【IO编程】5.对象流
1. 序列化与反序列化
- 序列化:保存数据时,保存数据的值和数据类型
- 反序列化:恢复数据时,恢复数据的值和数据类型
- 某个类的对象若想序列化,该类必须实现Serializable接口或Externalizable接口
- Serializable接口是一个标记接口,没有方法
- Externalizable接口需要有方法实现,因此一般使用Serializable接口
2. ObjectOutputStream介绍
ObjectOutputStream提供对基本类型或对象类型的序列化的方法。
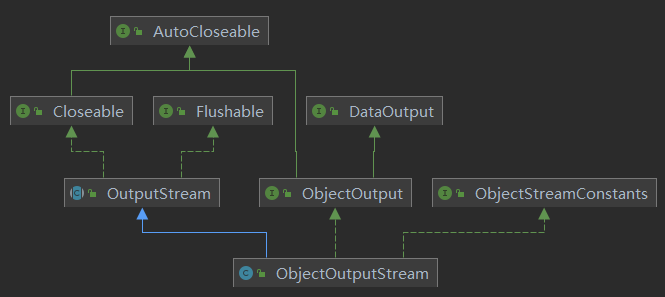
- 构造方法
- ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)
- 输出流对象
- ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)
- 成员方法
- void writeInt(int val)
- 序列化整型
- void writeLong(long val)
- 序列化长整型
- void writeFloat(float val)
- 序列化单精度浮点型
- void writeDouble(double val)
- 序列化双精度浮点型
- void writeChar(int val)
- 序列化字符型
- void writeUTF(String str)
- 序列化字符串
- void writeObject(Object obj)
- 序列化对象,该对象需要实现Serializable接口
- void close()
- 关闭流,需要捕获IO异常
- void writeInt(int val)
将数据序列化代码如下:
@Test
public void serialize() {
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("e:\\test.data"));
oos.writeInt(1);
oos.writeLong(2);
oos.writeFloat(3.0F);
oos.writeDouble(4.0);
oos.writeChar(5);
oos.writeUTF("6");
oos.writeObject(new Exception("exception"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (oos != null) {
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3. ObjectInputStream介绍
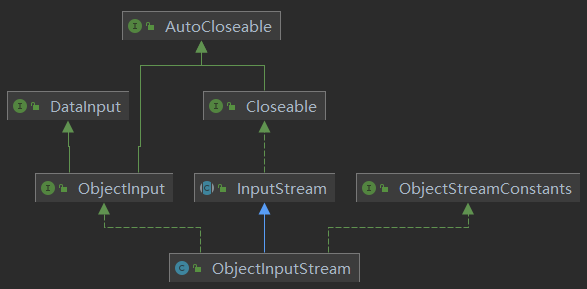
ObjectInputStream提供对基本类型或对象类型的反序列化的方法。
- 构造方法
- ObjectInputStream(InputStream in)
- 输入流对象
- ObjectInputStream(InputStream in)
- 成员方法
- int readInt()
- 反序列化得到整型
- long readLong()
- 反序列化得到长整型
- float readFloat()
- 反序列化得到单精度浮点型
- double readDouble()
- 反序列化得到双精度浮点型
- int readChar()
- 反序列化得到字符型
- String readUTF()
- 反序列化得到字符串
- Object readObject()
- 反序列化得到对象
- void close()
- 关闭流,需要捕获IO异常
- int readInt()
将数据反序列化代码如下:
@Test
public void deserialize() {
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("e:\\test.data"));
System.out.println(ois.readInt());
System.out.println(ois.readLong());
System.out.println(ois.readFloat());
System.out.println(ois.readDouble());
System.out.println(ois.readChar());
System.out.println(ois.readUTF());
System.out.println(ois.readObject());
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ois != null) {
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4. 对象流细节说明
- 读写顺序需要一致
- 序列化或反序列化对象需要实现Serializable接口
- 序列化的类添加SerialVersionUID可以提高版本的兼容性
- 序列化对象时默认将里面所有的属性都序列化,除非static和transient修饰
- 序列化对象时,属性的类型也必须实现序列化接口
- 序列化具备可继承性


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号