图像实验3- 空域滤波
一、实验目的
掌握利用模板对图像进行空域滤波操作,熟练掌握常用空域模板的使用。
1、掌握图像平滑的空域方法,熟练掌握均值模板和高斯模板平滑图像
2、掌握图像锐化的空域方法,熟练掌握 Laplacian、Robert、Sobel 模板锐化
图像
3、掌握利用高提升滤波算法对图像进行增强
二、实验内容
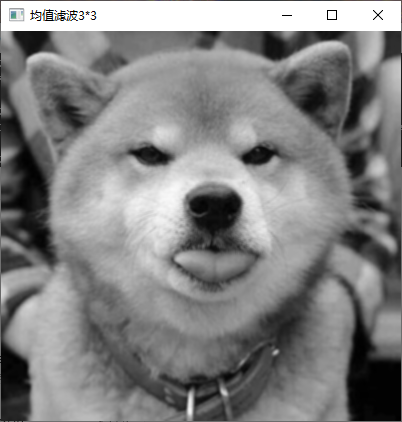
1、利用均值模板平滑灰度图像。
具体内容:利用 OpenCV 对图像像素进行操作,分别利用 33、55 和 99
尺寸的均值模板平滑灰度图像
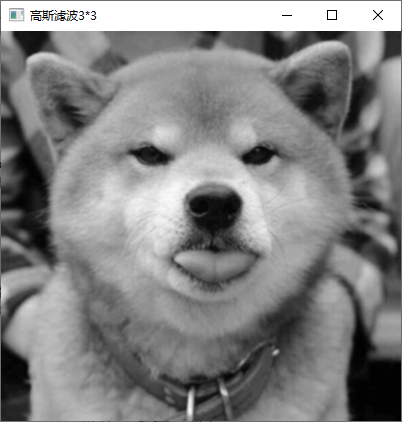
2、利用高斯模板平滑灰度图像。
具体内容:利用 OpenCV 对图像像素进行操作,分别利用 33、55 和 99
尺寸的高斯模板平滑灰度图像
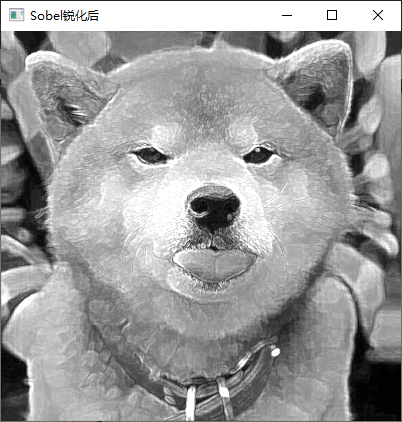
3、利用 Laplacian、Robert、Sobel 模板锐化灰度图像。
具体内容:利用 OpenCV 对图像像素进行操作,分别利用 Laplacian、Robert、
Sobel 模板锐化灰度图像
4、利用高提升滤波算法增强灰度图像。
具体内容:利用 OpenCV 对图像像素进行操作,设计高提升滤波算法增
强图像
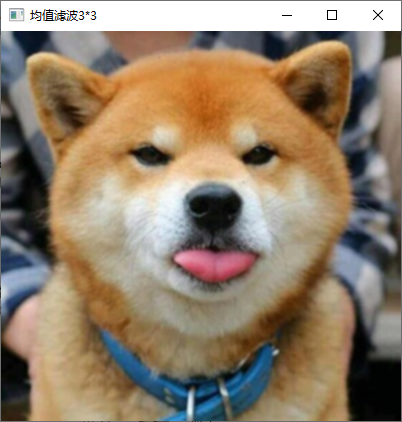
5、利用均值模板平滑彩色图像。
具体内容:利用 OpenCV 分别对图像像素的 RGB 三个通道进行操作,利
用 33、55 和 99 尺寸的均值模板平滑彩色图像
6、利用高斯模板平滑彩色图像。
具体内容:利用 OpenCV 分别对图像像素的 RGB 三个通道进行操作,分
别利用 33、55 和 99 尺寸的高斯模板平滑彩色图像
7、利用 Laplacian、Robert、Sobel 模板锐化灰度图像。
具体内容:利用 OpenCV 分别对图像像素的 RGB 三个通道进行操作,分
别利用 Laplacian、Robert、Sobel 模板锐化彩色图像
三、实验完成情况
1、利用均值模板平滑灰度图像。
核心代码
//均值滤波处理函数
Mat handleMeanFilter(int size) {
//输出图像
Mat target = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
//滤波器尺寸为size*size
Size ksize(size, size);
//锚点,即滤波器中进行处理的点,默认(-1,-1)表示滤波器中心点
Point p(-1, -1);
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//均值处理
blur(img, target, ksize, p, borderType);
return target;
}
实现截图



2、利用高斯模板平滑灰度图像。
核心代码
//高斯滤波处理函数
Mat handleGaussianFilter(int size, double sigama) {
//输出图像
Mat target = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
//滤波器尺寸为size*size,必须为正奇数
Size ksize(size, size);
//X轴方向上的高斯半径/高斯核,若取0.0则由opencv调用getGaussianKernel通过滤波器大小计算高斯核
double sigmaX = sigama;
//Y轴方向上的高斯半径/高斯核,由于需要满足对称性,因此X、Y轴上的高斯半径相等,取默认值0即与sigma相等
double sigmaY = 0.0;
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//高斯平滑处理
GaussianBlur(img, target, ksize, sigmaX, sigmaY, borderType);
return target;
}
实现截图



3、利用 Laplacian、Robert、Sobel 模板锐化灰度图像。
核心代码
//锐化图像叠加,saturate_cast用于色彩保护防止溢出
Mat handleImageAddition(Mat img, Mat add, bool ifadd = true) {
Mat target = img.clone();
vector<Mat> target_channels;
vector<Mat> add_channels;
split(target, target_channels);
split(add, add_channels);
for (int c = 0; c < target_channels.size(); c++) {
Mat curr = target_channels[c];
Mat cadd = add_channels[c];
for (int i = 0; i < curr.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < curr.cols; j++)
curr.at<uchar>(i, j) = saturate_cast<uchar>(ifadd ? curr.at<uchar>(i, j) + cvRound(cadd.at<uchar>(i, j)) : curr.at<uchar>(i, j) - cvRound(cadd.at<uchar>(i, j)));
}
merge(target_channels, target);
return target;
}
//Laplacian拉普拉斯滤波处理函数
Mat handleLaplacianFilter(int size) {
//输出图像
Mat target = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
//图像深度,输入为CV_8U,为了防止溢出(>255/<0)采用CV_8U,也可使用-1自动选择
int ddepth = CV_16S;
//拉普拉斯核的大小,必须为正奇数
int ksize = size;
//拉普拉斯核导数计算结果的缩放系数,此处使用默认值1,表示不进行缩放,作用类似于对数变换
double scale = 1.0;
//拉普拉斯计算结果的偏移量,默认为0,不进行偏移
double delta = 0.0;
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//拉普拉斯锐化处理
Laplacian(img, target, ddepth, ksize, scale, delta, borderType);
//对图像进行标定处理
convertScaleAbs(target, target);
return target;
}
//Robert模版处理函数
Mat handleRobertFilter() {
//输出图像
Mat target = img.clone();
double min_value, max_value;
vector<Mat> target_channels;
split(target, target_channels);
//手动计算robert算子
for (int c = 0; c < target_channels.size(); c++) {
Mat curr = target_channels[c];
for (int i = 0; i < curr.rows - 1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < curr.cols - 1; j++)
curr.at<uchar>(i, j) = saturate_cast<uchar>(abs(curr.at<uchar>(i + 1, j + 1) - curr.at<uchar>(i, j)) + abs(curr.at<uchar>(i + 1, j) - curr.at<uchar>(i, j + 1)));
//区间缩放到 [0,255]
minMaxLoc(curr, &min_value, &max_value);
curr.convertTo(curr, CV_8U, 255.0 / (max_value - min_value), -255.0 * min_value / (max_value - min_value));
}
merge(target_channels, target);
return target;
}
//Sobel锐化处理函数
Mat handleSobelFilter(int size, int x, int y, bool useScharr) {
if (size != 3)
useScharr = false;
//图像深度,输入为CV_8U,为了防止溢出(>255/<0)采用CV_8U,也可使用-1自动选择
int ddepth = CV_16S;
//sobel核的大小,必须为正奇数
int ksize = size;
//x方向上的阶数,即x方向上的sobel算子的中心权值
int dx = useScharr ? 1 : x;
//y方向上的阶数,即y方向上的sobel算子的中心权值
int dy = useScharr ? 1 : y;
//sobel核导数计算结果的缩放系数,此处使用默认值1,表示不进行缩放,作用类似于对数变换
double scale = 1.0;
//sobel计算结果的偏移量,默认为0,不进行偏移
double delta = 0.0;
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//锐化处理
Mat target_x = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
Mat target_y = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
if (useScharr) {
Scharr(img, target_x, ddepth, dx, 0, scale, delta, borderType);
Scharr(img, target_y, ddepth, 0, dy, scale, delta, borderType);
}
else {
Sobel(img, target_x, ddepth, dx, 0, ksize, scale, delta, borderType);
Sobel(img, target_y, ddepth, 0, dy, ksize, scale, delta, borderType);
}
//对图像进行标定处理
convertScaleAbs(target_x, target_x);
convertScaleAbs(target_y, target_y);
Mat target;
addWeighted(target_x, 0.5, target_y, 0.5, 0, target);
return target;
}
实现截图
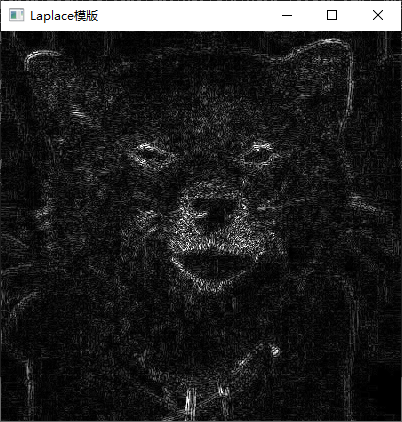

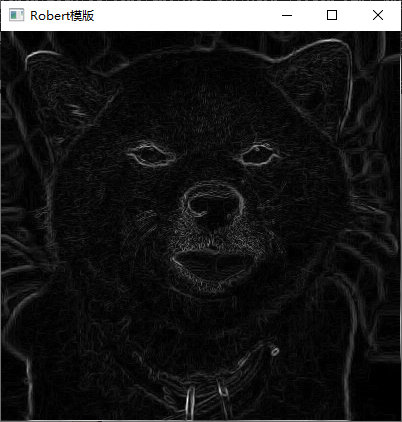

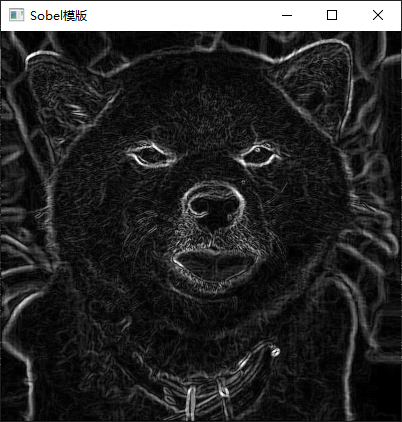

4、利用高提升滤波算法增强灰度图像。
核心代码
//高提升滤波
Mat handleHighLiftFiltering(Mat filtered, double k) {
return k * handleImageAddition(this->img, filtered, false);
}
//高提升滤波
void highLiftFiltering(int type = 0, int k = 1) {
Mat filtered;
switch (type)
{
case 1:
filtered = handleMeanFilter(3);
break;
default:
filtered = handleGaussianFilter(3,0);
break;
}
Mat highLift = handleHighLiftFiltering(filtered, k);
openWindows("高提升模版", highLift);
openWindows("高提升锐化后", handleImageAddition(this->img, highLift));
}
实现截图
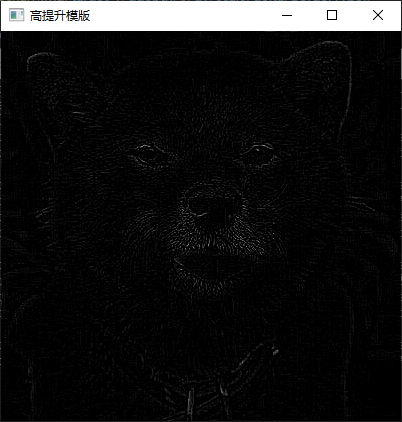

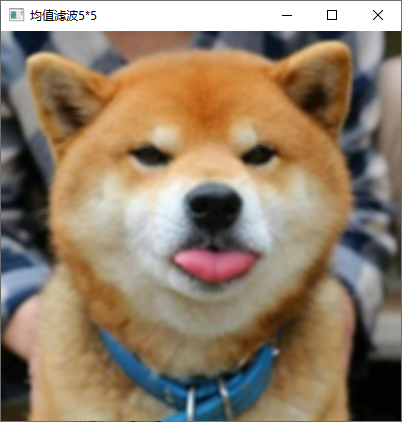
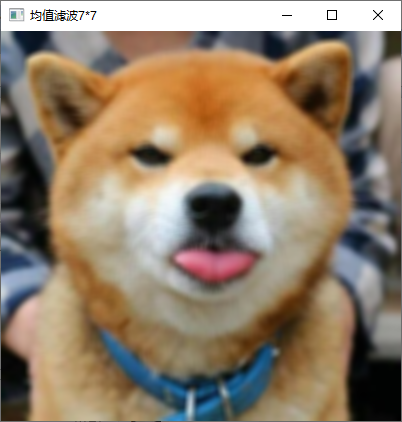
5、利用均值模板平滑彩色图像。
核心代码
同灰度图像均值模版处理,已包含彩色图像的处理操作。
实现截图



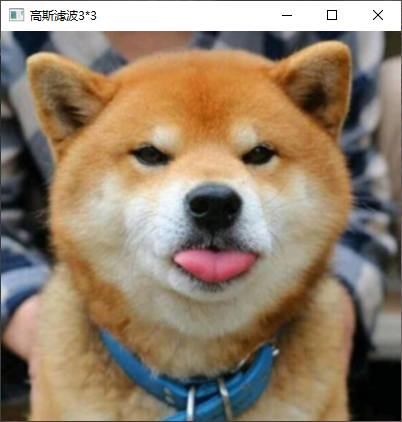
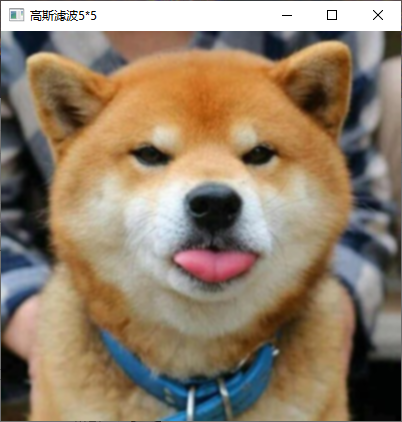
6、利用高斯模板平滑彩色图像。
核心代码
同灰度图像高斯模版处理,已包含彩色图像的处理操作。
实现截图
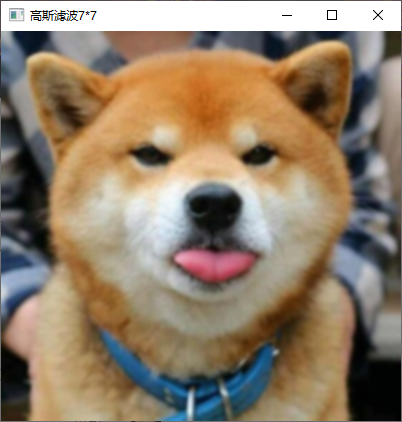



7、利用 Laplacian、Robert、Sobel 模板锐化彩色图像。
核心代码
代码同灰度图像锐化处理,已包含彩色图像的处理操作。
实现截图
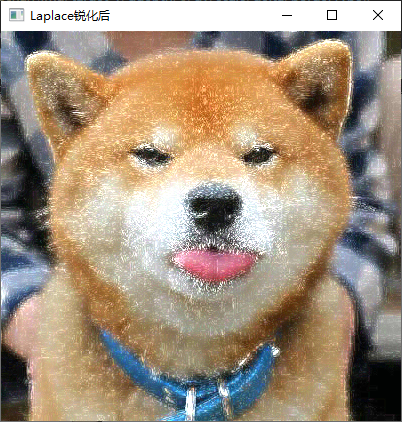
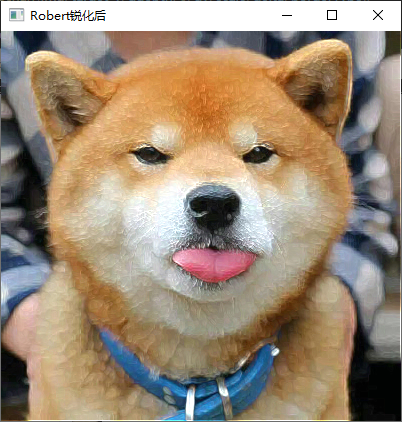
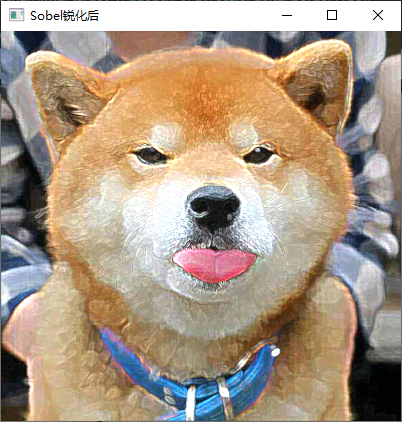
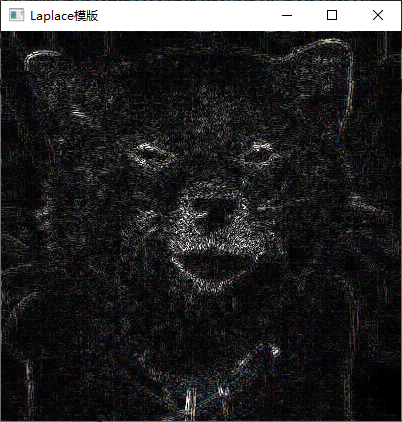

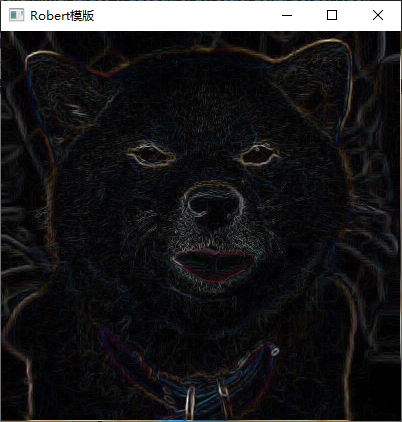

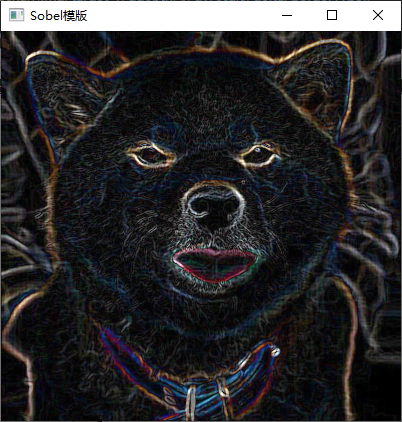

四、实验中的问题
- 不同于前两次实验,这次实验对于图像的操作更加细化,更具体,理解起来也更难一些。
- 由于牵扯到数学计算,因此难度较之前要大一些。
- 对于滤波操作还不是很熟悉,实际操作时碰到很多诸如是否需要划分通道、是否需要进行标定、图像的叠加方式等问题。
五、实验结果
源码
lab3.cpp
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
const static std::string path = "F:\\Documents\\高级图像处理\\Image\\";
//图片路径组合
string getFullPath(string name) {
return path + name;
}
//打开图片显示窗口
void openWindows(string win_name, Mat img, int x = 500, int y = 200) {
//窗口命名,指定大小,生成位置
namedWindow(win_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
moveWindow(win_name, x, y);
//生成窗口显示图片
imshow(win_name, img);
//等待键入
waitKey();
//关闭窗口
destroyWindow(win_name);
}
//统一数字输入函数
template<typename T>T inputNumber(string desc) {
system("cls");
T input;
cout << desc;
cin >> input;
cout << endl;
return input;
}
//统一图片打开函数,用于简化路径和处理打开图片错误
Mat openImage(string name, int type = 1) {
//图片读取函数,返回图像存储类(包含存储方式、存储矩阵、矩阵大小等)
Mat img = imread(getFullPath(name), type);
if (img.empty()) {
cout << "无效图片,读取失败" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
return img;
}
//图像基类
class Image {
protected:
Mat img;
public:
Mat getImage() {
return img.clone();
}
};
//彩色图像处理类
class ColorImage :public Image {
public:
//读取彩色图像并展示
ColorImage(string path) {
img = openImage(path, IMREAD_COLOR);
openWindows("彩色图像", img);
}
};
//灰度图像处理类
class GrayImage :public Image {
public:
//仅读取灰度方式读取图像并展示(IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
GrayImage(string path) {
img = openImage(path, IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
openWindows("灰度图像", img);
}
};
class SpatialFiltering {
private:
Mat img;
bool color;
//均值滤波处理函数
Mat handleMeanFilter(int size) {
//输出图像
Mat target = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
//滤波器尺寸为size*size
Size ksize(size, size);
//锚点,即滤波器中进行处理的点,默认(-1,-1)表示滤波器中心点
Point p(-1, -1);
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//均值处理
blur(img, target, ksize, p, borderType);
return target;
}
//高斯滤波处理函数
Mat handleGaussianFilter(int size, double sigama) {
//输出图像
Mat target = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
//滤波器尺寸为size*size,必须为正奇数
Size ksize(size, size);
//X轴方向上的高斯半径/高斯核,若取0.0则由opencv调用getGaussianKernel通过滤波器大小计算高斯核
double sigmaX = sigama;
//Y轴方向上的高斯半径/高斯核,由于需要满足对称性,因此X、Y轴上的高斯半径相等,取默认值0即与sigma相等
double sigmaY = 0.0;
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//高斯平滑处理
GaussianBlur(img, target, ksize, sigmaX, sigmaY, borderType);
return target;
}
//锐化图像叠加,saturate_cast用于色彩保护防止溢出
Mat handleImageAddition(Mat img, Mat add, bool ifadd = true) {
Mat target = img.clone();
vector<Mat> target_channels;
vector<Mat> add_channels;
split(target, target_channels);
split(add, add_channels);
for (int c = 0; c < target_channels.size(); c++) {
Mat curr = target_channels[c];
Mat cadd = add_channels[c];
for (int i = 0; i < curr.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < curr.cols; j++)
curr.at<uchar>(i, j) = saturate_cast<uchar>(ifadd ? curr.at<uchar>(i, j) + cvRound(cadd.at<uchar>(i, j)) : curr.at<uchar>(i, j) - cvRound(cadd.at<uchar>(i, j)));
}
merge(target_channels, target);
return target;
}
//Laplacian拉普拉斯滤波处理函数
Mat handleLaplacianFilter(int size) {
//输出图像
Mat target = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
//图像深度,输入为CV_8U,为了防止溢出(>255/<0)采用CV_8U,也可使用-1自动选择
int ddepth = CV_16S;
//拉普拉斯核的大小,必须为正奇数
int ksize = size;
//拉普拉斯核导数计算结果的缩放系数,此处使用默认值1,表示不进行缩放,作用类似于对数变换
double scale = 1.0;
//拉普拉斯计算结果的偏移量,默认为0,不进行偏移
double delta = 0.0;
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//拉普拉斯锐化处理
Laplacian(img, target, ddepth, ksize, scale, delta, borderType);
//对图像进行标定处理
convertScaleAbs(target, target);
return target;
}
//Robert模版处理函数
Mat handleRobertFilter() {
//输出图像
Mat target = img.clone();
double min_value, max_value;
vector<Mat> target_channels;
split(target, target_channels);
//手动计算robert算子
for (int c = 0; c < target_channels.size(); c++) {
Mat curr = target_channels[c];
for (int i = 0; i < curr.rows - 1; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < curr.cols - 1; j++)
curr.at<uchar>(i, j) = saturate_cast<uchar>(abs(curr.at<uchar>(i + 1, j + 1) - curr.at<uchar>(i, j)) + abs(curr.at<uchar>(i + 1, j) - curr.at<uchar>(i, j + 1)));
//区间缩放到 [0,255]
minMaxLoc(curr, &min_value, &max_value);
curr.convertTo(curr, CV_8U, 255.0 / (max_value - min_value), -255.0 * min_value / (max_value - min_value));
}
merge(target_channels, target);
return target;
}
//Sobel锐化处理函数
Mat handleSobelFilter(int size, int x, int y, bool useScharr) {
if (size != 3)
useScharr = false;
//图像深度,输入为CV_8U,为了防止溢出(>255/<0)采用CV_8U,也可使用-1自动选择
int ddepth = CV_16S;
//sobel核的大小,必须为正奇数
int ksize = size;
//x方向上的阶数,即x方向上的sobel算子的中心权值
int dx = useScharr ? 1 : x;
//y方向上的阶数,即y方向上的sobel算子的中心权值
int dy = useScharr ? 1 : y;
//sobel核导数计算结果的缩放系数,此处使用默认值1,表示不进行缩放,作用类似于对数变换
double scale = 1.0;
//sobel计算结果的偏移量,默认为0,不进行偏移
double delta = 0.0;
//边界处理方式,取默认值BORDER_DEFAULT
int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT;
//锐化处理
Mat target_x = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
Mat target_y = Mat::zeros(img.size(), img.type());
if (useScharr) {
Scharr(img, target_x, ddepth, dx, 0, scale, delta, borderType);
Scharr(img, target_y, ddepth, 0, dy, scale, delta, borderType);
}
else {
Sobel(img, target_x, ddepth, dx, 0, ksize, scale, delta, borderType);
Sobel(img, target_y, ddepth, 0, dy, ksize, scale, delta, borderType);
}
//对图像进行标定处理
convertScaleAbs(target_x, target_x);
convertScaleAbs(target_y, target_y);
Mat target;
addWeighted(target_x, 0.5, target_y, 0.5, 0, target);
return target;
}
//高提升滤波
Mat handleHighLiftFiltering(Mat filtered, double k) {
return k * handleImageAddition(this->img, filtered, false);
}
public:
SpatialFiltering(Image img) {
this->img = img.getImage();
this->color = this->img.channels() != 1;
}
//均值滤波
void meanFilter(int size = 3) {
string name = string("均值滤波") + (char)(size + '0') + '*' + (char)(size + '0');
openWindows(name, handleMeanFilter(size));
}
//高斯滤波
void gaussianFilter(int size = 3, double sigma = 0.0) {
if (!(size & 1) || size <= 0) {
cout << "高斯滤波器大小必须为正奇数" << endl;
return;
}
string name = string("高斯滤波") + (char)(size + '0') + '*' + (char)(size + '0');
openWindows(name, handleGaussianFilter(size, sigma));
}
//拉普拉斯滤波
void laplacian(int size = 3) {
if (!(size & 1) || size <= 0) {
cout << "滤波器大小必须为正奇数" << endl;
return;
}
Mat laplace = handleLaplacianFilter(size);
openWindows("Laplace模版", laplace);
openWindows("Laplace锐化后", handleImageAddition(this->img, laplace));
}
//robert滤波
void robert() {
Mat robert = handleRobertFilter();
openWindows("Robert模版", robert);
openWindows("Robert锐化后", handleImageAddition(this->img, robert));
}
//Sobel滤波
void sobel(int size = 3, bool useScharr = true, int dx = 1, int dy = 1) {
if (!(size & 1) || size <= 0) {
cout << "滤波器大小必须为正奇数" << endl;
return;
}
string name = useScharr ? "Scharr" : "Sobel";
Mat sobel = handleSobelFilter(size, dx, dy, useScharr);
openWindows(name + "模版", sobel);
openWindows(name + "锐化后", handleImageAddition(this->img, sobel));
}
//高提升滤波
void highLiftFiltering(int type = 0, int k = 1) {
Mat filtered;
switch (type)
{
case 1:
filtered = handleMeanFilter(3);
break;
default:
filtered = handleGaussianFilter(3,0);
break;
}
Mat highLift = handleHighLiftFiltering(filtered, k);
openWindows("高提升模版", highLift);
openWindows("高提升锐化后", handleImageAddition(this->img, highLift));
}
};
int main() {
string name = "test.jpg";
//灰度图像
GrayImage gray_img(name);
//滤波对象
SpatialFiltering gray_filter(gray_img);
//均值滤波
gray_filter.meanFilter(3);
gray_filter.meanFilter(5);
gray_filter.meanFilter(7);
//高斯滤波
gray_filter.gaussianFilter(3);
gray_filter.gaussianFilter(5);
gray_filter.gaussianFilter(7);
//laplacian锐化
gray_filter.laplacian();
//robert锐化
gray_filter.robert();
//sobel锐化
gray_filter.sobel(3,true);
//高提升锐化
gray_filter.highLiftFiltering(0,5);
//彩色图像
ColorImage color_img(name);
//滤波对象
SpatialFiltering color_filter(color_img);
//均值滤波
color_filter.meanFilter(3);
color_filter.meanFilter(5);
color_filter.meanFilter(7);
//高斯滤波
color_filter.gaussianFilter(3);
color_filter.gaussianFilter(5);
color_filter.gaussianFilter(7);
//laplacian锐化
color_filter.laplacian();
//robert锐化
color_filter.robert();
//sobel锐化
color_filter.sobel(3, false);
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号