注解和反射
Java代码的三个阶段
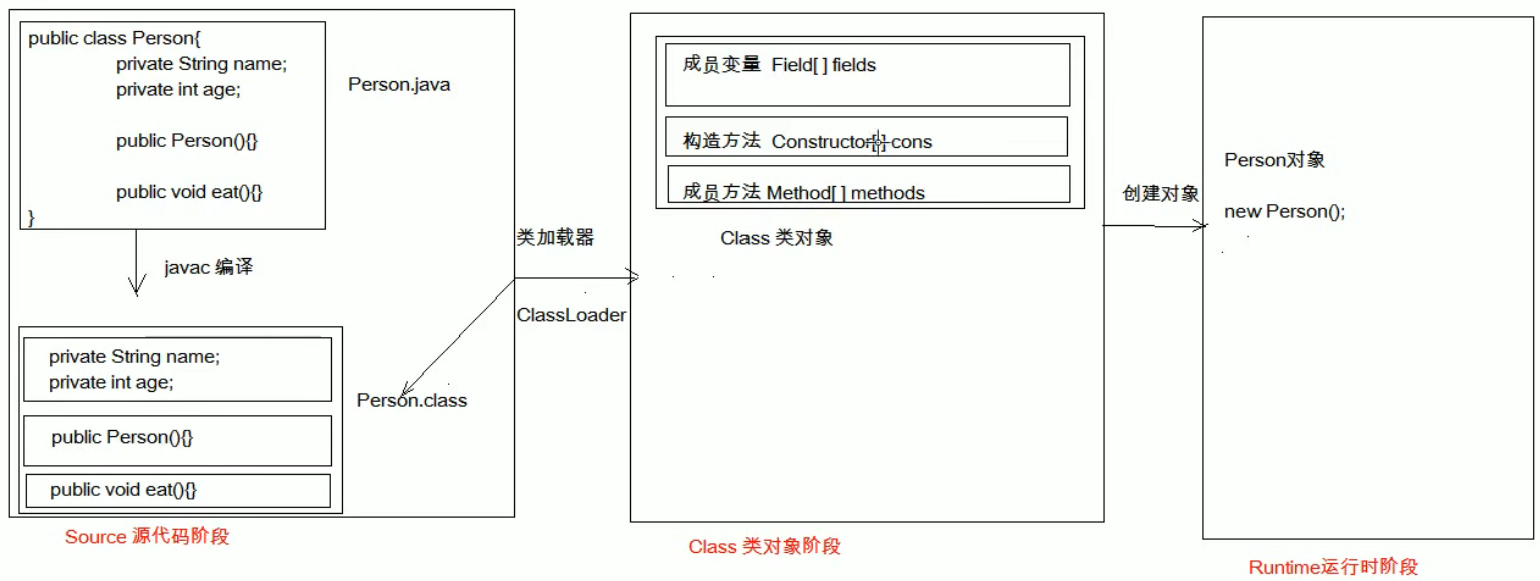
注解与反射
注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})//表示注解的作用域
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//什么时候生效
@Documented//表示方法已经过时,但是还能用
@Inherited//表示子类可以继承
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value() default "";
}
注解里面定义的是:注解类型元素!
定义注解类型元素时需要注意如下几点:
- 访问修饰符必须为public,不写默认为public;
- 该元素的类型只能是基本数据类型、String、Class、枚举类型、注解类型(体现了注解的嵌套效果)以及上述类型的一位数组;
- 该元素的名称一般定义为名词,如果注解中只有一个元素,请把名字起为value(后面使用会带来便利操作);
- ()不是定义方法参数的地方,也不能在括号中定义任何参数,仅仅只是一个特殊的语法;
- default代表默认值,值必须和第2点定义的类型一致;
- 如果没有默认值,代表后续使用注解时必须给该类型元素赋值。
反射
一个类只有一个class对象
类被加载后,类的整个结构都被封装在class对象中
获取反射对象
-
通过路径
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.smu.User"); - 通过对象获取
Class<? extends User> aClass = user.getClass();
- 通过类名获取
Class<User> userClass = User.class;
- 基本内置对象的封装类都有的TYPE属性
Class<Integer> type = Integer.TYPE;
通过反射获取类的信息
获取类名
- String name = c1.getName();
- String simpleName = c1.getSimpleName();
获取的样式为:class com.smu.reflect.B
获取字段(带有Declared的是获取包括private的当前类的字段,不带的是获取本类即父类的所有public字段)
- Field[] fields = c1.getFields();
- Field username = c1.getField("username");
- Field[] declaredFields = c1.getDeclaredFields();
- Field username1 = c1.getDeclaredField("username");
获取的样式为:public java.lang.String com.smu.reflect.B.nameB
获取方法(不带Declared是获取本类以及父类的public方法,带有Declared的是获得本类的所有包括private的方法)
- Method[] methods = c1.getMethods();
- Method getAge = c1.getMethod("getAge");
- Method[] declaredMethods = c1.getDeclaredMethods();
- Method setPassword = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setPassword", String.class);
获取的样式为:public java.lang.String com.smu.reflect.B.getLoverB()
获取构造器
- Constructor<?>[] constructors = c1.getConstructors();
- Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = c1.getDeclaredConstructors();
- Constructor<?> declaredConstructor1 = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, String.class, Integer.class);
获取的样式为:public com.smu.reflect.B()
获取对象
通过class对象获取(需要有无参构造器,需要是public修饰的),通过构造器获取,如果是private修饰的需要setAccessible(true);
- User o = (User) c1.newInstance();需要捕获异常
通过指定的构造器获取
- Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, String.class, Integer.class);
- declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
- User happy = (User) declaredConstructor.newInstance("happy", "889886", 21);
执行私有方法
需要借助Method类获取指定方法名字的方法,然后setAccessible(true),在执行,示例:
try { //借助B的类对象获取instance B instanceB =(B) b.newInstance(); try { //获取希望执行的方法,@parm希望执行的方法名,@parm方法需要的形参类型,没有就是null,或者不写 Method demo = b.getDeclaredMethod("setNameB", String.class); //私有方法需要关闭安全验证,且关闭后可以提升性能 demo.setAccessible(true); try { //方法执行,@parm执行方法的对象,@parm传入的形参 demo.invoke(instanceB,"happy"); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("调用invoke失败"); } } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("调用method方法失败"); } System.out.println(instanceB); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
修改成员变量(不借助方法修改)
借助Field类,获取指定的方法,然后修改,示例:
//定义成员变量 Field loverB = null; try { //获取指定名字的成员变量 loverB = b.getDeclaredField("loverB"); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Object o = null; try { //获取指定的构造器,@根据构造器的参数指定,无参就是null Constructor<?> constructor = b.getDeclaredConstructor(null); constructor.setAccessible(true); try { //通过构造器获取instance o = constructor.newInstance(); } catch (InstantiationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } loverB.setAccessible(true); try { //通过指定对象,修改成员变量 loverB.set(o, "xintui"); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(o);
通过反射获取注解
try { Method getLoverB = b.getDeclaredMethod("getLoverB"); if(getLoverB.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){ System.out.println("存在@MyAnnotation注解"); MyAnnotation annotation = getLoverB.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); System.out.println("注解的value值为"+annotation.value()); } } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
如果我们要获得的注解是配置在方法上的,那么我们要从Method对象上获取;
如果是配置在属性上,就需要从该属性对应的Field对象上去获取,如果是配置在类型上,需要从Class对象上去获取。总之在谁身上,就从谁身上去获取!
isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass)方法是专门判断该元素上是否配置有某个指定的注解;
getAnnotation(Class<A> annotationClass)方法是获取该元素上指定的注解。之后再调用该注解的注解类型元素方法就可以获得配置时的值数据;
反射对象上还有一个方法getAnnotations(),该方法可以获得该对象身上配置的所有的注解。它会返回给我们一个注解数组,需要注意的是该数组的类型是Annotation类型,这个
Annotation是一个来自于java.lang.annotation包的接口。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号