}else{
modelAndView.addObject("msg","未知的异常");
}
modelAndView.setViewName("error.jsp");
return modelAndView;
}
}
注解开发异常管理器
- 使用注解实现异常分类管理
名称: @ControllerAdvice
类型: 类注解
位置:异常处理器类上方
作用:设置当前类为异常处理器类
范例:
@Component
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionAdvice {
}
- 使用注解实现异常分类管理
名称: @ExceptionHandler
类型: 方法注解
位置:异常处理器类中针对指定异常进行处理的方法上方
作用:设置指定异常的处理方式
范例:
说明:处理器方法可以设定多个
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public String doOtherException(Exception ex){
return "出错啦,请联系管理员! ";
}
异常处理解决方案
异常处理方案
- 业务异常:
发送对应消息传递给用户,提醒规范操作 - 系统异常:
发送固定消息传递给用户,安抚用户
发送特定消息给运维人员,提醒维护
记录日志 - 其他异常:
发送固定消息传递给用户,安抚用户
发送特定消息给编程人员,提醒维护
纳入预期范围内
记录日志
自定义异常
-
异常定义格式
//自定义异常继承RuntimeException,覆盖父类所有的构造方法 public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException { public BusinessException() { } public BusinessException(String message) { super(message); } public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public BusinessException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } } -
异常触发方式
if(user.getName().trim().length()<4) { throw new BusinessException("用户名长度必须在2-4位之间,请重新输入! "); } -
通过自定义异常将所有的异常现象进行分类管理,以统一的格式对外呈现异常消息
文件上传下载
坐标
<!--文件上传下载-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
jsp页面
<%@page pageEncoding="UTF-8" language="java" contentType="text/html;UTF-8" %>
<form action="/fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<%--文件上传表单的name属性值一定要与controller处理器中方法的参数对应,否则无法实现文件上传--%>
上传LOGO:<input type="file" name="file"/><br/>
上传照片:<input type="file" name="file1"/><br/>
上传任意文件:<input type="file" name="file2"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="上传"/>
</form>
enctype="multipart/form-data" 开启文件上传下载
spring-mvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"/>
<!--配置文件上传处理器-->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="1024000000"/>
</bean>
</beans>
-
MultipartResolver接口
- MultipartResolver接口定义了文件上传过程中的相关操作,并对通用性操作进行了封装
- MultipartResolver接口底层实现类CommonsMultipartResovler
- CommonsMultipartResovler并未自主实现文件上传下载对应的功能,而是调用了apache的文件上传下载组件
<dependency> <groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId> <artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId> <version>1.4</version> </dependency> -
文件上传下载实现
-
页面表单
<form action="/fileupload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> 上传LOGO: <input type="file" name="file"/><br/> <input type="submit" value="上传"/> </form> -
SpringMVC配置
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> </bean> -
控制器
@RequestMapping(value = "/fileupload") public void fileupload(MultipartFile file){ file.transferTo(new File("file.png")); }
-
RestFul
Rest:一种网络资源的访问风格,定义了网络资源的 访问方式
-
传统风格访问路径
-
Rest风格访问路径
-
Restful是按照Rest风格访问网络资源
-
优点:
- 隐藏资源的访问行为,通过地址无法得知是何种操作
- 书写简化
-
Restful行为约定方式
- GET(查询) http://localhost/user/1 GET
- POST(保存) http://localhost/user POST
- PUT(更新) http://localhost/user PUT
- DELETE(删除) http://localhost/user DELETE
Restful开发入门
//设置rest风格的控制器
@RestController
//设置公共访问路径,配合下方访问路径使用
@RequestMapping("/user/")
public class UserController {
//rest风格访问路径完整书写方式
@RequestMapping("/user/{id}")
//使用@PathVariable注解获取路径上配置的具名变量,该配置可以使用多次
public String restLocation(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("restful is running ....");
return "success.jsp";
}
//rest风格访问路径简化书写方式,配合类注解@RequestMapping使用
@RequestMapping("{id}")
public String restLocation2(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("restful is running ....get:"+id);
return "success.jsp";
}
//接收GET请求配置方式
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
//接收GET请求简化配置方式
@GetMapping("{id}")
public String get(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("restful is running ....get:"+id);
return "success.jsp";
}
//接收POST请求配置方式
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.POST)
//接收POST请求简化配置方式
@PostMapping("{id}")
public String post(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("restful is running ....post:"+id);
return "success.jsp";
}
//接收PUT请求简化配置方式
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
//接收PUT请求简化配置方式
@PutMapping("{id}")
public String put(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("restful is running ....put:"+id);
return "success.jsp";
}
//接收DELETE请求简化配置方式
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
//接收DELETE请求简化配置方式
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("restful is running ....delete:"+id);
return "success.jsp";
}
}
<!--配置拦截器,解析请求中的参数_method,否则无法发起PUT请求与DELETE请求,配合页面表单使用-->
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
</filter-mapping>
开启SpringMVC对Restful风格的访问支持过滤器,即可通过页面表单提交PUT与DELETE请求
页面表单使用隐藏域提交请求类型,参数名称固定为_method,必须配合提交类型method=post使用
<form action="/user/1" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT"/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
-
Restful请求路径简化配置方式
@RestController public class UserController { @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) public String restDelete(@PathVariable String id){ System.out.println("restful is running ....delete:"+id); return "success.jsp"; } }
校验框架
校验框架入门
表单校验的重要性
- 表单校验保障了数据有效性、安全性
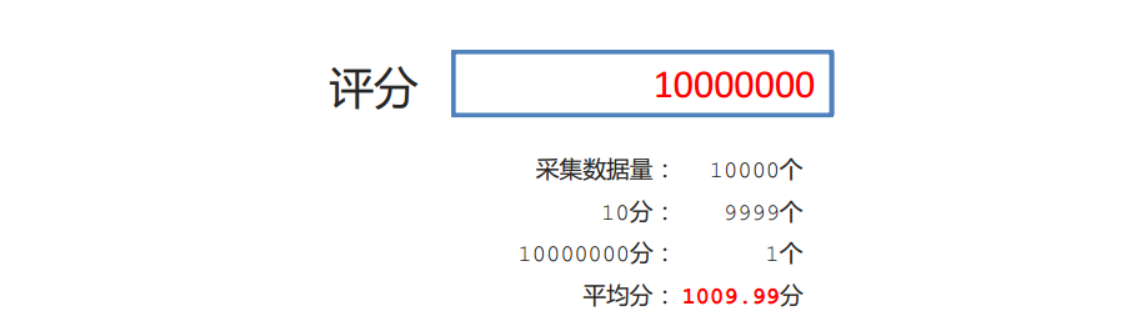
数据可以随意输入,导致错误的结果。后端表单校验的重要性。
表单校验分类
- 校验位置:
- 客户端校验
- 服务端校验
- 校验内容与对应方式:
- 格式校验
- 客户端:使用Js技术,利用正则表达式校验
- 服务端:使用校验框架
- 逻辑校验
- 客户端:使用ajax发送要校验的数据,在服务端完成逻辑校验,返回校验结果
- 服务端:接收到完整的请求后,在执行业务操作前,完成逻辑校验
- 格式校验
表单校验规则
- 长度:例如用户名长度,评论字符数量
- 非法字符:例如用户名组成
- 数据格式:例如Email格式、 IP地址格式
- 边界值:例如转账金额上限,年龄上下限
- 重复性:例如用户名是否重复
表单校验框架
-
JSR(Java Specification Requests):Java 规范提案
303:提供bean属性相关校验规则
-
JSR规范列表
- 企业应用技术
Contexts and Dependency Injection for Java (Web Beans 1.0) (JSR 299)
Dependency Injection for Java 1.0 (JSR 330)@postConstruct, @PreDestroy
Bean Validation 1.0 (JSR 303)
Enterprise JavaBeans 3.1 (includes Interceptors 1.1) (JSR 318)
Java EE Connector Architecture 1.6 (JSR 322)
Java Persistence 2.0 (JSR 317)
Common Annotations for the Java Platform 1.1 (JSR 250)
Java Message Service API 1.1 (JSR 914)
Java Transaction API (JTA) 1.1 (JSR 907)
JavaMail 1.4 (JSR 919) - Web应用技术
Java Servlet 3.0 (JSR 315)
JavaServer Faces 2.0 (JSR 314)
JavaServer Pages 2.2/Expression Language 2.2 (JSR 245)
Standard Tag Library for JavaServer Pages (JSTL) 1.2 (JSR 52)
Debugging Support for Other Languages 1.0 (JSR 45)
模块化 (JSR 294)
Swing应用框架 (JSR 296)
JavaBeans Activation Framework (JAF) 1.1 (JSR 925)
Streaming API for XML (StAX) 1.0 (JSR 173) - 管理与安全技术
Java Authentication Service Provider Interface for Containers (JSR 196)
Java Authorization Contract for Containers 1.3 (JSR 115)
Java EE Application Deployment 1.2 (JSR 88)
J2EE Management 1.1 (JSR 77)
Java SE中与Java EE有关的规范
JCache API (JSR 107)
Java Memory Model (JSR 133)
Concurrency Utilitie (JSR 166)
Java API for XML Processing (JAXP) 1.3 (JSR 206)
Java Database Connectivity 4.0 (JSR 221)
Java Management Extensions (JMX) 2.0 (JSR 255)
Java Portlet API (JSR 286)
- 企业应用技术
-
Web Service技术
Java Date与Time API (JSR 310)
Java API for RESTful Web Services (JAX-RS) 1.1 (JSR 311)
Implementing Enterprise Web Services 1.3 (JSR 109)
Java API for XML-Based Web Services (JAX-WS) 2.2 (JSR 224)
Java Architecture for XML Binding (JAXB) 2.2 (JSR 222)
Web Services Metadata for the Java Platform (JSR 181)
Java API for XML-Based RPC (JAX-RPC) 1.1 (JSR 101)
Java APIs for XML Messaging 1.3 (JSR 67)
Java API for XML Registries (JAXR) 1.0 (JSR 93) -
JCP(Java Community Process):Java社区
-
Hibernate框架中包含一套独立的校验框架hibernate-validator
导入坐标
<dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>6.1.0.Final</version> </dependency>注意:
tomcat7 :搭配hibernate-validator版本5...Final
tomcat8.5↑ :搭配hibernate-validator版本6...Final
快速使用
1.开启校验
名称:@Valid 、 @Validated
类型:形参注解
位置:处理器类中的实体类类型的方法形参前方
作用:设定对当前实体类类型参数进行校验
范例:
@RequestMapping(value = "/addemployee")
public String addEmployee(@Valid Employee employee) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
2.设置校验规则
名称:@NotNull
类型:属性注解 等
位置:实体类属性上方
作用:设定当前属性校验规则
范例:
每个校验规则所携带的参数不同,根据校验规则进行相应的调整
具体的校验规则查看对应的校验框架进行获取
public class Employee{
@NotNull(message = "姓名不能为空")
private String name;//员工姓名
}
3.获取错误信息
@RequestMapping(value = "/addemployee")
public String addEmployee(@Valid Employee employee, Errors errors, Model model){
System.out.println(employee);
if(errors.hasErrors()){
for(FieldError error : errors.getFieldErrors()){
model.addAttribute(error.getField(),error.getDefaultMessage());
}
return "addemployee.jsp";
}
return "success.jsp";
}
通过形参Errors获取校验结果数据,通过Model接口将数据封装后传递到页面显示
<form action="/addemployee" method="post">
员工姓名:<input type="text" name="name"><span style="color:red">${name}</span><br/>
员工年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><span style="color:red">${age}</span><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
通过形参Errors获取校验结果数据,通过Model接口将数据封装后传递到页面显示
页面获取后台封装的校验结果信息
多规则校验
- 同一个属性可以添加多个校验器
@NotNull(message = "请输入您的年龄")
@Max(value = 60,message = "年龄最大值不允许超过60岁")
@Min(value = 18,message = "年龄最小值不允许低于18岁")
private Integer age;//员工年龄
- 3种判定空校验器的区别
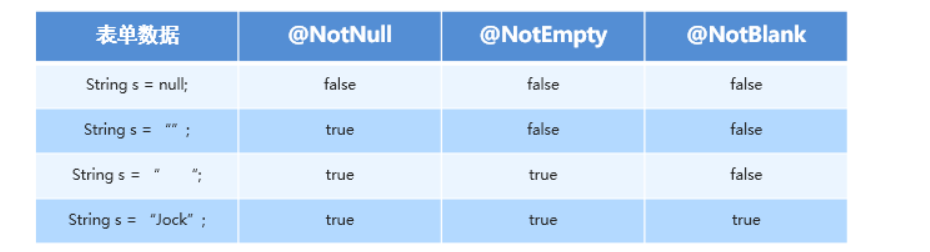
嵌套校验
名称:@Valid
类型:属性注解
位置:实体类中的引用类型属性上方
作用:设定当前应用类型属性中的属性开启校验
范例:
public class Employee {
//实体类中的引用类型通过标注@Valid注解,设定开启当前引用类型字段中的属性参与校验
@Valid
private Address address;
}
注意:开启嵌套校验后,被校验对象内部需要添加对应的校验规则
分组校验
- 同一个模块,根据执行的业务不同,需要校验的属性会有不同
- 新增用户
- 修改用户
- 对不同种类的属性进行分组,在校验时可以指定参与校验的字段所属的组类别
- 定义组(通用)
- 为属性设置所属组,可以设置多个
- 开启组校验
public interface GroupOne {
}
public String addEmployee(@Validated({GroupOne.class}) Employee employee){
}
@NotEmpty(message = "姓名不能为空",groups = {GroupOne.class})
private String name;//员工姓名
SSM整合
整合流程简介
整合步骤分析
SSM(Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis)
-
Spring
- 框架基础
-
MyBatis
- mysql+druid+pagehelper
-
Spring整合MyBatis
-
junit测试业务层接口
-
SpringMVC
- rest风格(postman测试请求结果)
- 数据封装json(jackson)
-
Spring整合SpringMVC
- Controller调用Service
-
其他
- 表现层数据封装
- 自定义异常
最重要的5个步骤
- Spring
- MyBatis
- Spring整合MyBatis
- SpringMVC
- Spring整合SpringMVC
项目结构搭建
Part0: 项目基础结构搭建
-
创建项目,组织项目结构,创建包
-
创建表与实体类
-
创建三层架构对应的模块、接口与实体类,建立关联关系
-
数据层接口(代理自动创建实现类)
- 业务层接口+业务层实现类
- 表现层类
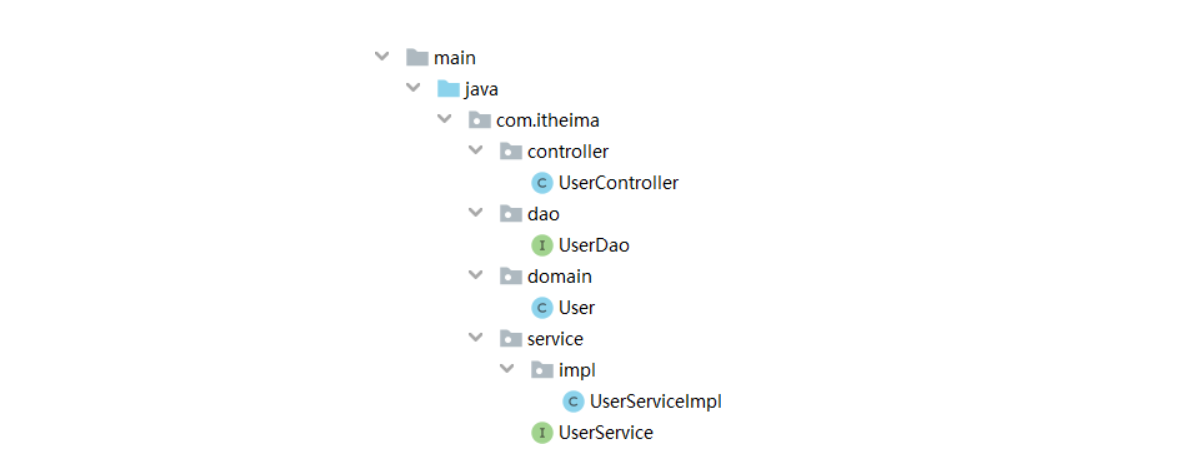
public interface UserDao {
public boolean save(User user); public boolean update(User user);
public boolean delete(Integer uuid); public User get(Integer uuid);
public List<User> getAll(int page,int size);
public interface UserService {
public boolean save(User user); public boolean update(User user);
public boolean delete(Integer uuid);
public User get(Integer uuid);
public List<User> getAll(int page, int size);
/**
用户登录
@param userName 用户名
@param password 密码信息
@return
*/
public User login(String userName,String password);
}
Spring整合Mybatis

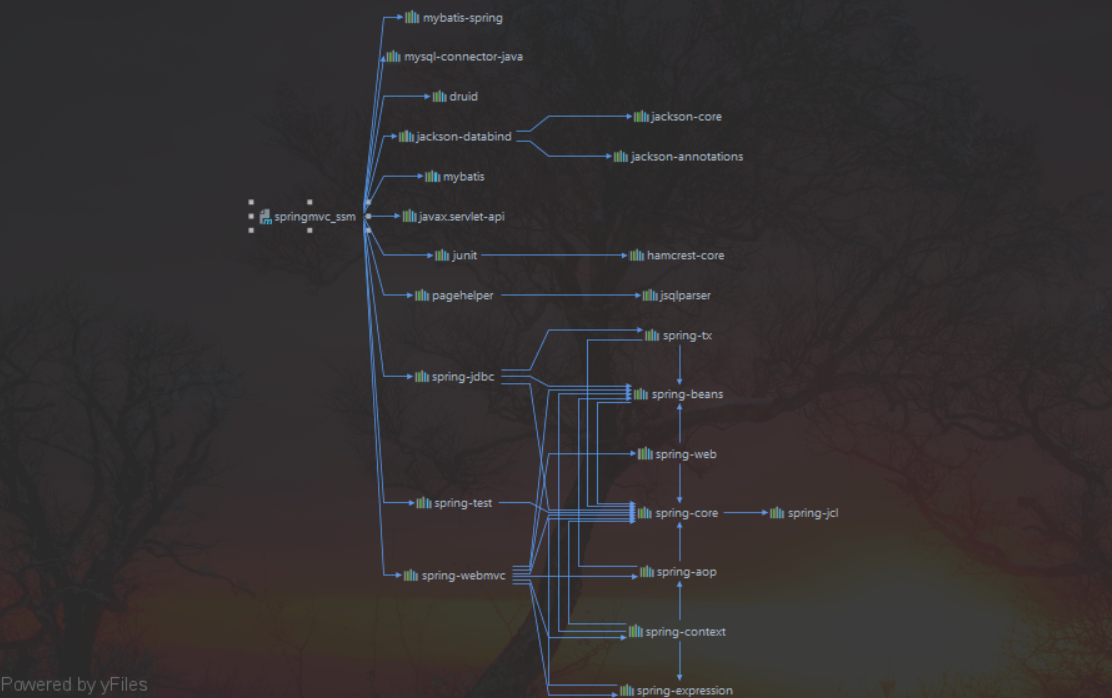
- 导入pom依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cloudcore</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc_ssm</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--spring环境-->
<!--spring环境-->
<!--spring环境-->
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>-->
<!--mybatis环境-->
<!--mybatis环境-->
<!--mybatis环境-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql环境-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring整合jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring整合mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--druid连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
<!--分页插件坐标-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--springmvc环境-->
<!--springmvc环境-->
<!--springmvc环境-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--jackson相关坐标3个-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>-->
<!--servlet环境-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--其他组件-->
<!--其他组件-->
<!--其他组件-->
<!--junit单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring整合junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
- 配置spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--开启扫描组件-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.cloudcore"/>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
<!--加载properties文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
<!--整合mybatis到spring中-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.cloudcore.domain"/>
<!--分页插件-->
<property name="plugins">
<array>
<bean class="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="helperDialect">mysql</prop>
<prop key="reasonable">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
<!--映射扫描-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.cloudcore.dao"/>
</bean>
<!--事务管理器-->
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
</beans>
- MyBatis映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.cloudcore.dao.UserDao">
<!--添加-->
<insert id="save" parameterType="com.cloudcore.domain.User">
insert into user(userName,password,realName,gender,birthday)values(#{userName},#{password},#{realName},#{gender},#{birthday})
</insert>
<!--删除-->
<delete id="delete" parameterType="int">
delete from user where uuid = #{uuid}
</delete>
<!--修改-->
<update id="update" parameterType="com.cloudcore.domain.User">
update user set userName=#{userName},password=#{password},realName=#{realName},gender=#{gender},birthday=#{birthday} where uuid=#{uuid}
</update>
<!--查询单个-->
<select id="get" resultType="com.cloudcore.domain.User" parameterType="int">
select * from user where uuid= #{uuid}
</select>
<!--分页查询-->
<select id="getAll" resultType="com.cloudcore.domain.User">
select * from user
</select>
<!--登录-->
<select id="getByUserNameAndPassword" resultType="com.cloudcore.domain.User" >
select * from user where userName=#{userName} and password=#{password}
</select>
</mapper>
- 配置jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=
- web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"
version="3.1">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--启动服务器时,通过监听器加载spring的运行环境-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:spring-mvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
- spring-mvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.cloudcore.controller"/>
</beans>
整合junit
单元测试整合junit
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class UserServiceTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testDelete(){
User user = new User(); userService.delete(3);
}
}
表现层数据封装
-
返回数据格式设置
- 状态
- 数据
- 消息
-
返回数据状态设计
- 404
- 500
- 200
- ...
public class Result {
//操作结果编码
private Integer code;
//操作结果数据
private Object data;
//消息
private String message;
public Result(Integer code, Object data) {
this.code = code;
this.data = data;
}
}
public class Code {
//操作结果编码
public static final Integer SAVE_OK = 20011;
public static final Integer UPDATE_OK = 20021;
public static final Integer DELETE_OK = 20031;
public static final Integer GET_OK = 20041;
public static final Integer SAVE_ERROR = 20010;
public static final Integer UPDATE_ERROR= 20020;
public static final Integer DELETE_ERROR = 20030;
public static final Integer GET_ERROR = 20040;
//系统错误编码
//操作权限相关编码
//校验结果编码
}
- controller
package com.cloudcore.controller;
import com.cloudcore.controller.results.Code;
import com.cloudcore.controller.results.Result;
import com.cloudcore.domain.User;
import com.cloudcore.service.UserService;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @Author: hepeng
* @Date: 2021/11/7 17:28
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping
public Result save(User user){
Boolean flag = userService.save(user);
return new Result(flag ? Code.SAVE_OK : Code.SAVE_ERROR);
}
@PutMapping
public Result update(User user){
Boolean flag = userService.update(user);
return new Result(flag ? Code.UPDATE_OK : Code.SAVE_ERROR);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{uuid}")
public Result delete(@PathVariable Integer uuid){
boolean flag = userService.delete(uuid);
return new Result(flag ? Code.DELETE_OK : Code.DELETE_ERROR);
}
@GetMapping("/{uuid}")
public Result get(@PathVariable Integer uuid){
User user = userService.get(uuid);
return new Result(null != user ? Code.GET_OK : Code.GET_ERROR,user);
}
@GetMapping("/{page}/{size}")
public Result getAll(@PathVariable Integer page,@PathVariable Integer size){
PageInfo<User> all = userService.getAll(page, size);
return new Result(null != all ? Code.GET_OK : Code.GET_ERROR,all);
}
@PostMapping("/login")
public Result login(String userName,String password){
User user = userService.login(userName, password);
return new Result(null != user ? Code.GET_OK : Code.GET_ERROR,user);
}
}
自定义异常
ProjectExceptionAdvice
@Component
@ControllerAdvice
public class ProjectExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result doBusinessException(BusinessException e){
return new Result(e.getCode(),e.getMessage());
}
}
BusinessException
package com.cloudcore.system.exception;
/**
* @Author: hepeng
* @Date: 2021/11/10 21:42
*/
public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException{
private Integer code;
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(String message,Integer code) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause,Integer code) {
super(message, cause);
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(Throwable cause,Integer code) {
super(cause);
this.code = code;
}
public BusinessException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace,Integer code) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
this.code = code;
}
}
SystemException
package com.cloudcore.system.exception;
/**
* @Author: hepeng
* @Date: 2021/11/10 21:42
*/
public class SystemException extends RuntimeException{
public SystemException() {
}
public SystemException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public SystemException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public SystemException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
public SystemException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号