shell 脚本使用方法
1. 变量
1. 变量命名与赋值
一般变量定义
name="hany"
注:变量名与等号之间不能有空格。
环境变量定义
export 变量名=变量值将shell 变量输出为环境变量
2. 使用变量
echo $name
echo ${name} #推荐方法
将变量名追加到现有字符串
VER="123"
echo "hello_${VER}.bin"
结果为:hello_123.bin
3. 获取命令的返回值
A=`ls -a`
or
A=$(ls -a)
eg.
VER="123"
echo "hello_${VER}.bin"
结果为:hello_123.bin
2. 字符串的操作
获取字符串的长度
${#变量名}
hany@ubuntu:~$ test="hany"
hany@ubuntu:~$ echo ${#test}
4
截取字符串
从position处开始一直取到最后
${string:position}在string中,从位置position处开始提取字符串
从position处开始向后取一段长度
${变量名:起始:长度}从起始位置,向后取固定长度的内容
hany@ubuntu:~$ test="hany is a good man"
hany@ubuntu:~$ echo ${#test}
18
hany@ubuntu:~$ echo ${test:4:6}
is a
字符串删除
1. 前删到第一个匹配位置
${变量名#*substring} 从字符串头部开始删除直到第一个与substring相配的位置,删除substring
2. 前删到最后一个匹配位置
${变量名##*substring} 从字符串头部开始删除直到最后一个与substring相配的位置,删除substring
hany@ubuntu:~$ test=/bin/sh/file/new/realfile
hany@ubuntu:~$ echo ${test#*/}
bin/sh/file/new/realfile
hany@ubuntu:~$ echo ${test##*/}
realfile
1. 后删到第一个匹配位置
${变量名%substring*}从字符串尾部开始删除直到第一个与substring相配的位置,删除substring
2. 后删到最后一个匹配位置
${变量名%%substring*}从字符串尾部开始删除直到最后一个与substring相配的位置,删除substring
hany@ubuntu:~$ test=root/bin/sh/file/new/realfile
hany@ubuntu:~$ echo ${test%/*}
root/bin/sh/file/new
hany@ubuntu:~$ echo ${test%%/*}
root
注:
${变量名##*/}常用来提取文件名;${变量名%/}常用来提取目录
同时,也可用dirname $path提取目录basename $path提取文件名
综合练习
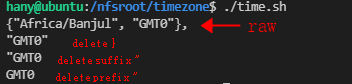
#!/bin/sh #表明脚本使用的解释器是 sh(POSIX Shell)
TIME_POS="{\"Africa/Banjul\", \"GMT0\"}," #原始数据,“要使用转义字符\
echo "$TIME_POS" #输出原始字符串
TIME_POS_0=`echo $TIME_POS | cut -d ',' -f 2` #提取第一个`,`后面的字符串
TIME_POS_1=${TIME_POS_0%\}} #后删至`}`部分
echo $TIME_POS_1
TIME_POS_2=${TIME_POS_1%\*"} #后删至“部分
echo $TIME_POS_2
TIME_POS_3=${TIME_POS_2#*\"} #前删至"部分
echo $TIME_POS_3
运行结果
字符串替换
替换第一个
${string/substring/replacement}从string开头,用replacement替换第一个匹配的substring
str="hello'
str2=${str/o/w}
echo ${str2}
...
hellw
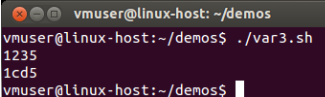
#!/bin/bash
a=1234
let "a += 1"
echo $a
b=${a/23/cd}
echo $b
运行结果:
替换所有
${string//substring/replacement}从string开关,用replacement替换所有匹配的substring
按前缀替换
${string/#substring/replacement}
按后缀替换
{string/%substring/replacement}
字符串比较
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| = | 相同 |
| != | 不同 |
| -z | 长度为0 |
| -n | 长度不为0 |
| $ | 输出字符串的内容,不为空,返回为真 |
常用判断表达式
数字比较
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -eq | 相等 |
| -ne | 不等 |
| -gt | 大于 |
| -lt | 小于 |
| -ge | 大于等于 |
| -le | 小于等于 |
文件测试操作
| 操作符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -e | 文件存在 |
| -s | 文件的大小,若不为空,则返回true |
| -f | 文件为普通文件 |
逻辑操作
-a 表示 and 与操作
-o 表示 or 或操作
控制语句
条件选择
情形1
if condition;then
do something
fi
情形2
if condition;then
do something1
else
do something2
fi
情形3
if condition1;then
do something1
elif codition2;then
do something2
else
do something3
fi
for loop
for loop用于依次遍历in list
for var in item1 item2 ... itemN
do
do something
done
var为当前变量,会依次从in list里获得值
顺序输出当前列表中的数字
for var in 1 2 3 4 5
do
echo "The value is : $var"
done
输出结果
The value is: 1
The value is: 2
The value is: 3
The value is: 4
The value is: 5
顺序输出当前列表中的字符
for var in this is a string
do
echo $var
done
输出结果
this
is
a
string
while loop
while loop用于在满足条件的情况下,不断地执行动作
while condition
do
do something
done
实例
当i<=5时,i从1开始,每次loop,i加1, 直到结束
i=1
while(( $i<=5))
do
echo $i
let i++
done
输出结果
1
2
3
4
5
无限循环
while true
do
do something
done
shell函数
定义格式如下
function_name()
{
action
[return value(0-255)]
}
函数定义与调用实例
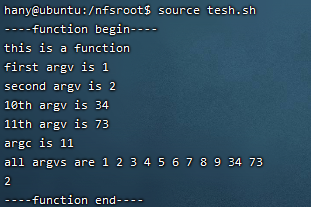
demofun()
{
echo "this is a function"
echo "first argv is $1"
echo "second argv is $2"
echo "10th argv is ${10}"
echo "11th argv is ${11}"
echo "arg count is $#"
echo "all argvs are $*"
return 2
}
echo "----function begin----"
demofun 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 34 73
echo $?
echo "----function end----"
输出结果
脚本使用部分
获取输入参数
bash shell用位置参数变量(position parameter)存储命令行输入的所有参数,包括程序名。其中,
0表示程序名;
1表示第1个参数;
2表示第2个参数;
3表示第3个参数;
...
9表示第9个参数
获得当前脚本名
首先想到的是利用0号参数,
echo $0能获取到./test.sh
若不想要./,就可以使用basename命令
name=`basename $0`
echo ${name}
获得输入命令行参数的个数
$#
param_count=$#
echo ${param_count}
执行其它脚本
#!/bin/sh
CMD="./info/info.sh"
$CMD
在任意当前路径执行包含相对路径的shell脚本
若脚本中使用了相对路径,那么在别的目录执行时会出现找到不相关路径的情况。
解决方法是,在使用相对路径的脚本中加上下面命令即可。
#!/bin/sh
CURDIR=`dirname $0` #获得此脚本的所在目录
echo "$CURDIR"
cd "$CURDIR" #切换到此目录后再执行
程序示例
1. 判断分数
从终端输入内容
判断输入的内容是不是数字,若不是,就退出,退出值为10;
分数>100,就提示错误,并退出,退出值为20;
分数>=85,提示good
分数>=60,提示soso
其它分数,提示loser
#!/bin/bash
read -p "please input the score: " score
if [[ $score =~ [^0-9] ]]; then
echo "not a int"
exit 10
elif [ $score -gt 100 ]; then
echo "wrong"
exit 20
elif [ $score -ge 85 ]; then
echo "good"
elif [ $score -ge 60 ]; then
echo "soso"
else
echo "loser"
fi
2. 判断进程有没有运行
若当前进程demo 运行数量大于等于1,就提示 已运行;
若没有,就进行运行demo
#!/bin/bash
if [ `ps | grep demo | grep -v grep | wc -l` -ge 1 ];then
echo "demo is already running"
else
demo > /dev/null &
if
grep -v grep是为了排除自身查找命令
3 过滤掉首行有“#”的行
#!/bin/sh
TEST=`cat test_config | grep -v ^#`
echo $TEST
4 将name="hany"追加到文件中
echo name=\"hany\" > test_config
5 提取上面文件中的name值
STRING=`cat test_config`
name=${STRING##*name=\"}
name=${name%%\"}
echo $name
6 在shell脚本中,如何传带有空格的参数
只需要将参数用双引号,引起来就可以了
ARG1=XMIAO MIN
ARG2=123
test "ARG1" "ARG2"
7 使用cut命令提取有规律的字段
[root@rhel6164 ~]# echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@rhel6164 ~]# echo $PATH | cut -d ':' -f 2,4-6 #使用:分割后,选择打印出第2,4,5,6段信息
/usr/local/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
————————————————
[root@rhel6164 ~]# echo $PATH | cut -c 2 #以字符为单位来分割,然后打印出第二个字符
u
————————————————
[root@rhel6164 ~]# echo $PATH | cut -b 2,4 #打印出第二个和第四个字节
8 获取文件名与后缀
file="a.txt"
filename=${file%.*}
suffix=${file##*.}
echo ${filename}
echo ${suffix}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号